* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3-Cells copy - Woodland Christian School
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
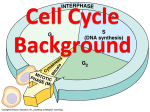
Chapter 3Cells I will describe the intricacies of how the cell and its different parts work together to enable the organism to survive i similar to solving a puzzle. My goal is ________________________. Cells- Chapter 3 Study guide • mutation-a change in DNA sequence • DNA-molecule that contains the genetic material of a cell • cell membrane- controls what goes in and out of a cell • cytoplasm- a jelly-like substance that contains the organelles • organelle-one of several tiny structures within a cell • cell wall-the rigid outer layer that protects and supports plant cells • trait-a characteristic that can be passed on to offspring • gene-a segment of DNA located on the chromosome • chromosome-a structure that contains DNA • cell cycle-a series of events occurring in the life of a cell • interphase-the stage of cell growth occurring at the beginning of the cell cycle • mitosis-the process by which the cell divides its nucleus into 2 nuclei • cytokinesis-the process in which a cell’s cytoplasm is divided in half • cancer-a disease caused by cells that go through uncontrolled cell division Three Parts of the Cell Theory All living things are made of cells. Cells are the basic unit of all organisms. All cells come from other cells The Order of The Main Stages of a Cell interphase > mitosis> cytokinesis Chapter 3-Cells Quiz Write the correct letter of each definition on the blank provided beside the term • ________ cancer • ________ mutation • ________ cytokinesis • ________ DNA • _________ mitosis • __________ cell membrane • __________ interphase • __________ cell cycle • ___________ cytoplasm • __________ organelle a. one of several tiny structures within a cell b. a series of events occurring in the life of a cell c. molecule that contains the genetic material of a cell d. the stage of cell growth occurring at the beginning of the cell cycle e. the process by which the cell divides its nucleus into two nuclei f. the rigid outer layer that protects and supports plant cells g. the process in which cell’s cytoplasm is divided in half h. a structure that contains the DNA i. a characteristic that can be passed in to offspring j. a change in the DNA sequence k. a jelly-like substance that contains the organelles l. controls what goes in and out of the cell m. a disease caused by cells that go through uncontrollable cell division n. a segment of DNA located in the chromosome Answer the following questions in complete sentences. • __________ chromosome • __________ gene • _________ trait • _________ cell wall 1. List the three parts of the cell theory ._________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________. 2. List the 3 main stages of the cell cycle in order. __________________________>__________________________>____________________ Cell Structure • organelle-one of several tiny structure within a cell • cell membrane- a flexible structure that protects and controls what goes on an out of the cell • cytoplasm-the jelly-like substance found inside the cell that contains organelles • cell wall-the rigid outer layer that protects and supports plant cells • In 1663, Robert Hooke was one of the first people to view cells when he built a compound microscope • Plants and animals have a nucleus that contains the genetic instructions for the brain • The cell membrane selects what goes in and out of the cell • cell walls make fruit and vegetables crunchy Genetics • DNA-the molecule that contains the genetic material of a cell • chromosome-a structure located in the nucleus that contains DNA • gene- a segment of DNA located on the chromosome that, among other things, controls specific traits • trait- a characteristic that can be passed on to an organism’s offspring. • DNA determines the type of cell and directs the cell’s function • dark spot is the nucleus • Chromosomes look like an X • People have 46 chromosomes • Traits make an organism look the way it does The Cell Cycle • cell cycle-a series of events occurring during the life of a cell • interphase-the stage of a cell growth occurring at the beginning of the cell cycle • mitosis-the stage of the cell cycle in which cell’s nucleus divides in two • cytokinesis-the final stage of the cell cycle in which the cytoplasm divides • Organisms grow as they produce more cells and they multiply by dividing • The cell cycle stages are interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis • Interphase occurs at the beginning of the cell cycle and the organelles and DNA are copied • Mitosis begins after interphase where the cell divides its nucleus in two • The third stage is cytokinesis Cell Organization • In multicellular organisms cells work together to perform specific functions. • During fertilization a cell obtains its complete set of DNA from both parents • This cell divides by mitosis and forms an embryo Cancer • mutation- a change in the DNA sequence of a gene or chromosome • cancer-a disease caused by cells that go through uncontrolled cell division • The life span of a cell depends on whether the total number of cell cycles has occurred, whether the cell is damaged and infected, or whether the DNA is damaged in any way. • Cancer begins when DNA in a cell is damaged, causing a mutation. A lot of times these mutations can be repaired • Sometimes they cannot be repaired and cause the cell the grow and become cancerous • Three methods of cancer treatment are surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy