* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Period 3
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
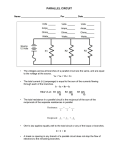
ELECTRICITY-CIRCUITS Joe Walker Ryan Loyland Ozan Berlinguette ELECTRICITY VOCABULARY Electricity = Caused by the flow of electrons Positive charge = lacking electrons Negative charge = excess of electrons Ion = An atom that has a different amount of electrons than what is normal Insulator = A material that resists electrical flow (Rubber) Conductor = A material that does not have a high resistance (Copper) CONCEPTS • Electricity flows from negative charge to positive charge • Any path for electrons to flow is a circuit • An open circuit will not have any electrical flow • The flow of charge in a circuit is very much like the flow of water in a closed circuit • Neither water nor the electrons concentrate in certain places. • They flow in a continuous loop, or circuit. CIRCUITS VOCABULARY Wire = Allows electricity to flow in a circuit Battery = Pushes electricity threw the circuit Switch = can stop or control the flow of electricity Resistor = provides resistance to the circuit Fuse = Prevents too much current from passing through the circuit Junction = where branches of the circuit join or split EQUATIONS I = V/R I = Current in amperes V = Volts R = Resistance in ohms W=VI W=Watts=Power Series circuit: R(total) = R1+R2+… Parallel circuit: 1/R(total)= 1/R1+1/R2+… SERIES CIRCUIT • No Branches • Current is calculated by: V/Total Resistance • Total Resistance is the sum of resistances • When one part of he circuit is open, the whole circuit will break PARALLEL CIRCUIT • Each device operates independent of the other devices. • A break in any of the paths does not interrupt the flow of the other paths. • Voltage is the same across each device • The total current is divided among the separate branches. • The total current is the sum of the currents in its branches. SAMPLE PROBLEM Two identical resistors, each with a resistance of 1500 ohms, are wired in series with a 9 volt battery. (A) Find the current through each resistor (B) find the voltage difference across each resistor. (A) C= V/R C=9V/3000 ohms C= .3mA (B) Product/Sum = (9V * 9V)/ (9V + 9V)=4.5V EXAMPLES OF CIRCUITS Simple Circuit Parallel Circuit COMBINATIONS OF RESISTORS series parallel Current through same add Voltage across add same resistance R(total)= R1+R2… 1/Rtotal=1/R1+1/R2… CIRCUIT SAMPLE PROBLEM You have an 800W microwave oven, a 450W toaster, and a 650W blender all plugged into the same 110V household circuit, which has a 15A circuit breaker installed. Can you turn on all three devices at the same time without tripping the breaker? Answer: No, the require 17.3 A MULTIPLE CHOICE! 1. Any path along which electrons can flow is a(n)__________? A. Current B. Electron path C. Circuit D. Resistor 2. When connected in a _____, the devices in a circuit form (a) _______, for electron flow. A. series, single pathway B. series, branches C. parallel, single pathway D. parallel, no pathway 3. If one device fails in a series circuit, current in the whole circuit stops and none of the devices will work. A. True B. False 4. Which is not a characteristic of parallel connections? A. The total current divides among the parallel branches. B. The total amount of current in each branch is inversely proportional to the resistance of the branch. C. The total current is the sum of the currents in the branches. D. The total current is the product of the currents in its branches. 5. The equivalent resistances of three 4 ohm resistors in series is? A. 11 ohms B. 12 ohms C. 10 ohms D. 7 ohms 6. Does current flow through a resistor or across a resistor? A. Through B. Across 7. Is voltage established through a resistor or across a resistor? A. Through B. Across 8. A 200 ohm resistor is connected to a 6-V battery. How much current flows through the resistor? A. 0.03 A B. 1200 A C. 0.012 A D. 40 A 9. A 100 ohm resistor and a 500 ohm resistor are wired in series with a 15-V battery. How much current flows from the battery? A. 0.020 A B. 0.025 A C. 60 A D. 0.15 A 10. A light bulb has a resistance of 300 ohms and a current of 0.20 A flows through the bulb. What is the voltage difference across the bulb? A. 60 V B. 20 V C. 70 V D. 30 V MC ANSWERS 1. C. 2. A. 3. A. 4. D. 5. B. 6. A. 7. B. 8. A. 9. B. 10. A.