* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pre-public Exam Review#2 with Solutions
Survey
Document related concepts
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear physics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic mass wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
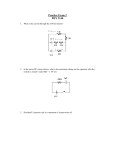
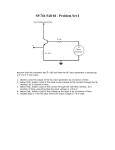
Physics 3204 Final Review (Based on June 2014 exam) Name:__________________ Scan this QR code (or go to http://www.ed.gov.nl.ca/edu/k12/evaluation/physics3204/ june_2014_physics_3204_outcome_report.pdf) to see the Exam Report for the 2014 Public Exam. The questions below are based on this report. (The questions will make more sense if you read them in the context of the exam report.) UNIT 1 1. (L1) Draw a sketch to show the horizontal and vertical velocity of a projectile at three points along its path. 2. (L2) A projectile is shot at 15 m/s at 60o above the horizontal. Determine how much time is needed for it to travel 10.0 m horizontally. 3. (L2) A coin is shot horizontally off a 0.95-m high table, and lands 1.2 m away from the table’s edge. Determine its initial speed. 4. (L1) A soccer ball is kicked at 30.0 m/s at 45o above the horizontal. Determine the magnitude of its final velocity as it lands on the ground. 1|Page 5. (L2) A ball is thrown upwards at 12 m/s, 30o above the horizontal. Determine its maximum height reached. 6. (L2) A cannonball is launched horizontally at a speed of 250 m/s from a 45-m high cliff. Determine its range. 7. (L1) A 10-kg object is sliding down a 30o incline. Determine the magnitude of the normal force on it. 8. (L2) A 5.0-kg object is at rest on a 25 o incline. Determine the magnitude of the frictional force on it. 2|Page 9. (L1) Draw a sketch of an object at rest on an inclined plane. Label all forces on the object. 10. (L2) A mass is held in static equilibrium by two ropes as shown. Determine the object’s mass. 11. (L2) A system of masses (M1 = 5.0 kg, M2 = 2.5 kg) is connected on a frictionless table as shown. Determine the acceleration of the system. 12. (L1) A car is traveling in a circular path on a horizontal road. What is the direction of the centripetal force on the car? 3|Page 13. (L2) A car is traveling along a hill, which is a vertical circle of radius 8.0 m. At what speed will the car lose contact with the road at the top of the hill? 14. (L2) A ball is tied to a 1.5-m long string, and swung in a horizontal circle, with a period of 0.50 s. Determine its centripetal acceleration. 15. (L2) When an object is traveling at 3.0 m/s in a horizontal circle of radius 0.50 m, the tension in the string is 45 N. Determine the object’s mass. 4|Page 16. (L1) A racecar is traveling at 42 m/s on a frictionless turn that is banked at 31 o. Determine the radius of the turn. 17. (L3) When an object of mass “m” is swung in a horizontal circle, the tension in the string is 39 N and the angle is 60o as shown. Determine the centripetal force on the mass. 18. (L1) Define “centre of mass.” The point representing the mean position of the mass in a body or system of bodies. 19. (L3) A boy is walking along a plank that is overhanging a patio as shown. Explain what happens to the Force and the Torque on the plank as the boy continues to walk further along the plank. 5|Page 20. (L1) Which situation produces a clockwise torque on the uniform beam? 51 a) 3%, LEVEL 3 A baseball is thrown at 15.0 m/s, at 30.0o above the horizontal as shown. A 0.500-m high target is located 18.0 m away. If the baseball is thrown from the same height as the centre of the target, determine if it will strike the target. 51 b) 2%, LEVEL 2 Explain how uniform circular motion is an example of acceleration. 6|Page Acceleration means changing VELOCITY. This can be changing speed or direction, or both. In UCM, the object's speed is constant, but the direction is changing. 51 c) (i) 4% (**Science Communication Mark), LEVEL 2 Two masses (M1 = 5.00 kg, M2 = 10.0 kg) are connected via a string as shown. The horizontal surface has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.350, while the inclined plane is frictionless. Determine the acceleration of the system of masses. 51 c) (ii) 2%, LEVEL 2 Determine the tension in the string connecting the masses. 7|Page 51 d) 2%, LEVEL 2 A 1.50-kg mass is swung in a vertical circle on a 75.0-cm long string. Determine the tension in the string when the mass is at the top of the circle. 51 e) 3%, LEVEL 3 A 4.00-m long uniform beam has a mass of 15.0 kg, and is supported on each end by a saw horse as shown. Determine where a 75.0-kg student should stand on the beam so that F1 = 487 N and F2 = 395 N. 8|Page 51 f) 4%, LEVEL 2 A 5.00-m long, 10.0-kg ladder leans against a frictionless wall as shown. A 75.0-kg student is located 3.00 m up the ladder. Determine the force of friction provided by the ground to keep the ladder at rest. UNIT 2 21. (L1) With the aid of sketches, explain what happens to a neutral electroscope as a positive object is brought nearby. The + object attracts electrons in the 'scope, moving them towards the + object. This makes the side of the 'scope closest to the + object to be Negatively charged, and the side of the 'scope furthest from the + object to be Positively charged. This charge rearrangement is only temporary, and shifts back to normal when the + object is removed. 9|Page 22. (L2) What is the charge on an object that has an excess of 2.81 x 1013 electrons? 23. (L1) Sketch the electric field surrounding a positive and a negative charge. 24. (L3) An object with charge “q” is placed in an electric field, experiencing an electric force “F.” Determine the force on the object if its charge is doubled. 25. (L2) Determine the work required to move an electron through a potential difference of 12 V. 10 | P a g e 26. (L1) Determine the current in a wire if 900 C flows through it in 60 s. 27. (L1) Determine the electric field strength 15.0 cm away from a 4.5 µC charge. 28. (L1) Sketch a series circuit, and show the correct placement of a voltmeter and an ammeter. 29. (L2) Sketch a V vs I graph for a material with a resistance of 100 Ω. 11 | P a g e 30. (L1) Given that the resistivity of copper is 1.71 x 10-8 Ω m, what is the resistance of a copper wire 1.50 m long and 2.00 mm in diameter? 31. (L2) Determine the current through resistor 2. 32. (L2) What is the cost to operate a 60-W light bulb for a full year, if electric energy costs 11.178 ¢/kWh? 33. (L2) What is total resistance for the circuit below, if all resistors are 10.0 Ω? 12 | P a g e 34. (L3) What is the voltage across resistor 3? 35. (L1) Sketch a bar magnet and 4 compasses placed around it. Show the direction that the compass needles will point. 36. (L1) Sketch a current-carrying conductor, and the magnetic field surrounding it. 37. (L2) Sketch a current-carrying conductor placed inside an external magnetic field. Determine the direction of force on the conductor. 13 | P a g e 38. (L2) Sketch a current-carrying coil and 2 compasses placed near each end of the coil. Show the direction that the compass needles will point. 39. (L2) Determine the direction of induced current in coil B, just as switch A is opened. When switch A is opened, the mag field around coil A collapses. This gives a S-pole getting weaker nearest to coil B. The induced I in coil B will create a mag field that attempts to STOP the CHANGE in the original mag field, thus creating a N-pole nearest coil A. Thus the induced I in coil B flows DOWN in the FRONT of coil B. 40. (L2) An electron experiences a 1.20 x 10-6 N force when projected perpendicularly into a 5.0 x 10-5 T magnetic field. Determine the electron’s speed. 52 a) 4% (*Science Communication Mark), Level 2 Three charged objects, A, B and C have charges of -1.5 µC, +2.0 µC, and + 3.0 µC, respectively, and are arranged as shown. Calculate the net electric force on charge B. 14 | P a g e 52 b) 3%, Level 3 A charged object with mass 1.00 g has an excess of 2.45 x 10 11 electrons. Calculate the electric field strength necessary to suspend the mass between two charged plates as shown. 52 c) 3%, Level 3 A resistor is in parallel to a 12-V battery in a circuit. The resistor is 0.28 m long and is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.25 T. If the resistor experiences a force of 4.0 x 10 -2 N when it is perpendicular to the magnetic field, what is its resistance? 15 | P a g e 52 d) Use the circuit given to answer the questions below. (i) 1%, Level 2 Determine the total resistance of the circuit. (ii) 2%, Level 2 Determine the voltage across resistor 3. (iii) 1%, Level 2 Determine the power dissipated by resistor 4. 16 | P a g e 52 e) 3%, Level 2 A long, straight conductor has a current through it, and creates a magnetic field around it. At point P, 0.020 m to the side of the wire, the magnetic field is 5.0 x 10 -5 T [into the page]. Determine the magnitude and direction of the current in the conductor. 52 f) 3%, Level 2 Sketch the current output from an AC and DC generator, and explain how and why they are different. 17 | P a g e AC current alternates (changes) direction, while DC current never changes direction. This is because the DC generator has a SPLIT RING, which allows the connections to the external circuit to be reversed at the same instant that the current in the coil reverses. This "double-negative" gives a DC output. 41. (L1) Define a “blackbody.” An object that absorbs all radiation incident on it, and then re-emits a continuous spectrum of radiation. 42. (L2) Copper has a work function of 4.65 eV. Determine the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons if copper is illuminated with light of wavelength 210 nm. 43. (L2) Determine the DeBroglie wavelength of a photon with momentum 1.656 x 10 -27 kg·m/s. 44. (L1) A photon has 4.967 x 10-19 J of energy. What is this energy, expressed in eV? 18 | P a g e 45. (L1) Determine the orbital radius for an electron in the third energy level of a hydrogen atom. 46. (L1) Determine the energy of a 650 nm wavelength photon. 47. (L3) The graph below shows the mass of a radioactive isotope versus time. What is the half-life of the isotope? 19 | P a g e 48. (L2) Determine the energy released in the alpha decay of radon-198 into polonium-194. (atomic mass 198Ra = 197.998679 u, 194Po = 193.988186 u, 4α = 4.001506 u) 49. (L2) Determine the daughter nucleus in the beta minus decay of 198 Ra. 50. (L1) Define “nuclear fusion.” Joining lighter elements to make a heavier element , and release energy. 53 a) 3%, Level 3 A graph of maximum kinetic energy vs frequency is given below. Determine which metals will exhibit the photoelectric effect when illuminated by light with frequency 7.0 x 10 14 Hz. Metal Work Function (eV) Sodium 2.28 Copper 4.70 Gold 5.10 20 | P a g e 53 b) 2%, Level 2 Determine the energy gained by an electron when is moves from n = 2 to n = 4 in a hydrogen atom. 53 c) 3% (**Science Communication Mark), Level 3 The half-life of 131Ba is 11.5 days. If a sample containing 150.0 mg is left to decay, determine the time required so that 15.0 mg of 131Ba remain. 21 | P a g e 53 d) 2%, Level 2 The radioactive element 210Po undergoes radioactive decay as shown in the equation: Determine the energy released per atom. Express your answer in J, and in MeV. 22 | P a g e