* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kingdom Protista Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
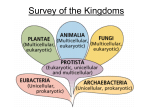
Kingdom Protista Review Describe the basic characteristics of the organisms found in Kingdom Protista Cell Type: ( Prokaryotic / Eukaryotic / Both ) What is the nickname of Kingdom Protista? Why is this an appropriate nickname? Cell Number: ( Unicellular / Multicellular / Both ) Reproduction Type : ( Asexual / Sexual Both ) Obtaining Nutrition : ( Autotrophic / Heterotrophic / Both ) Complete the chart to demonstrate your understanding of the protist classification categories. Characteristics Protist Type (How are they “like”?) Significant Cell Structures Examples Plant-like Protists Animal-like Protists Fungus-like Protists Label the following terms seen in the paramecium diagram below: macronucleus , micronucleus , contractile vacuole , food vacuole , cilia , oral groove Label the following terms seen in the amoeba diagram below: nucleus , contractile vacuole , food vacuole , pseudopod , cell membrane Label the three protist examples as either plant like, animal like, or fungus like. Match the euglena structures below. ____ Detects light ____ Site of photosynthesis ____ Controls cell ____ Support & protection ____ Movement ____ Rids excess water A B D E F Kingdom Protista , Kingdom Fungi , Kingdom Plantae , and Kingdom Animalia all belong to which domain? Kingdom Fungi Review Summarize the endosymbiotic theory. The endosymbiotic theory explains the origin of _____________________________________. Describe the basic characteristics of the organisms found in Kingdom Fungi Cell Type: ( Prokaryotic / Eukaryotic / Both ) Cell Number: ( Unicellular / Multicellular / Both ) Reproduction Type : ( Asexual / Sexual Both ) Obtaining Nutrition : ( Autotrophic / Heterotrophic / Both ) Cell walls made of _________________________. What did the fungus say to the algae? I’m lichen you! Why is this joke hilarious? Label the following in the mushroom diagram above: Hyphae, Mycelium, Fruiting Body, Cap, Gills, Spores Generally speaking, describe the process of how fungi “eat.” Give at least two examples of each of the following. Saprophytic Fungi: Which plant below has mychorrizae? How do you know? Parasitic Fungi: Mutualistic Fungi: Demonstrate your understanding of how fungi reproduce by completing the venn diagram below. Asexual Reproduction Budding: Fragmentation: Spore Production: Sexual Reproduction Spore Production: Kingdom Plantae Review Describe the basic characteristics of the organisms found in Kingdom Plantae Cell Type: ( Prokaryotic / Eukaryotic / Both ) Identify at least three adaptations that allow plants to fully live on dry ground. Cell Number: ( Unicellular / Multicellular / Both ) Reproduction Type : ( Asexual / Sexual Both ) Obtaining Nutrition : ( Autotrophic / Heterotrophic / Both ) Cell walls made of _________________________. In terms of evolution, put the following in order from oldest to most recently evolved: ANGIOSPERMS , SEEDLESS VASCULAR , NONVASCULAR , GYMNOSPERMS , ALGAE Give the function & direction of the vascular tissues in plants. Xylem Xylem Phloem Xylem Use the space below to draw a plant cell. Label at least 3 structures significant to plant cells. Label each of the following: Petal , Stigma , Style , Ovary , Anther, Filament The female portion of a flower? _______________ Male portion? _________________ Demonstrate your understanding of plant evolution by completing the following chart. Category Major Characteristics Example(s) Reproduce with spores No true roots, rhizoids Ferns Horsetails Gymnosperms Magnolias Apple Trees Grasses Describe the basic characteristics of the organisms found in Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia Review Cell Type: ( Prokaryotic / Eukaryotic / Both ) Write the INVERTEBRATE Phylum name that matches the description. Cell Number: ( Unicellular / Multicellular / Both ) Reproduction Type : ( Asexual / Sexual Both ) Means “soft bodied” – includes snails and octopus Obtaining Nutrition : ( Autotrophic / Heterotrophic / Both ) Means “jointed foot” – includes insects Label the following anatomical terms on the cat seen below: Anterior , Posterior , Dorsal , Ventral Means “stinging animal” – includes jellyfish Means “pore bearing” – includes sponges Means “flat worm” – includes planaria Means “spiny skin” – includes starfish Means “round worm” – includes hookworms Means “little rings” – includes earthworms Demonstrate your understanding of the VERTEBRATE Classes by completing the chart below. Chordate Class Major Features Examples Identify the body plan symmetry for the following animals ( assymmetry, radial, bilateral ): Jellyfish – Chondrichthyes Dog – Sponge – Fish with “bony” skeletons Worm – Frogs, Newts, Salamanders Crab – Coral – Dry, scaly skin First amniotic eggs List at least two characteristics shared by all vertebrate animals: Aves Koalas, Kangaroos (Marsupial) Platypus (Egg laying) Pandas, Dogs, Humans (Placental)