* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Study Guide: 7
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
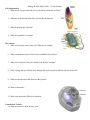
Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus? 3. What do prokaryotic cells lack? 4. What are organelles? List some. The Nucleus 5. What is the control center of the cell? What does it contain? 6. What surrounds the nucleus? How many membranes does it have? 7. What is the function of the pores found in the nuclear envelope? 8. Write 2 things that specifically move through the nuclear pores to and from the rest of the cell? 9. What are chromosomes and where are they found? 10. What is chromatin? 11. What is the nucleolus? What is its function? Vacuoles and Vesicles 12. What are vacuoles? What do they store? 13. Why are vacuoles important in plants? 14. Why type of vacuole is found in paramecium? Why is this important to it? 15. What are the functions of the vesicles found in eukaryotic cells? Lysosomes 16. ________________________ are small organelles filled with enzymes that function as the cell’s cleanup crew. 17. Write 3 important functions of lysosomes? The Cytoskeleton 18. What is the function of the cytoskeleton? 19. What are the 2 principal proteins that make up the cytoskeleton? Microfilaments 20. What are microfilaments? What is the name of the protein that makes it up? 21. Write 2 functions of the microfilament. Microtubules 22. What are microtubules? What is the name of the protein that makes it up? 23. Write 2 important functions of the microtubules. Ribosomes 24. What are ribosomes? 25. Where does the instruction to make proteins come from? Endoplasmic Reticulum 26. The internal membrane system of the cell is known as the ___________________ 27. What is the function of the ER? 28. What are the 2 divisions of the ER? 29. What is the function of the Rough ER? 30. Why is the rough ER said to be “rough”? 31. What is the function of the smooth ER? 32. Why is the smooth ER said to be “smooth”? Golgi Apparatus 33. Where do the proteins produced in the rough ER move to? 34. Describe the golgi apparatus? 35. What is the function of the Golgi apparatus? 36. Where do the proteins go after they leave the Golgi apparatus? Organelles That Capture and Release Energy 37. What is the primary source of energy for plants? 38. Where do your own body cells get its energy from? 39. What are the 2 organelles involved in energy conversion within the cell? Chloroplasts 40. Where are chloroplasts found? 41. What are chloroplasts? (INCLUDE FUNCTION) 42. What is photosynthesis? 43. How many membranes surround the chloroplasts? 44. Inside the organelle are large stacks of other ___________________, which contain the green pigment ___________________________. Mitochondria 45. Where would you find the mitochondria? 46. What are mitochondria? (INCLUDE FUNCTION) 47. How many membranes enclose the mitochondria? List them. 48. Humans get nearly all their mitochondria from___________________________ 49. __________________________ and ____________________ contain their own genetic information in the form of small DNA molecules. 50. What does the endosymbiotic theory suggest? Cellular Boundaries 51. What is the barrier surrounding a cell called? 52. What are the functions of the cell membrane? List 3 53. What do plant cells and prokaryotes have surrounding the cell membrane? What is the function? 54. ___________________, ___________________, ________________, and __________________ have cell walls. ______________________ cells do not have cell walls. 55. Cell walls lie outside the cell membrane and most are porous enough to allow ___________________, ____________________, __________________, and certain other substances to pass through easily. 56. Describe the lipid bilayer? Where is it found? 57. What are the functions of the lipid bilayer? 58. What is the lipid bilayer composed of? 59. The fatty acid portions of such a lipid are _________________________, or “water-hating,” while the opposite end of the molecule is ____________________________, or “water-loving.” The Fluid Mosaic Model 60. What do most cell membranes have embedded in the lipid bilayer? 61. What are attached to many of these proteins? 62. Why do scientists refer to the cell membrane as a “fluid mosaic?” 63. What do the proteins do in the cell membrane? 64. What is the function of many of the carbohydrate molecules? 65. When is a substance the said to be impermeable to the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane? 66. When is a substance said to be permeable to the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane? 67. Why are biological or cell membranes said to be selectively permeable? 68. What is another word for “selectively permeable membranes? DRAW AN ANIMAL CELL DRAW A PLANT CELL