* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AIR Genetics Review PPT
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
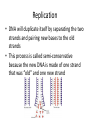
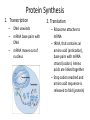
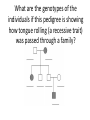
Replication • DNA will duplicate itself by separating the two strands and pairing new bases to the old strands • This process is called semi-conservative because the new DNA is made of one strand that was “old” and one new strand Protein Synthesis 1. Transcription – – – DNA unwinds mRNA base pairs with DNA mRNA moves out of nucleus 2. Translation – Ribosome attaches to mRNA – tRNA, that contains an amino acid (anticodon), base pairs with mRNA strand (codon). Amino acids are linked together. – Stop codon reached and amino acid sequence is released to fold (protein) Mutations • During either of these processes, the copying of the DNA can result in mistakes (mutations) Types of Mutations • Point – one base is changed • Substitution – one letter replaces another • Insertion – one letter is added • Deletion – one letter is removed Biotechnology • Genes can be manipulated through several techniques: – PCR: one copy of DNA is made into many copies – DNA can be cut using restriction enzymes and inserted into a new cell – Gel Electrophoresis: cutting DNA with restriction enzymes and separating the DNA based on size – Cloning: using DNA from an organism and inserting it into a new cell and promoting growth Punnett Squares • Dihybrid Crosses: two traits are examined and how they are passed to offspring • Steps (for unlinked traits): – Write the cross – Write all possible gamete combinations – Use gamete combinations to create Punnett square In horses, black is dependent upon a dominant gene, B, and chestnut upon its recessive allele, b. The trotting gait is due to a dominant gene, T, the pacing gait to its recessive allele, t. If a heterozygous black pacer is mated to a chestnut trotter (heterozygous), what will be the appearance of the F1 generation? Linked Traits • Some dihybrid crosses will have traits that are linked, meaning the alleles do not separate from each other. • For Example: If someone has the genotype BbTt and the traits are linked, instead of having four gamete combinations, now there are only two: BT, and bt Let's say Mr. and Mrs. Smiley both have the genotype EeTt. That means they are both hybrids, BUT the dominant alleles are linked. What are the possible outcomes for offspring? Punnett Squares • Sex-Linked Traits: show how a trait is passed on that is linked to an X or Y chromosome • Steps: – Show cross using XX for females, XY for males – Use exponents for the particular trait – Create Punnett square to see outcomes Hemophilia is a recessive sex-linked disease carried on the X chromosome in humans. A woman who is a carrier for hemophilia marries a man with hemophilia. Could any of their children have hemophilia? If so, would the child be male or female? Punnett Squares • Co-dominance: When the heterozygous individual has a both the dominant and recessive trait – Example: A white and red spotted flower • Incomplete Dominance: When the heterozygous individual has a blending of the dominant and recessive trait – Example: A pink flower A pink-flowered plant is crossed with a whiteflowered plant. What is the probability of producing a pink-flowered plant? In some chickens, the gene for feather color is controlled by codominance. The allele for black is B and the allele for white is W. The heterozygous phenotype is known as erminette. A black chicken and a white chicken are crossed. What is the probability that they will have erminette chicks? Pedigrees • A pedigree is a diagram of family relationships that uses symbols to represent people and lines to represent genetic relationships • A pedigree can also help determine how a trait is passed on through generations What are the genotypes of the individuals if this pedigree is showing how tongue rolling (a recessive trait) was passed through a family? Chi-Square