* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology EOC Review 6 Cell Cycle, Transport and Differentiation
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
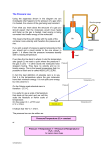
Biology EOC Review 6 Cell Cycle, Transport and Differentiation Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement. 1. Which phrase best describes the property of selective permeability? A. some molecules pass B. all molecules pass C. large molecules pass D. no molecules pass 2. What is this a picture of? 9. During G1, the cell A. splits into two new cells. B. carries out its normal functions. C. duplicates its DNA. D. divides its cytoplasm. 10. Which is the term for a group of proteins that organizes and concedes long strands of DNA into tight coils? A. telomeres B. centromeres C. chromatids D. histones 11. During which stage of mitosis do sister chromatids spate from one another? A. prophase B. metaphase C. anaphase D. telophase 12. Substances known to produce or promote cancer are A. carcinogens. B. kinases. C. cyclins. D. malignancies. 3. Which word best describes the cell membrane? A. layered B. rigid C. impermeable D. nonpolar 4. The movement of molecules down a concentration gradient through transport proteins in the cell membrane is a type of A. selective transport. B. osmosis. C. energy expenditure. D. facilitated diffusion. 5. Water moves out of a cell when the concentration surrounding the cell is A. hypertonic. B. isotonic. C. hypotonic. 6. Cells use active transport to A. obtain molecules they need. B. break down molecules. C. engulf large particles. D. detect the charge of molecules. 7. A membrane-bound sac used to transport materials into and out of the cell is a A. pump. B. macrophage. C. lysosome. D. vesicle. 8. Why do cells lining the stomach divide more quickly than those in the liver? A. They are much smaller cells. B. They have fewer chromosomes. C. They need much more surface area. D. They undergo more wear and tear. 13. What is the term for programmed cell death? A. kinase B. cyclin C. apoptosis D. mutate 14. The most common form of reproduction among prokaryotes is A. mitosis. B. budding. C. binary fission. D. fragmentation. 15. Which of the following is a direct result of a normal cell’s ability to express only certain genes? A. cells can become totipotent B. cells can grow and reproduce C. cells can mutate and adapt D. cells can differentiate and specialize 16. Which type of stem cell can grow into any other cell type? A. somatic B. multipotent C. totipotent D. pluripotent 17. Cancer cells that have moved from their original location are considered A. benign. B. mutated. C. malignant. D. good. 18. Which type of cells undergo mitosis? A. somatic cells B. germ cells 19. Uncontrolled cell growth is called A. meiosis. B. mitosis. C. cancer. D. tumor. 20. What does a cell make during the synthesis stage of the cell cycle? A. more organelles B. a copy of DNA C. daughter cells D. greater surface area