* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 18
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biomolecular engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Horizontal gene transfer wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Disinfectant wikipedia , lookup
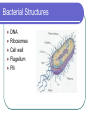
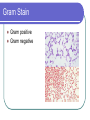
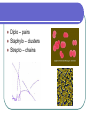
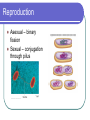
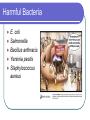
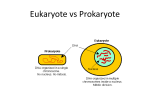
Chapter 18 - Bacteria Bacterial Structures DNA Ribosomes Cell wall Flagellum Pili Gram Stain Gram positive Gram negative Bacteria Shape Cocci (coccus) Bacilli (bacillus) Spirilla (spirillum) Diplo – pairs Staphylo – clusters Strepto – chains Streptococcus Movement & Support Have cell walls to support shape and provide protection Some have flagellum for movement Digestion/Obtaining Nutrients Some are autotrophs Photosynthetic Chemosynthetic Some are heterotrophs that use organic molecules that they engulf & breakdown Some use aerobic respiration and others use fermentation (anaerobic). These processes produce energy Nervous/Response Circular chromosome with DNA Some produce endospores Some produce toxins Circulation Rely on flow of cytoplasm to move materials through cell Gas Exchange Gases are exchanged directly to the environment through diffusion Excretion Waste is secreted through the cell membrane by diffusion or exocytosis Reproduction Asexual – binary fission Sexual – conjugation through pilus What makes bacteria so great? They reproduce rapidly Their DNA mutates frequently They can exist in extreme environments They are able to use substances that other organisms cannot Helpful Bacteria Nitrogen fixation Recycling nutrients (saprophytes & decomposers) Medicine Food Harmful Bacteria E. coli Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Yersinia pestis Staphylococcus aureus Antibiotic Resistance Vaccines & Immunity Vaccines consist of dead/destroyed virus or bacteria Sensitizes the body to the foreign objects Creates antibodies that recognize foreign antigen Allows the body to react more quickly when it encounters the “real deal” How do we protect ourselves from infectious agents? Skin Body secretions Inflammation & fever Antibodies Antibiotics & vaccines