* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Bioinformatics? - UNC
Survey
Document related concepts
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
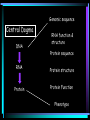
Introduction to Bioinformatics Dr. Rybarczyk, PhD University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill [email protected] What is Bioinformatics? What is Bioinformatics? Conceptualizing biology in terms of molecules and then applying “informatics” techniques from math, computer science, and statistics to understand and organize the information associated with these molecules on a large scale Objectives: • Identify appropriate search tools for your needs • Perform searches using ‘unknown’ sequence data • Analyze protein structure using Protein Explorer Why do we use Bioinformatics? • Store/retrieve biological information (databases) • Retrieve/compare gene sequences • Predict function of unknown genes/proteins • Search for previously known functions of a gene • Compare data with other researchers • Compile/distribute data for other researchers Genomic sequence Central Dogma DNA RNA function & structure Protein sequence RNA Protein structure Protein Protein Function Phenotype Computer Tools Used in Bioinformatics Sequence retrieval: NCBI GenBank Internet resources Sequence comparison programs: BLAST GCG MacVector Protein Structure: modeling prediction programs – RasMol, Protein Explorer Similarity Searching: A tool for searching gene or protein sequence databases for related genes of interest Alignments between the query sequence and any given database sequence, allowing for mismatches and gaps, indicate their degree of similarity The structure, function, and evolution of a gene may be determined by such comparisons Algorithms Computer comparisons using mathematical probabilities input output Finds best matching pair comparisons of sequences % similarity CATTATGATA 70% GTTTATGATT MRCKTETGAR 90% MRCGTETGAR Sequence Analysis: Determine correct sequence of DNA Compare sequence with known sequences Translate DNA into protein sequence Understand protein function in context Current Tools Used in Bioinformatics Strengths: Accessibility Growing rapidly User friendly Weaknesses: Sometimes not up-to-date Limited possibilities Limited comparisons and information Not accurate Need for improved Bioinformatics Genomics: Human Genome Project Gene array technology Comparative genomics Functional genomics Proteomics: Global view of protein function Protein motifs Structural databases Data Mining Handling enormous amounts of data Sort through what is important and what is not Manipulate and analyze data to find patterns and variations that correlate with biological function http://bioinformatics.weizmann.ac.il/cards/ 3-D Protein Modeling • Uses information determined by crystal structure methods • Visualization of protein structure • Make protein-protein comparisons • Used to determine: conformation/folding antibody binding sites protein-protein interaction sites computer aided drug design Summary • Introduction to Bioinformatics tools: Genbank, BLAST, GCG, GeneCard, Chime • How Bioinformatics is used • Advantages and disadvantages of tools • Applications educators students bioinformatics researchers institutions