* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 15.3
Kerr metric wikipedia , lookup
Laplace transform wikipedia , lookup
Unification (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
BKL singularity wikipedia , lookup
Two-body problem in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Euler equations (fluid dynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Van der Waals equation wikipedia , lookup
Dirac equation wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Neumann–Poincaré operator wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Schwarzschild geodesics wikipedia , lookup
Heat equation wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
New seats today, you may sit where you wish. Partial Derivatives A partial derivative of a function with multiple variables is the derivative with respect to one variable, treating other variables as constants. If z = f (x,y), then z wrt x: f x x, y f x, y z x x x z f x, y z y wrt y: f y x, y y y Ex. Let f x, y xe , find fx and fy and evaluate them at (1,ln 2). x2 y zx and zy are the slopes in the x- and ydirection Ex. Find the slopes in the x- and y-direction 2 1 2 of the surface f x, y 2 x y 258 at 1 2 ,1,2 Ex. For f (x,y) = x2 – xy + y2 – 5x + y, find all values of x and y such that fx and fy are zero simultaneously. Ex. Let f (x,y,z) = xy + yz2 + xz, find all partial derivatives. Higher-order Derivatives f f x 2 f xx x x 2 f fx f xy y yx 2 f fy f yx x xy 2 f f y 2 f yy y y 2 mixed partial derivatives Ex. Find the second partial derivatives of f (x,y) = 3xy2 – 2y + 5x2y2. fxy = fyx Ex. Let f (x,y) = yex + x ln y, find fxyy, fxxy, and fxyx. A partial differential equation can be used to express certain physical laws. u u 2 0 2 x y 2 2 This is Laplace’s equation. The solutions, called harmonic equations, play a role in problems of heat conduction, fluid flow, and electrical potential. Ex. Show that u(x,y) = exsin y is a solution to Laplace’s equation. Another PDE is called the wave equation: 2 2 u 2 u a 2 2 t x Solutions can be used to describe the motion of waves such as tidal, sound, light, or vibration. The function u(x,t) = sin(x – at) is a solution.


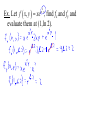


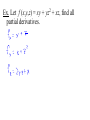
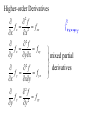



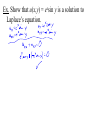






















![1,2-DIHYDROPYRAZOLO[1,2-A]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002555217_1-0c89b3c15753508fdc505e732fbfe183-150x150.png)