* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Water Cycle
Survey
Document related concepts
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
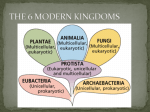
PreAP Biology Spring EOS Review KEY Six hundred plants were divided into 6 groups of 100 each. Each group was placed in lights of different colors for 600 hours. Group I was kept in red light, Group II in yellow light, Group III in green light, Group IV in blue light, Group V in white light and Group VI in ultraviolet light. Every 60 hours the number of leaves on the plants were counted and the width of the leaf at its broadest point was measured. 1. Identify the components of the experiment. Independent variable: __ color of light _____________________________ Dependent variable: ____ leaf width ______________ Constants: ___ type of plant, size of plant, soil, amount of water, time in light _____ Hypothesis: If plants are grown under various colors of light, then the plants will grow best in ______ light. Describe a control set-up or control group: ____ plants in sunlight ___ 2. Set up a graph. Label the X and Y axes. Title the graph. Leaf Width of Plants Under Various Colors of Light for 600hrs. Width of Leaf (cm) Hours Under Colors of Light Evolution 3. Define Evolution. Change of species over time. 4. What are the two goals for evolution? survive and reproduce 5. Define natural selection. Organisms best fit to their environment will be able to survive and reproduce. What else is it called? Survival of the Fittest 6. Define the 4 sources of scientific evidence for evolution. A. fossil record a. fossil— trace of dead organisms b. relative dating— based on rock layer – older are deeper B. comparative anatomy a. homologous structures (and ex.)— similar origin and structure, not function (limbs of human, whale, bat) 1 b. analogous structures (and ex.)— similar function, not origin/structure ex. butterfly wing & bird wing c. vestigial structures (and ex.)— no useful function (whale pelvis) C. embryology— study of organisms in their earliest stage of development D. biochemical evidence— similar DNA sequence/amino acids = more closely related More differences = least closely related 7. Answer the following questions based on the diagram to the right. a. Which layer contains the newest fossils? A A B b. Which layer has the oldest fossils? E C c. D Based on the fossils, this area was most likely what type of environment in the ancient past? ocean E 8. Differentiate between convergent and divergent evolution. Convergent = unrelated species become similar because of similar environments Divergent = common ancestors give rise to many new species Use the table below to answer the following question: GROUP NAME ORGANISM HUMAN KINGDOM Animalia CHIMPANZE E Animalia PHYLUM Chordate Chordate Chordate Chordate Arthropoda CLASS Mammal Mammal Mammal Mammal Insect ORDER Primates Primates Carnivora Carnivora Diptera FAMILY Hominidae Pongidae Felidae Felidae Muscidae GENUS Homo Pan Felis Felis Musca SPECIES sapiens troglodytes domestica leo domestica Scientific Homo sapiens Pan troglodytes Felis domestica Felis leo Musca domestica HOUSE CAT LION HOUSEFLY Animalia Animalia Animalia Name 9. Which two animals are most closely related according to the chart? House cat and lion 10. Use the chart to the right to answer the following questions: A. Does the phylogenetic tree represent convergent or divergent evolution? ______divergent_____________ B. What is the scientific name of the species most closely related to the woodpecker-like finch? C. heliobates C. Are the insect-eating finches related to the cactus-eating finches? Very distant 2 Classification & Kingdoms 11. What is binomial nomenclature? It is a two named naming system developed by Linnaeus. Why is it important? Universal naming system in Latin 12. How are genus and species correctly written? Italics/underlined; Genus = Capitalized; species = lower case 13. What is the genus name of Canis familiaris? Canis 14. What is the species name of Canis familiaris? familiaris Use the dichotomous key below to identify the aliens 15 & 16: 1a. The creature has a large wide head............................go to 2 1b. The creature has a small narrow head..........................go to 11 2a. It has 3 eyes ................................................go to 3 2b. It has 2 eyes ................................................go to 7 3a. There is a star in the middle of its chest....................go to 4 3b. There is no star in the middle of its chest ..................go to 6 4a. The creature has hair spikes .................................Broadus hairus 4b. The creature has no hair spikes...............................go to 5 5a. The bottom of the creature is arch-shaped ....................Broadus archus 5b. The bottom of the creature is M-shaped .......................Broadus emmus 6a. The creature has an arch-shaped bottom .......................Broadus plainus 15. Name ___Broadus tritops 16. Name _Broadus hairus 6b. The creature has an M-shaped bottom...........................Broadus tritops 17. What are the names and shapes of bacteria? Draw the shapes off to the side ___coccus____ is ___sphere__ shaped. Picture: ___bacillus_____ is ___rod__ shaped. Picture: __spirillum___ is ___spiral__ shaped. Picture: 18. When bacteria are arranged in chains it is called: ______strepto_______ 19. When bacteria are arranged in clusters it is called: _____staphylo___________ 20. Identify how Escherichia coli can be beneficial to us and how they can be harmful to us. Escherichia coli is beneficial because it helps digest nutrients and make vitamins; some strains are pathogenic (cause disease) 21. Draw an amoeba and label with the name of the structure that allows it to move: - What other function does this structure perform? Obtain food 22. Draw a paramecium and label the structure that allows it to move: cilia (small hair like structures) 23. Draw euglena and label the structure that allows it to move: flagella (whip-like tail) 24. What are the 3 organelles that plant cells that animal cells do not have? __chloroplast__, __cell wall___, __large central vacuole__ 25. List 2 organelles that animal cells have that plant cells don’t have. ___lysosome___ & _centrioles_____ Use the characteristics chart to complete the table below it. 3 SIX KINGDOMS CHARACTERISTICS CHART Cell Type prokayotic eukaryotic 26. Number Of Cells unicellular multicellular Level of Organization cell tissue organs systems Cell Wall peptidoglycan uncommon lipids chitin cellulose Mode of Nutrition autotrophic heterotrophic Reproduction asexual sexual Symbiosis Examples (symbiotic relationship examples) Other Examples (interesting or indicative characteristic – things that make you remember that group) (examples of kingdom) Archaebacteria Eubacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia P P E E E E U U U/M M/U M M C C C C C,T,O C,T,O,S Cell Wall LIPIDS PEPTIDOGLYCAN UNCOMMON CHITIN CELLULOSE NONE Mode of Nutrition A/H A/H A/H H A H Reproduction A/S A/S A/S A/S S S Y Y Y N N Y Unknown E.coli & human intestine = mutual Lichen Mycorrhizae Lichen Athletes foot Parasite Mycorrhizae & roots mutual Bees/flowers mutual Whale/bar nacle Clownfish/ anemone mutualism Chemo/autotro phs; Base of some food chains Decomposers; Nitrogen Fixation Oxygen; Base of many food chains Decomposer; Nitrogen Fixation Oxygen; Food Shelter Food; Clothing Extreme Environments Common environments; Disease Food; Disease Water and Land Very Diverse halophiles E.coli Mushroom, yeast Trees, grass Sponge, human, cat Cell Type Number of Cells Level of Organization Motility Symbiotic Relationships Ecological Importance Other Examples Makes 1/3 of Earths Oxygen; Disease Amoeba, algae Plants 27. Identify all of the structures in the leaf diagram AND put their function. A. __cuticle__ - helps prevent dessication B. _epidermis_ - outer layer of leaf C. _palisade layer__ - photosynthetic layer D. _spongy layer__ - some photosynthesis and stores gases E. _guard cells__ - open/close stomata F. __ xylem __ - carries water up G. ___vein_ - contains xylem and phloem H. phloem ___ _ - carries sugar down I. __equation stomata __ where gases areDon’t exchanged 28. Write the equation for photosynthesis, then write the for- respiration. forget energy. 4 Circle the reactants for photosynthesis and the products of respiration. What do you notice? Underline the products of photosynthesis and the reactants for respiration. What do you notice? Can you relate this to the water, oxygen, and carbon cycles? Can you relate the energy in the reactions to energy flow through an ecosystem? (Reactants) 6 CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 (Products) C6H12O6 + 6O2 6 CO2 + 6H2O + Energy 29. Which kingdoms have cells that perform photosynthesis? Protista and Plantae 30. Which kingdoms have cells that perform cell respiration? Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista (mitochondria) Eubacteria, Archaebacteria (no mitochondria) 31. What gas do plants release during photosynthesis? oxygen 32. What adaptations did plants make to allow them to live on land (there were 3 main problems, what were the solutions)? 1. Prevent drying out – waxy cuticle, stomata/guard cells, specialized leaves, seeds 2. Reproduce without water – pollen, flowers, fruits, seeds 3. Absorb nutrients – roots, myccorhizae, vascular tissue 33. Complete the following chart comparing monocots and dicots. 34. How are non-vascular plants different from vascular plants? Xylem/phloem in vascular plants 35. How are gymnosperms different from angiosperms? Gymnosperms = naked seeds in cones, needle like leaves; Angiosperm = flowering and seeds are in fruits, blade-like leaves 36. Where are the sugars made in plants and what vascular tissue transports it? Leaf; phloem 37. What 2 things are absorbed by roots? Water, minerals 38. From the demonstration of water movement in celery or carnations, what are the definitions of adhesion and cohesion? Adhesion: attraction of water molecules to another substance Cohesion: attraction of water molecules to other water molecules 5 39. Label the parts of the plant and give the function of each part: Functions of Flower Parts Anther – produces pollen (sperm) Filament – supports anther Sepal – protects bud Receptacle – base of flower, attaches to stem Ovule – eggs Ovary – produces ovules (eggs) Style – sperm travels down tube Stigma – pollen sticks to it Petal – attracts pollinators 40. Color in the boxes of the male and female parts of the plant using 2 different colors of pencil. Stamen – male; Pistil - female 41. What are 4 ways that seeds are dispersed away from the mother plant? Wind, water, animals, fruit 42. How are the following fruits or seeds dispersed? Dispersed by ___wind_____ Dispersed by _____animals______ 43. What are some plant adaptations that plants use as defense mechanisms? Spines, leaves that close Animals & Comparative Anatomy 44. What is the purpose of villi in the intestines & root hairs in plants? Increase surface area for absorption 45. Relate the following plant parts to the corresponding animal systems (you might use some more than once and not use others at all): __I___a. flowers I. reproductive __III_b. stems II. skeletal _II__c. roots III. muscular __IV__d. leaves IV. digestive 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. What system does the human body use to fight off viral infections? ___Immune______ What system does the human body use to process nutrients? ______Digestive____ What system does the body use to move gases and nutrients around? ______Circulatory_______ What system does the body use to move the bones? ________muscular______ What system does the body use to protect itself from drying out? ____integumentary_____ Plants make sugar and store it in the form of a polysaccharide called __starch__. Animals eat sugar and store it in the form of a polysaccharide called __glycogen_ (in liver and muscles). 6 53. What are some characteristics of water that make it so good for the human body? High specific heat 54. How does the integumentary system help the body maintain homeostasis? Sweating to cool the body 55. The human urinary (excretory) system consists of the kidneys, ureter, bladder and urethra. Sketch these organs and describe what each of them does in the system. Kidneys – filter blood to make urine Ureter – carries urine to the bladder from the kidneys Bladder – holding tank for urine Urethra – carries urine out of the bladder out of the body 56. Complete the following set of words that describe the increasing complexity of organisms. Atoms, molecules, _cells__, tissues, __organs___, systems, _organism__ 57. Describe how each of the following sets of animal systems work together: skeletal and muscular – muscles move skeleton digestive and circulatory – nutrients absorbed by digestive system are carried by circulatory system circulatory and respiratory – O2/CO2 are carried by the circulatory and enter/exit via respiratory endocrine and reproductive – glands of endocrine produce hormones, reproductive systems contain ovaries & testes that produce hormones 58. What animal organ system would you put the following organs in: A. malpigian tubules, kidneys, green gland __excretory/urinary___ B. tympanic membrane, eardrum, lateral line system ___nervous___ 59. Use the nutritional label to answer the questions in the box. How many calories would one get if he ate the whole container of this food? 500 How many fat grams are in 2 servings? 24 How many calories would a person consume if they ate enough to receive 100% of the RDA for calcium? 1250 If a person ate 2 servings of this food, what percent of their daily sodium level would they consume? 40 % What percent of their daily Vitamin C would they get by eating 2 servings? 4% 7 ECOLOGY 60. Define ecology. The study of organisms and their interactions with one another and their physical environment 61. What is the difference between abiotic and biotic factors. List two examples of each. Abiotic—nonliving/never was living. Ex. Air, rocks, soil, water Biotic—living or was once living. Ex. Bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, animals 62. Define ecosystem. Self-sustaining collection of organisms and their physical environment 63. What are 5 limiting factors in an ecosystem? Competition, predation, crowding, stress, disease, parasitism 64. What does the term carrying capacity mean? The maximum population size that an environment can support 65. Draw an example of a food chain that starts with grass and ends with a coyote. Then connect it to two other food chains, making a food web. Coyote 66. Compare Producers, Primary consumers, Secondary consumers, Tertiary consumers and decomposers and list examples of organisms for each. (Draw them in an energy pyramid). Producers—autotrophs (make own food by photosynthesis (usually)) Ex. Plants, photosynthetic protists, some bacteria Primary consumers—herbivores (eat producers) Ex. Krill, shrimp Secondary Consumers—carnivores or omnivores (eat primary consumers, some eat producers also) Ex. Fish Tertiary Consumers—carnivores or omnivores (eat secondary consumers, some eat primary consumers and producers) Ex. Bigger fish 67. Give examples of at least three predator-prey relationships. Predator vs. Prey Cat mouse Rabbit grass Owl snake 68. Fill in the chart below for the three types of symbiosis. Use + = benefits; - = harms; ~ = neutral. Organism 1 + Mutualism Organism 2 + Commensalism Organism 1 Organism 2 + ~ Organism 1 + Parasitism Organism 2 - 8 Match the following scenarios with the correct example of symbiosis or relationship . 69. __B__mistletoe on elm trees (mistletoe takes nutrients from the tree) 70. __C__hummingbirds and trumpet flowers (bird helps pollination occur while it is drinking nectar) 71. __A__whale and barnacle (whale is unharmed as barnacle gets a ride in the ocean for food) 72. __B__tapeworm and pig (tapeworm feeds off of pig) 73. __D__cat and mouse (cat chases, catches, and eats the mouse) A. commensalism B. parasitism C. mutalism D. predator/prey 74. What is the major source of energy for all living things on the earth? _sun__ 75. Animals use a variety of adaptations and methods to camouflage themselves for protection. Give 5 examples of this. Coloration to blend, patterns that look like eyes, bury self in sand, play dead, etc…. 76. Animals also have other mechanisms that they use in order to avoid being eaten by other animals. What do the following animals use to avoid being eaten? a. armadillos – protective shell c. poison dart frog - poisonous b. monarch butterflies – taste bad d. porcupine – spiny quills 77. What is the best way to sample the following populations: a. flock of geese ___approximate count by arial view or traps (catch/release)__ b. pack of coyotes ___approximate count by arial view or traps (catch/release)__ c. field of pine trees ___randomly or in pattern around entire field__ 78. What are the differences among an omnivore, herbivore, carnivore, and detrivore? 79. Compare a J Curve and an S curve. J curve= exponential growth (not seen in nature S curve = logistic growth curve (population tends to level off at carrying capacity then oscillate near carrying capacity 80. There are three cycles that circulate Water, Carbon, and Nitrogen. Briefly describe each one and its major steps. Water Cycle Water is the most important, non-living component of the ecosystem. Nonliving cycle: involves condensation (gas to liquid—how clouds form), precipitation (liquid falling to Earth), & evaporation (liquid to gas). Living cycle: involves plants in a process called transpiration (evaporation of water out of the stomata of the plant leaves). Carbon Cycle Remember photosynthesis (sunlight, carbon dioxide and water converted into glucose and oxygen), respiration (converts carbon compounds and oxygen into ATP energy, carbon dioxide, and water) & combustion (burning of fossil fuels) Nitrogen Cycle Atmospheric nitrogen cannot be used by plants and animals. Remember bacteria, such as Nitrogen fixing, nitrifying, and denitrifying, are involved in converting nitrogen into a usable form then sending it back to atmosphere. 9 Virus 81. The Sabin vaccine is a liquid containing weakened polio viruses. What does the body of the individual who receives the vaccine do in order to “protect” it from polio? _produces antibodies that recognize and fight off the virus when it “attacks”__ 82. Why does a virus require a host cell? Must be in a living host cell to reproduce 83. How are viruses similar to cells? Contain nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) and protein (makes up the capsid); also, can mutate 84. Why do must scientists today consider viruses to be nonliving? (hint: what do they not have or what can they not do) No metabolism, cannot maintain homeostasis, cannot reproduce on own (must be in a host cell) 85. Many viruses have glycoproteins that project spikes from its envelope. Different viruses have different glycoproteins. What is the purpose of these spikes? To mimic the proteins on the outside of cells to trick the cells into taking the virus inside. They fit like a puzzle piece to the cells receptors. Ex. Virus Cell 86. Identify whether the diseases/conditions are caused by Viruses (V), Bacteria (B), Protists (P), or Fungi (F). Influenza _V_ Athlete’s Foot _F Malaria _P_ Ebola _V_ Common cold _V_ African Sleeping Sickness _P_ Ringworm _F_ Tobacco Mosaic _V Dental cavities _B_ Acne _B_ Toxoplasmosis _P_ 87. Discuss the HIV virus by answering the questions below. A. What shape and type of virus is it? Spherical RNA retrovirus B. What disease does it cause? AIDS C. What body system does it attack? Immune D. What specific type of cells does it attack? Helper T cells 88. Can you take antibiotics for viral infections? _NO__ Why or why not? Antibiotics (“against life”) can only treat living cells (viruses are nonliving) usually by damaging the cell walls or cell membranes causing the bacteria, protist, etc. to die______ 89. Draw the 5 shapes of viruses, label them with their shape name, label the capsid and nucleic acid, and give an example for each of a virus that has that shape. A. binal B. filovirus Ex. bacteriophage Ex. Ebola C. helical D. polyhedral E. spherical Ex. TMV Ex. Adenovirus Ex. HIV, Flu 10