* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islam`s Origins as History and Heritage Fred M. Donner – University
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Iran wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
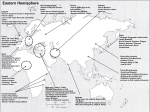
Islam’s Origins as History and Heritage Fred M. Donner – University of Chicago February 1, 2011 (1) Origins phase [600-700 CE] (2) Caliphal Empire and Articulation of the Classical Islamic Paradigm [700-1200 CE] (3) Diversification and Diffusion to New World Areas [1000-1700 CE] (4) The Early Modern Empires [1400-1900 CE] (5) The Western Onslaught [1500-present] Byzantine (Later Roman) Empire Sasanian (Persian) Empire Zoroastrianism Mecca Kaaba (Ar. ka‘ba, “cube”) Koran (Qur’ān) “5 Pillars of Islam”: statement of faith (shahāda) ritual prayer (ṣalāt) almsgiving (zakāt) fasting (ṣawm) in month of Ramadan ṣajj—pilgrimage to Mecca caliph (Ar. khalifa, “successor,” representative”) mu’min, “Believer”; muslim ‘Uthman (r. 644-656) ‘Ali (r. 656-661) Shi‘a / shīat ‘Alī, “party of ‘Ali” Kharijites / Khawarij Umayyad dynasty (661-750)—Damascus Abbasid dynasty (750-1258)—Baghdad Islamic law (shari‘a) Oghuz migrations (11th-12th century) Saljuq Sultanates (1040-14th century) Ghaznavids (977-1186) madrasa (religous school, seminary) Khurasan (N.E. Iran) Sufis (mystics) Muhammad dies 632 CE Ridda wars 632-634 Syria conquered ca. 636 Iraq conquered ca. 637 W. Iran 642 Marv (C. Asia) 651 Egypt—Fustat 642 Qayrawan—N. Africa 670 Spain conquered 711-713 Samarqand 712 Sind (Indus Valley) 714 Khazars, Georgia 730 Battle of Tours (?) 732 Battle of Talas 751 Constantinople besieged: 655, 669, 673-78, 717-18, 783-85 al-Husayn ibn ‘Ali Karbala (battle, 680) Samarra Mongol conquest (Baghdad, 1258) Ottoman Empire (ca. 1275-1924) Safavid Empire (1501-1722) Mogul Empire (1526-1858) Bibliography: Fred M. Donner, Muhammad and the Believers: at the origins of Islam (Harvard University Press, 2010); Vernon O. Egger, A history of the Muslim World to 1405 (Pearson-Prentice-Hall, 2004; William L. Cleveland, A history of the modern Middle East (Westview, 2004); Marshall G. S. Hodgson, The Venture of Islam (3 vols., University of Chicago Press, 1974).