* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Non - Mendelian Genetics
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
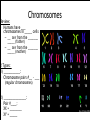
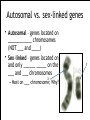
Non - Mendelian Genetics Patterns of Inheritance that don’t quite follow Mendel’s laws Non-Mendelian Genetics • Mendel’s pea experiments displayed _______ ___________ patterns ! • Many traits, however, are inherited through more _______ patterns – _____________ ___________ – _____________ – ______ _______ Difference in dominant traits *Important to Note* Some alleles are neither __________ nor ___________, and many ______ are controlled by __________ alleles or genes. Incomplete Dominance ! • Incomplete dominance: – When ______ trait is _________. – The ______________ phenotype will show a ______ of the traits – “_________” of Dominance ! • Allele forms mix together to give an ______________ appearance ! • One allele does ______ completely _______ the other ! • Note: Both homozygous forms are designated by distinct ___________ letters ! R = allele for red flowers W = allele for white flowers red x white ---> pink RR x WW ---> 100% RW Incomplete Dominance Codominance • Codominance: – _________ allele forms • Both alleles can _______ , meaning both _____ at the ______ time • More than _____ possible alleles exist in a population – Speckled sussex chickens, black and white feathers Codominance • _________ _________ – A and B are ________ over O, but “_____” dominant with each other. ABO Blood System • Notation: use capital letter “___” to show domiance over “___” and __________ to show _____________. ABO Blood System • Blood type is determined by ________ (markers) on the _______ of the cells • If antigens are mixed _________ , they react with _________ which cause blood to clot. Polygenic Traits • Trait controlled by many different genes. – ____ _______ – _____ ______ – ________ Chromosomes Review: • Humans have ___ chromosomes in _____ cells – __ are from the _______ _____ (father) – __ are from the _______ _____ (mother) ! 2 Types: 1) ___________: • Chromosome pairs #__ - ___ (regular chromosomes) ! 2) _______________: • Pair #____: • XX = ________ • XY = _____ _____________ • Why do you think theses chromosomes are arranged this way? ! • Is this from a male or female? ! ! ! • _____ eggs carry the ___ chromosome ! • ONLY ______ of sperm carry the ___ chromosome; what would the other half carry? Autosomal vs. sex-linked genes • Autosomal – genes located on ____________ chromosomes (NOT ___ and ____) • Sex-linked – genes located on and only ______ _____ on the ___ and ___ chromosomes X – Most on ___ chromosome; Why? Y Autosomal vs. sex-linked genes • ________ sex-linked traits appear more often in _____ – No ___________ to _____ or ____ the trait. ! • Males have 1 X chromosome • They don’t have another X to hide a gene • ____ __- _______ genes are ___________ in males (even if _________) • Common disorders – _______ ___________ – __________________ Color Blindness • Colorblindness: ________ , ___________trait – Mostly in ______ (1:10) • _____-______ • _____-_________ • Achromatopsia very rare – Can only see in shades of ______ Color Blindness • Colorblindness: recessive, sex-linked trait XE = _______ _________ Xe = ______________ Y = ___, but does not have an _______for the gene ! • • • • • XE XE = ? XE Xe = ? Xe Xe = ? XE Y = ? Xe Y = ? Pedigree Charts • A _________ showing the _____________ of ______ within a ________ • _________ tree – Traces traits through the ____________. Pedigree Charts • A diagram showing the inheritance of traits within a family – ________ are females; _________ are Males – Connecting ____________ line= marriage – Connecting _________ line = child ! • _______ filled in shape= _________ of gene • _______ shaded shape = __________ gene Pedigree Charts • A diagram showing the inheritance of traits within a family Pedigree of a Sex-linked Trait • A diagram showing the inheritance of traits within a family