* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10-3
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
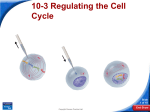
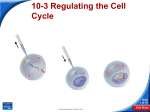
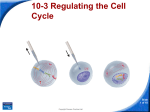
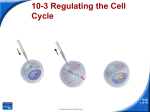
Biology Slide 1 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Slide 2 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Controls on Cell Division 1.Controls on Cell Division (Experiments show that) a. normal cells will reproduce until they come into contact with other cells. b. When cells come into contact with other cells, they respond by not growing. c. controls on cell growth and division can be turned on and off. Slide 3 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Controls on Cell Division Contact Inhibition Slide 4 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Regulators How is the cell cycle regulated? Slide 5 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Regulators 2. Cell Cycle Regulators a. regulated by specific protein. b. amount of this protein in the cell rises and falls in time with the cell cycle. c. Cyclins regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. Slide 6 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Regulators Cyclins were discovered during a similar experiment to this one. A sample of cytoplasm is removed from a cell in mitosis. The sample is injected into a second cell in G2 of interphase. As a result, the second cell enters mitosis. Slide 7 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Regulators 3. Internal Regulators a. Proteins that respond to events inside the cell (Internal regulators allow the cell cycle to proceed only when certain processes have happened inside the cell.) Slide 8 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Regulators 4. External Regulators a. Proteins that respond to events outside the cell (External regulators direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle.) Slide 9 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Uncontrolled Cell Growth 5. Uncontrolled Cell Growth (Cancer is a disorder in which some of the body's own cells lose the ability to control growth.) How are cancer cells different from other cells? Slide 10 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Uncontrolled Cell Growth a. Cancer cells do not respond to the signals that regulate the growth of most cells. Slide 11 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Uncontrolled Cell Growth (Cancer cells divide uncontrollably and form masses of cells called tumors that can damage the surrounding tissues. Cancer cells may break loose from tumors and spread throughout the body, disrupting normal activities and causing serious medical problems or even death.) Slide 12 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 Click to Launch: Continue to: - or - Slide 13 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 The cell cycle is believed to be controlled by proteins called a. spindles. b. cyclins. c. regulators. d. centrosomes. Slide 14 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 Proteins that respond to events inside the cell are called a. internal regulators. b. external regulators. c. cyclins. d. growth factors. Slide 15 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 Once a multicellular organism reaches adult size, the cells in its body a. stop dividing. b. grow and divide at different rates, depending on the type. c. have the same life span between cell divisions. d. undergo cell division randomly. Slide 16 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 One effect of an internal regulator is that a cell will not begin mitosis until a. it becomes too large. b. the cell’s growth is stimulated. c. it is in physical contact with other cells. d. all its chromosomes have been replicated. Slide 17 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 10-3 One factor common to almost all cancer cells is a. a lack of cyclin. b. a defect in gene p53. c. exposure to tobacco smoke. d. exposure to radiation. Slide 18 of 18 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall END OF SECTION