* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 9 Study Guide
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Acquired characteristic wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Taxonomy (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
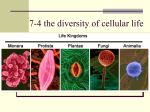
Name _____________________________________________________ Period ___ Study Guide Living Things & Classification Directions: Respond to the short answer questions using complete sentences. Remember, A SENTENCE SHARES A COMPLETE THOUGHT. Structure your responses in a way similar to the sample below. Identify the subject. Select a verb. Restate the topic addressed in the question. Choose an appropriate action word. Kingdoms that have both unicellular and multicellular organisms include Complete your thought with the details of the answer. Provide a specific answer to the question. Example Question: Which kingdoms include both unicellular and multicellular organisms? the Protist and Fungi kingdoms. 1. Explain the difference between the terms unicellular and multicellular (6). 2. Explain the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell (23-24). 3. Explain the difference between an autotroph and a heterotroph (11). Name _____________________________________________________ Period ___ 4. List 6 characteristics of living things (6-7). This is review. 1-__________________________________________________ 2-__________________________________________________ 3-__________________________________________________ 4-__________________________________________________ 5-__________________________________________________ 6-__________________________________________________ 5. Describe three characteristics about our planet, Earth, that make it a habitable environment for organisms (11-13). 1-__________________________________________________ 2-__________________________________________________ 3-__________________________________________________ 6. What is homeostasis (13)? 7. Give an example of a stimulus and a response (7). 8. Arrange the following from smallest to largest: __ organ system __organ __cell __tissue __organism 9. Identify the following as a molecule of life, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, or organism. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. ______________ monkey ______________ DNA & RNA ______________ blood ______________ digestive organs ______________ skin piece ______________ carbohydrate ______________ sperm ______________ lipids (fats) ______________ stomach ______________ sensory organs and nerves ______________ piece of liver ______________ protein Name _____________________________________________________ Period ___ m. ______________ intestine n. ______________ paramecium 10. What are the 8 levels of classification (18-19)? a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. Level 1:____________________ (most general) Level 2:____________________ Level 3:____________________ Level 4:____________________ Level 5:____________________ Level 6:____________________ Level 7:____________________ Level 8:____________________ (most specific) 11. Create an acronym that will help you to remember the order of the 8 levels of classification (from most general to most specific). 12. Fill out the chart below: Kingdom Domain Prokaryotic Autotroph, or eukaryotic heterotroph, cells? or either? Unicellular, multicelluar or either? 13. What is binomial nomenclature (16)? 14. The scientific name for an organism comes from its __________ and __________ (16). 15. What do we do to the first letters of each of these two words (16)? Name _____________________________________________________ Period ___ 16. What do we do to the font (16)? 17. What is the purpose of a dichotomous key (20-21)? 18. What is taxonomy(15)? 19. Who is Carolus Linnaeus and why is he an important scientist (16)? 20. Read the list of organisms. To which kingdom does each organism belong (22-25)? Plantae Animalia a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. Fungi Protista Archaebacteria Bacteria slime mold ____________________ Euglena ____________________ Brown trout ____________________ Paramecium ____________________ Hot springs bacteria ____________________ E. coli ____________________ T-rex ____________________ Sunflower ____________________ Ferns ____________________ Beetle ____________________ 21. Review the chart below (18-19). Some Types of Trees Common Name of Tree Bird cherry Flowering cherry Smooth-leafed elm Whitebeam Kingdom Family Species Plants Plants Plants Plants Rosaceae Rosaceae Ulmaceae Rosaceae Prunus avlum Prunus serrula Ultimus minor Sorbus aria Which one of the four trees is most different from the other three? Explain your answer. Name _____________________________________________________ Period ___ 22. Match the kingdom with the most appropriate description of each kingdom (22-25). a. ___ Multicellular, moves, and has a nervous system. b. ___ Uses the sun’s energy to make food (photosynthesis). c. ___ Can live in extreme environments like hot springs and acidic areas. d. ___ Single-celled or simple multicellular (Ex: paramecium). e. ___ Digests food outside of body and then absorbs it. f. ___ Bacteria that live almost everywhere (most bacteria). A. B. C. D. E. F. Animalia Plantae Protista Fungi Archaebacteria Eubacteria 23. Match the class with the most appropriate description of each class (160-163). a. ___ Has hair and feeds milk to its young. b. ___ Moist skin, lays eggs without shells, lives early life in water and adult life on land. c. ___ Scaly skin, lays eggs with shells. d. ___ Has an exoskeleton, jointed limbs, six legs and three body segments. e. ___ Adapted for flight, has feathers, lays eggs with shells. A. B. C. D. E. Insecta Amphibia Mammalia Reptilia Aves