* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Characteristics of Stars
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
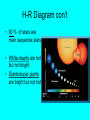
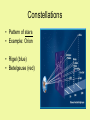
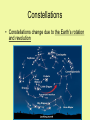
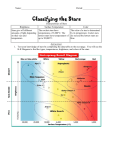
Characteristics of Stars Star classification • Stars are classified based on the following characteristics: Size, Temperature/color and Brightness Size (smallest to largest) Neutron star White dwarf Medium (Sun) Giant Super giant Temperature/Color (coolest to hottest) • Red (3,200 degrees C) • Yellow (Our sun 5,500 degrees C) • White-blue (15,000 degrees C) Brightness of Stars • Absolute magnitude – measure of the amount of light given off by a star • Apparent magnitude – a measure of the amount of light received on Earth (a dim star can appear bright if its close to Earth; a bright star can appear dim if its far away) H-R Diagram (Hertzbrung and Russell) Stars with higher temperatures have greater absolute magnitudes H-R Diagram con’t • 90 % of stars are main sequence stars • White dwarfs are hot but not bright • Giants/super giants are bright but not hot Measuring distances to stars • Measure parallax – the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions. • Knowing the angle that the star’s position changes and the size of Earth’s orbit, astronomers can calculate the distance of the star from earth. Light year • *** is a measure of distance, not time! • Unit representing the distance light travels in one year – (300,000 km/sec) or about 9.5 trillion km/year used to record distances between stars and galaxies • Proxima Centauri is 4.3 light years away • Looking back in time Constellations • Pattern of stars • Example: Orion • Rigel (blue) • Betelgeuse (red) Constellations • Constellations change due to the Earth’s rotation and revolution • According to the H-R diagram, as a star’s temperature increases its brightness ________.