* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PYRIMIDINE METABOLISM
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Mitogen-activated protein kinase wikipedia , lookup
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
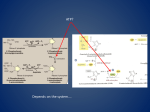
• C H A P T E R • 20 • • • PYRIMIDINE METABOLISM • Pyrimidine Synthesis Pyrimidine Salvage Pyrimidine Degradation • • • • • • • • • • PYRIMIDINE SYNTHESIS Function: To make pyrimidine nucleotides (U, T, C) for DNA and RNA synthesis. Location: Cytoplasm of most cells. Connections: To amino acid metabolism by the requirement for glutamine and aspartate. Regulation: UTP inhibits synthesis of carbamoylphosphate. Equation: Gln CO2 Asp PRPP some ATP ¡ UTP CTP The major difference between purine and pyrimidine de novo biosynthesis is that the pyrimidine ring is assembled and then added to PRPP (Fig. 20-1). With purines, the purine ring is built directly on the PRPP. 230 BG McGraw-Hill: Gilbert, Basic Concepts in Biochemistry, JN 5036 20 • Pyrimidine Metabolism 231 • PYRIMIDINES aspartate carbamoyl phosphate carbamoyl aspartate aspartate transcarbamoylase earth, air, fire, water, and orotate PRPP OMP UMP ribonucleotide reductase ATP UDP ATP CTP NADPH thioredoxin deoxy UDP UTP deoxy UMP glutamine deoxy UMP CH2 — H4 — folate thymidylate synthase deoxy TMP CH2 — H4 — folate H2 — folate gly H4 — folate serine dihydrofolate reductase deoxy TTP NADPH Figure 20-1 Pyrimidine Synthesis and Salvage PYRIMIDINE SALVAGE Uracil PRPP ¡ UMP PPi (only uracil) Nucleoside phosphorylase: U, C, T ribose 1-phosphate ¡ nucleosides Pi There are basically two types of salvage. The first involves attachment of the base to PRPP with the formation of pyrophosphate. This pathway is available for salvage of purines and uracil but not for cytosine or thymine. The other pathway involves attachment of the base to ribose 1-phosphate, which occurs to some extent for most of the purines and pyrimidines. This second pathway requires the presence of specific BG McGraw-Hill: Gilbert, Basic Concepts in Biochemistry, JN 5036 • 232 • Basic Concepts in Biochemistry kinases to convert the nucleoside to the monophosphate. Except for thymidine kinase, these kinases do not exist in most cells. PYRIMIDINE DEGRADATION CMP ¡ cytidine ¡ uridine ¡ uracil ¡ ¡ -alanine ¡ malonate semialdehyde ¡ CO2 Thymidine ¡ thymine ¡ -aminobutyrate ¡ methylmalonate semialdehyde ¡ CO2 After removal of the phosphates by various phosphatases, the nucleosides are cleaved to the base by the same nucleoside phosphorylase that catalyzes the salvage reaction. The equilibrium constant for this reaction is near 1, so that it can go in either direction depending on the relative levels of the substrates and products. Base–ribose Pi ∆ base ribose 1-phosphate The nitrogen from the pyrimidine bases is removed by transamination and dumped onto glutamate. The carbon skeleton ends up as CO2. BG McGraw-Hill: Gilbert, Basic Concepts in Biochemistry, JN 5036