* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download forensics - bayo2pisay
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
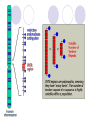
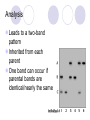
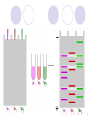
FORENSICS Cabanto, Ecat, Talampas, Vocal, Beleran, Mina IV-Gluon DNA fingerprinting: Overview 1984 - Sir Alec Jeffreys Also known as genetic fingerprinting or DNA profiling Way of identifying an individual* Applications Forensics Paternity/Maternity tests Why it is better than a fingerprint. Fingerprints are easily obscured DNA is in every cell of the body Hair strand Skin follicle Drop of blood How it works 99.9% of our genes are identical The remaining 0.1% is used to determine the individual Microsatellites Short repetitive sequences that are highly variable in humans Reflect individual genetic make-up A.k.a. Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTR) VNTR’s short sequence in the introns of DNA that is repeated in a head-to-tail manner at a specific chromosomal locus interspersed in genome Number of repeated units vary per human Loci – VNTR’s One VNTR – 17 bp, repeated 70 to 450 times Total: 1190 to 7650 base pairs Southern hybridization DNA with VNTR is cut with a restriction endonuclease Size varies, creating RFLPs, or restriction fragment length polymorphisms Analysis Leads to a two-band pattern Inherited from each parent One band can occur if parental bands are identical/nearly the same Basic Genetic Principles Identity matching VNTR alleles should be the same if samples are from the same individual. Inheritance matching He or she could have VNTRs inherited from his or her mother or father, or a combination Never a VNTR either of his or her parents do not have. Other Uses Personal Identification Casualties Paternity/Maternity testing Family reunions yehey :D Other Uses Diagnosis of inherited disorders Alzheimer’s disease Huntington’s disease Determining risks of having an affected child Identify patterns associated with disease May lead to cure for the disorder Other Uses Mapping genography Find patterns of migration Trace human species’ history National Geographic Society Study distinct trail left by humans since we left Africa Understand more about our background In the Philippines Case study: Ray de Villa Jan. 9, 1995- Arrested for the rape of 13 yo niece DNA testing was not done at that time Sole evidence was birth of a child Counter evidence – 76 yo suspect suffered physical condition Case Study Victim did not report assault until confronted of pregnancy Problem: Court did not allow paternity testing Dr. Cora de Ungria of UP devised a way to be able to profile the child’s paternity Both parties (child’s family and prison) refused for samples “Spitting game” to get saliva from child and 4 other children Blood from De Villa without assistance from prison staff Results: genetic markers proved that De Villa could not have fathered any of the children Parole was granted to De Villa after extensive legal action Since then, Philippine Parliament has introduced DNA database legislation and the Supreme Court has issued rules for the admission of DNA profiling results in court UP Diliman’s DNA analysis lab has also created a “rape kit”- Sexual Assault Investigation Kit for the Collection of Biological Samples In the Philippines Crop biology analysis of genetic diversity within breeding populations in plants Differentiation between cultivars Identification of plants containing a gene of interest Issues Privacy of suspects Studies regarding human population DNA evidence may place a person at a crime scene, but it also does not necessarily mean that he or she committed the crime DNA can still be tampered with, and still be used to frame people Issues Pattern narrows down a million people to around 2-10 Sometimes cannot identify individual However, if there are suspects in hand, the match can be easily made