* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basics in Confocal Microscopy Handouts
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Optical rogue waves wikipedia , lookup
Optical amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Fiber-optic communication wikipedia , lookup
Ellipsometry wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Preclinical imaging wikipedia , lookup
Hyperspectral imaging wikipedia , lookup
Passive optical network wikipedia , lookup
Vibrational analysis with scanning probe microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Silicon photonics wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Chemical imaging wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Interferometry wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical tweezers wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
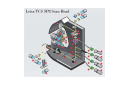
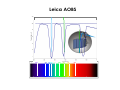
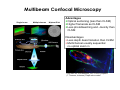
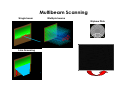
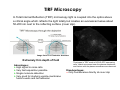
Basics in Confocal Microscopy Handouts 23.2. – 26.2.2015 EMBL internal course Advanced Light Microscopy Facility [email protected] Confocal Principle Photomultiplier Confocal Pinhole Dichroic beamsplitter Point Scanning Illumination Pinhole Objective lens Focal plane Advantages + High resolution + Optical sectioning + Multiple channels simultaneously + FRAP and photo -activation studies possible Disadvantages − Less light efficient bleaching − Slower acquisition − Expensive Optical sectioning Z Arabidopsis root, transmission image overlaid with isosurface rendered GFP fluorescence indicating the beginning of cell division (reporter construct by P. Dörner, Edinburgh) AOTF Acousto Optical Tunable Filter Leica AOBS 120 100 T r a n s m itta n c e % 80 60 40 20 0 400 450 500 550 600 wavelength (nm) 405 458 476488 514 543 561 594 633 650 700 Carl Zeiss LSM710 / 510 META Olympus Fluoview 1000 Multibeam Confocal Microscopy Single beam Multiple beams Nipkow Disk Advantages + Optical sectioning (less than CLSM) + Higher framerate as CLSM + Less photobleaching and –toxicity than CLSM Disadvantages − Less depth descrimination than CLSM − Multichannel usually sequential no optical zoom in Root hair cell of Arabidopsis, GFP in the Cytoplasm (T. Timmers, toulouse). Depth color coded. Multibeam Scanning Single beam Multiple beams Nipkow Disk Line Scanning Spectral Detection Imaging e.g. CFP and YFP simultaneous is important for some biological applications. Emission spectra of different FPs Using a multitude of different dyes, e.g. marking several genes on chromosomes, leads to spectral overlap which can be corrected by linear unmixing. Leica SP2 AOBS Zeiss LSM META Olympus Fluoview1000 TIRF Microscopy In Total Internal Reflection (TIRF) microscopy light is coupled into the optics above a critical angle which reflects the light totally but creates an evanescent wave about 50-200 nm next to the reflecting surface (cover slip). Image from TILL Photonics brochure Extremely thin depth of field Advantages: + High signal to noise ratio + Very fast acquisition possible + Single molecule detection + Very good for studying vesicle-membrane fusion events and cell adhesion Laser adjustment to TIRF mode visualized with fluorescein solution Time-lapse in TIRF mode of VSVG-GFP expressing cells. Vesicle movement near the plasma membrane and fusions with the plasma membrane are observed. Disadvantages: − Only fluorescence directly at cover slip Which Microscope Type To Use ? Non-confocal Multi-beam confocal Single-beam confocal Applications: Non-confocal: • fast and long-term time-lapse of flat samples • FRAP + Photoactivation with additional laser Multibeam: • Fast and long-term time-lapse with increased Z-resolution and less phototoxicity than CLSM Confocal: • Imaging for high resolution 3D rendering • Multi-channel time-lapse • FRAP + Photoactivation z xy