* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Deforming the Earth`s Crust
Survey
Document related concepts
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Paleostress inversion wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
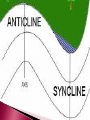
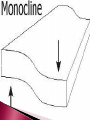
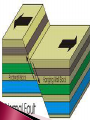
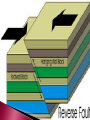
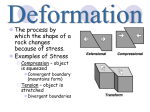
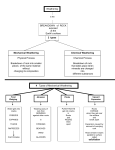
Change Over Time CO: SWBAT describe the forces that deform Earth’s crust. LO: SWBAT create a “cootie catcher” to review plate boundaries, motion, and features. Describe two types of stress that deform rocks Describe three major types of folds Explain the differences between the three major types of faults Identify the most common types of mountains Explain the difference between uplift and subsidence Explain how weathering changes the Earth’s surface Have you ever tried to bend something only to have it break? How can a material bend at one time and break at another? It has to do with stress. ◦ Stress is the amount of force per unit area on a given material. ◦ Stress can deform the Earth’s crust. The process by which the shape of a rock changes because of stress Two types of stress ◦ Compression the type of stress that occurs when an object is squeezed occurs at convergent plate boundaries ◦ Tension The type of stress that occurs when forces act to stretch an object Occurs at divergent plate boundaries The bending of rock layers because of stress in the Earth’s crust Common types of fold ◦ Anticline – upward-arching fold ◦ Syncline – downward, troughlike folds ◦ Monocline – rock layers are folded so that both ends of the fold are horizontal The surface along which rocks break and slide past each other ◦ The blocks of crust on each side of the fault are called fault blocks Hanging wall Footwall Three main types ◦ Normal faults ◦ Reverse faults ◦ Strike-slip faults When rocks are pulled apart because of tension Causes the hanging wall to move down relative to the foot wall Usually occur when tectonic forces cause tension that pulls rocks apart When rocks are pushed together by compression Hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall When rocks are moved horizontally by opposing forces Mountains exist because tectonic plates are continually moving around and colliding with one another Three common types ◦ Folded mountains ◦ Fault-block mountains ◦ Volcanic mountains Make up the highest mountain ranges Form when rock layers are squeezed together and pushed upward Appalachian Mountains – formed when North America and Africa collided Alps in central Europe, the Ural Mountains in Russia, and the Himalayas in Asia Form when tension causes large blocks of the Earth’s crust to drop down relative to other blocks Sharp jagged peaks Tetons in Wyoming Most located at convergent boundaries where oceanic crust sinks into the asthenosphere at subduction zones The rock that is melted in subduction zones forms magma, which rises to the Earth’s surface and erupts Can also form under sea ◦ Can rise about the ocean surface to become islands ◦ Ring of Fire Vertical movements in the crust ◦ Uplift Rising of regions of Earth’s crust to higher elevations Rocks may or may not be highly deformed ◦ Subsidence Sinking of regions of Earth’s crust to lower elevations Rocks do not undergo much deformation Types of uplift ◦ Formation of mountains ◦ Rebound When large areas of land rise without deforming Slowly springs back to its previous elevation Rocks that are hot take up more space than cooler rocks ◦ As the lithosphere cools, it becomes denser and takes up less volume causing the crust to sink Can also occur when the lithosphere becomes stretched in rift zones ◦ A rift zone is a set of deep cracks that forms between two tectonic plates that are pulling away from each other ◦ As tectonic plates pull apart, stress between the plates causes a series of faults to form along the rift zone Major events such as earthquakes and volcanoes are not the only processes that shape Earth’s surface. Earth’s surface is gradually changed through weathering. ◦ Weathering is a process in which rocks are broken down into smaller pieces through the action of wind, water, roots, and animals. Mechanical weathering ◦ Breaks rock apart without changing their chemical composition Water seeps into cracks in a rock and freezes Plant roots Burrowing animals Rock, sand, and soil particles carried by wind or water Chemical weathering ◦ Changes the chemical composition of the rocks Air, water, salts, and acids may react with the minerals in the rocks to form new substances Weakens the rock