* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download JRA1.4 AAs in eduGAIN
Survey
Document related concepts
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Next-Generation Secure Computing Base wikipedia , lookup
Trusted Computing wikipedia , lookup
Information security wikipedia , lookup
Medical privacy wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Secure multi-party computation wikipedia , lookup
Security and safety features new to Windows Vista wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Social engineering (security) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
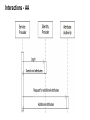
Example Use Case for Attribute Authorities and Token Translation Services - the case for eduGAIN Andrea Biancini The architecture ● eduGAIN is a SAML based identity federation, in this scenario Attribute Providers has been implemented leveraging two main protocols: ○ the Attribute Authority role for a SAML federation entity, for orline information flows to be retrieved during user login; ○ the VOOT protocol (based on SCHIM) to describe groups and memberships offline from user authentication. Interactions - AA Interactions - VOOT VOOT is a protocol for exchanging group information externally to applications. Very simple API: Benefits and issues ● The architecture shown permitted to: 1. Distribute the responsibility to provide information about known users to different subjects within the federation. 2. Decouple authentication and authorization processes. ● AAs in eduGAIN still have some significant limitation: 1. AAs still have some issue regarding privacy and security. 2. User enrolment must be supported to reduce effort. Conclusions, challenges addressed ● Permit delegation of the management of user information in a clear and secure way. ● Provide new architectural elements that could seamlessly integrate with existing architectures (to simplify technical adoption of such a solution by all the participants to the federation). ● Leverage the existing federations in building the reciprocal trust, needed to guarantee security.