* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Byzantine Empire - Miami Beach Senior High School
History of the Jews in the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Komnenos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine music wikipedia , lookup
Law school of Beirut wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Angelos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Papacy wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Isaurian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
History of the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine art wikipedia , lookup
Constantinople wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine dress wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine economy wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Heraclian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
State church of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
The Byzantine Empire
{
Mr. Ermer
World History; Miami Beach Senior High
Emperor Justinian
When western Roman Empire collapses, and was
replaced by Germanic states, the eastern Roman
Empire continues to exist
Centered around Constantinople, later
renamed Byzantine Empire
527: Justinian becomes Emperor, wanted to
reestablish Roman Empire in Mediterranean
552: Roman Empire almost back to old boarders
Empire shrinks after Justinian’s death
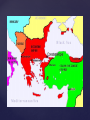
Justinian’s Roman Empire
Justinian’s Contributions
Eastern empire inherits complex legal system
Justinian set out to simplify the laws
The Body of Civil Law: The results of
Justinian’s efforts, became basis for Byzantine
law to 1453
Justinian’s code also influenced western law
Eastern Roman Problems
After Justinian, empire is left with problems:
Too much land to defend
Empty treasuries
Decline in population due to plague
Threats on its boarders
Muslim Arabs sweep through empire, taking more than
half its territory
ERE defeated at Yarmuk in 636, ceding control of Syria
and Palestine to Arab control
679: Defeated by Bulgarians in the north, losing control
of Danube River Valley
From Roman To Byzantine
Empire shrunk to include just Balkans and
Asia Minor
Greek replaces Latin as official language
Emperor viewed as chosen by God, and his
power was absolute
Emperor appointed the leaders of the
Eastern church known as a patriarch
The emperor was the leader of both church
and state, protecting the true Christian faith
Constantinople
Europe’s greatest city until 1100s
City grew rich facilitating trade b/w east & west
Justinian’s buildings dominate landscape
Hippodrome=arena for races and gladiators
Hagia Sophia: main church built in 537
The Hagia Sophia—Church of the Holy
Wisdom—is the most famous Byzantine
building, today known as the Blue Mosque
The Hagia
Sophia
New Success, New
Troubles
Macedonian emperors bring new prosperity
Rule from 867 to 1081, expand empire
Early success undone by political infighting
Macedonians do not accept pope’s claim to
be sole head of Christian faith
1054 Pope Leo IX and Patriarch Michael
Cerularius excommunicate each other—
causes schism
Seljuk Turks defeat Byzantines at Manzikert
On page 41, write and answer
questions 1-5
Chapter 2, Lesson 5 Review