* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Building a 5 volt power supply
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Power supply wikipedia , lookup
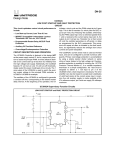
Building a 5 volt power supply Most digital logic circuits and processors need a 5 volt power supply. To use these parts we need to build a regulated 5 volt source. Usually you start with an unregulated power supply ranging from 9 volts to 24 volts DC (To make a 5 volt power supply, we use a LM7805 voltage regulator IC (Integrated Circuit). The IC is shown below. The LM7805 is simple to use. You simply connect the positive lead of your unregulated DC power supply (anything from 9VDC to 24VDC) to the Input pin, connect the negative lead to the Common pin and then when you turn on the power, you get a 5 volt supply from the Output pin. The bread boarded circuit is shown below. The 5 Volt output is connected to the red power supply line of the breadboard. The ground from the input is connected to the blue ground line of the breadboard and a jumper wire is used to connect ground from there to the common (ground) pin of the 7805. Sometimes the input supply line may be noisy. To help smooth out this noise and get a better 5 volt output, a capacitor is usually added to the circuit, going between the 5 volt output and ground (GND). We use a 220 uF capacitor.