* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5-3 - Mahtomedi Middle School
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering in science fiction wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
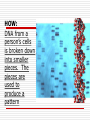
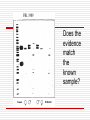
Chapter 5-3 Putting it all together for the Advances in Genetics – where are scientists going with all this? Three Methods people have use to develop organisms with desirable traits Selective breeding Inbreeding Hybridization #2: Selective Breeding Process of selecting a few organisms with the desired traits to serve as parents of the next generation is selective breeding Selective Breeding continued This is selecting organisms with desired traits to be parents of the next generation This has been done for 1000’s of years Inbreeding: 3. Crossing two individuals that have similar characteristics. Inbreeding continued Example: cross two turkeys that are plump and grow quickly Usually genetically very similar Can increase the probability that organisms may inherit alleles that lead to genetic disorders. Inbreeding continued a. Can increase the probability that organisms may inherit alleles that lead to genetic disorders. Hybridization: 4. Crossing two individuals that are genetically different a. They are bred to have the best traits from both parents True or False In hybridization, breeders cross two individuals that are genetically identical. FALSE Why???? Hybridization crosses two genetically different individuals Question: When breeders cross two genetically different individuals to produce an organism with the best traits from both parents, this breeding method is called ________________ Answer: Hybridization Clone 5. an organism that has exactly the same genes as the organism from which it was produced Cloning: info Plants are easy to clone: cut a stem from one plant and put the stem in soil, water it and it will grow into a new plant…NOT ALL PLANTS will do this, however! Cloning in animals: More complex!!! Take the nucleus of an animal’s body cell and use that to produce a new animal by injecting the information into an “empty” egg Discover video clip (8 minutes) – Modern Genetics…more about cloning What letters are true for #6? a. A clone has exactly the same genes as the organism from which it was produced. b. A cutting is one way to make a clone of an animal. c. It’s easier to clone an animal than it is to clone a plant. Answer: A. A clone has exactly the same genes as the organism from which it was produced. True or False Cloning can be done only in animals. False Why? Cloning animals can be done, it’s just more complex than plants. Genetic Engineering: #8 Genes from one organism are transferred into the DNA of another organism Genetic Engineering continued This is used for: Producing medicine and improving food crops Genetic Engineering, continued Human genes can be inserted into the cells of cows so the cows produce the human protein for milk Same technique used for producing blood clotting protein needed by people with hemophilia Allow plants to resist cold temperatures Enable plants to resist insect pests Using genetic engineering to fix some genetic disorders in humans Gene Therapy - Inserting copies of a gene directly into a person’s cells Example: treat hemophilia by replacing the defective allele on the X chromosome Concerns about Genetic Engineering Are crops that have been genetic engineered safe? Will they harm the environment or cause health problems in humans? Will other genetic disorders be caused by correcting one genetic disorder? The Human Genome Project: #11 & 12 Genome: All the DNA in one cell of an organism. Goal of the Human Genome Project Pinpoint the DNA sequence of every gene on every chromosome DNA of humans has at least 30,000 genes and each gene is made up of at least 30,000 bases DNA Fingerprinting Identify people from their DNA DNA Fingerprinting Show whether people are related or not – useful for criminal investigations No two people have the same DNA EXCEPT for identical twins HOW: DNA from a person’s cells is broken down into smaller pieces. The pieces are used to produce a pattern LOTS & LOTS OF CONTROVERSY Human cloning may produce subhumans to fight in our wars. Genetically modified food = not good for you. Will it lead to health problems in the future? Will it lead to designer babies? What if it leads to babies with disorders? Lack of genetic variety Many more issues!!!!!!! Does the evidence match the known sample? http://www.perfectdna.com/products.htm