* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psychology - HGunnWikiMHS
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Humanistic psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Index of psychology articles wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Health psychology wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical psychology wikipedia , lookup
Occupational health psychology wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Indigenous psychology wikipedia , lookup
Political psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cyberpsychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychological evaluation wikipedia , lookup
Developmental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychological injury wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
International psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Forensic psychology wikipedia , lookup
History of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Experimental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Subfields of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Society for the Psychological Study of Social Issues wikipedia , lookup
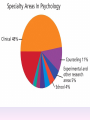
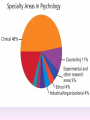
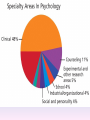
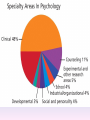
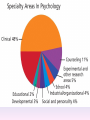
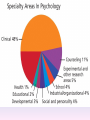
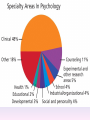
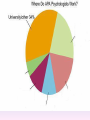
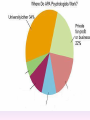
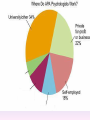
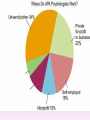
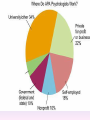
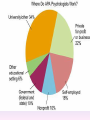
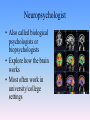
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Methods Domain Introductory Chapter Human Behavior • Write down a question you have about human behavior. (Nothing “naughty”) No names. Switch. • Read the one you get and consider how you would answer that question: Why would someone do that? Think that? Live that way? • Trade with someone near you and read this one. • Get up and find someone new, and trade with them. • Repeat five times; move around the room. Psychology’s Biggest Question: Is Human Nature Fixed or Changeable? 1. Entity Theorists think traits are fixed. They think a person’s character can be revealed by a single behavior or performance. This is true for both positive and negative acts. In other words, they think that what we see on the outside reflects what people are like on the inside. They see setbacks as a reflection of lack of ability. They think that, as a result, people become defensive and often feel helpless. 2. Incremental Theorists • They think that traits are changeable (good or bad). • They value learning and growth and respond to adversity with increased effort and strategies for change. • They think people tend to be resilient. Carol Dweck’s Studies Study One: Measured the brain waves of students with these contrasting mindsets. • Took a test with difficult questions. 1.5 seconds after they answered a question, the computer indicated whether they had responded correctly or not. • Their brain’s electrical activity was measured. • Students with an entity (fixed) mindset stopped paying attention once they learned if they were right or not. • Those with incremental (growth) mindset were more focused on learning than on the answer. Study Two:The Brain is a Muscle • Junior High students with low math scores were given 8 sessions of training in study skills. • Half also received instruction in the malleability of intelligence. They were told that the brain was a muscle that can be strengthened with hard work. • Those who were given this instruction rebounded with better grades than those who had not received the instruction. Teachers reported that their motivation also improved. Study Three: Love Relationships • Those with fixed and growth mindsets are likely to respond differently to rejection in a love relationship. • Those with a fixed mindset feel judged and labeled by the rejection. They see themselves as unlovable and are likely to lash out. Their goal is revenge. • Those with a growth mindset are likely to respond to the rejection with understanding and forgiveness and a desire to move on. Fact or Falsehood 1. Psychologists are only interested in treating people with mental illness. 2. Psychology is not considered a scientific field because psychologists only diagnose and treat mental illness. 3. To be a psychologist, you need a degree beyond the 4-year bachelor’s degree. 4. Psychology is best defined today as the study of mental life. 5. Today, half of Ph.D degrees in psychology are awarded to women. 6. Evolution has become an important principle for psychology. 7. In contrast to sociology and anthropology, contemporary psychology has little interest in how behavior varies across cultures. 8. Psychology aims to answer the ultimate question, “Why should I live?” 9. Psychiatry is a branch of psychology that involves the assessment and treatment of psychological disorders. 10. There are two types of psychology – those who work in hospitals and those who work in private practice. 5 Adjectives • Write 5 adjectives that describe “scientist” and 5 adjectives that describe “psychologist”. • Share with the class The Results • Typically, students perceive “psychologist” and “scientist” differently. • Did you describe psychologist as accepting, caring, genuine or attentive? • Did you describe scientist as methodical, analytical, intelligent or thorough? Module 01 Introduction and Careers Module 1: Introduction and Careers The Definition of Psychology Psychology • The scientific study of behavior and mental processes. – Uses scientific research methods. – Behavior includes all observable behavior. – Mental processes include thoughts, feelings and dreams. True or False 1. Most people suffer from unrealistically low self-esteem. 2. The opinions of 1500 randomly selected people can provide a fairly accurate picture of the opinions of an entire nation. 3. The scientific finding that depressed people tend to have low self-esteem proves that depression causes people to be down on themselves. Critical Thinking • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=haP7Ys 9ocTk&feature=player_embedded Darren Brown: astrology “I’d Like to Have an Argument” Podcast http://www.thepsychfiles.com/ Critical Thinking Skills The Hindsight Bias • How many seconds do you think it would have taken you to unscramble each of these? WREAT > WATER ETRYN > ENTRY GRABE > BARGE Famous Examples of The Hindsight Error • 1. “We don’t like their sound. Groups of guitars are on their way out.” Decca Records in turning down a recording contract with the Beatles. • 2. “They couldn’t hit an elephant at this distance.” General Sedgwick just before being killed during a US Civil War battle, 1864 • 3. Computers in the future may weigh no more than 1.5 tons. Popular Mechanics, 1949 Be a Skeptic • “A skeptic is one who is willing to question any truth claim, asking for clarity in definition, consistency in logic, and adequacy of evidence.” Philosopher Paul Kurtz, 1994 The Scientific Approach • Science is not the only way to approach life. It can answer some questions, but not others. • How could you establish the validity of each statement? Have you taken any classes that might have addressed one of these issues? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. The best things in life are free. Hamlet is a better play than King Lear. Abortion is wrong. There is a genetic predisposition to schizophrenia. The mind is just like a computer. 2+2=4 Attitudes affect cancer. Module 1: Introduction and Careers Careers in Psychology Psychologist • Need a doctorate graduate degree • May take 4-6 years to earn a doctorate in a subfield • You take a doctorate after an undergrad degree (4 years). Clinical Psychologist • Diagnose and treat patients with psychological problems • Largest number of professional psychologists Basic Research • Pure science or research • Research for the sake of finding new information and expanding the knowledge base of psychology • These psychologists are “academic psychologists” & they work in colleges and universities, conducting basic research. • Examples: neuropsychologists, social psychologists, developmental psychologists, cognitive psychologists, experimental or research psychologists. Neuropsychologist • Also called biological psychologists or biopsychologists • Explore how the brain works • Most often work in university/college settings Social Psychologist • Explore how behaviors, feelings, and beliefs are influenced by others • Study conformity, attitudes, leadership, prejudice, group behavior, etc. • Work in the business setting, government, and universities Developmental Psychologist • Study the growth or development that takes place from the womb to death • Work in senior centers, hospitals, daycares or universities Cognitive Psychologist • Study thought processes including intelligence, problem solving, attention, decision making, language, etc. • Work in educational settings and the business world Experimental Psychologist • Also called research psychologist • Specialize in doing research in any of the other subfields • Most work at universities, but some work for the government, or in a business setting Applied Research • Research designed to solve specific practical problems • These are the psychologists who are interested in solving problems and who do applied research, rather than expanding the scientific knowledge base of psychology Forensic Psychologist • Apply law and psychology to legal issues • Work in correctional settings, law enforcement, and academic settings Sports Psychologist • Explore psychological issues in improving athletic performance • Work for sports teams or in private practice Educational Psychologist • Study how humans learn and how to improve the learning process • Work in school systems, the government, or at universities Human-factors Psychologist • Study how people and machines interact at home and in the workplace • Try to minimize frustration and increase safety and production • Work in the business world or for the government Industrial/Organizational (I/O) Psychologist • Try to apply psychology to help business and organizations operate • Work for the government, business or in academic settings School Psychologist • Use psychology to improve the development of children in the school system • Are involved in assessments (testing) • Work for school systems, the government or universities Consumer Psychologist • Study why people buy certain products and not others • Work in the business or academic world Rehabilitation Psychologist • Help those who have been involved in an accident or have been ill • Work in medical rehabilitation centers Health Psychologist • Find ways to prevent disease and promote good health • Work for health agencies, hospitals, rehabilitation centers, and universities Social Worker • Only have an undergraduate or masters degree in psychology or social work • Work to improve the lives of others • Work for the government, schools, and residential facilities Assignment • Consider the 16 different psychological careers described in this chapter. Write (one page) about which career you are most attracted to right now, which assignment you are least attracted to right now, and why. In your answer, describe the kinds of work and psychological questions relevant to the careers you chose. The End Paper Personality • http://www.pbs.org/saf/1210/video/watcho nline.htm • Activity