* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cold War - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
War in Vietnam (1954–59) wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
North Vietnam wikipedia , lookup
Sino-Vietnamese War wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1953–1962) wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1947–1953) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
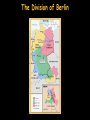
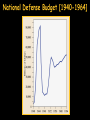
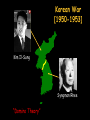
The Cold War [1945-1991]: An Ideological Struggle Soviet & Eastern Bloc Nations [“Iron Curtain”] GOAL spread worldwide Communism METHODOLOGIES: US & the Western Democracies GOAL “Containment” of Communism & the eventual collapse of the Communist world. [George Kennan] 1. Espionage [KGB vs. CIA] 2. Arms Race [nuclear escalation] 3. Ideological Competition for the minds and hearts of Third World peoples [Communist govt. & command economy vs. democratic govt. & capitalist economy] “proxy wars” “Limited War” 4. Bi-Polarization of Europe [NATO vs. Warsaw Pact] Reasons We Resisted Communism • “Soviet power, unlike that of Hitlerite Germany, is neither schematic nor adventuristic. It does not work by fixed plans. It does not take unnecessary risks. Impervious to logic of reason, and it is highly sensitive to logic of force. For this reason it can easily withdraw—and usually does when strong resistance is encountered at any point.” According to Kennan: • The Soviets perceived themselves to be in a state of perpetual war with capitalism; • The Soviets would use controllable Marxists in the capitalist world as allies; • Soviet aggression was not aligned with the views of the Russian people or with economic reality, but with historic Russian xenophobia and paranoia; • The Soviet government's structure prevented objective or accurate pictures of internal and external reality. Map of NATO vs. Soviet Union Why is it a Cold War? • Places where it got Hot (“Limited War”) – Korea (1950-1953) • North Korea (Communist supported by China) – Kim il-Sung – North Korean Leader • South Korea (Democratic supported by U.S./NATO) – Vietnam (1955-1973 or 75) • North Vietnamese (weapons provided by China) – Ho Chi Minh – North Vietnamese Leader • South Vietnamese (support provided by U.S.) – Cuban Missile Crisis (1962) – Fidel Castro attempted to receive a nuclear missile from Soviet Union • U.S. threatened nuclear war if Cuba received weapon The Division of Berlin The Bipolarization of Europe Two Superpowers Left in the World • North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) – Founded in 1949 – Western Democracies – Supported Capitalism abroad • Warsaw Pact – Founded in 1955 – Eastern Nations under Stalin – Supported spread of Communism U.S. Policies to Fight the Cold War • Marshall Plan – Announced in 1947 – Give loans ($) to European nations to rebuild after WWII – Total of $12.4 billion dollars loaned to Europe – Significant success in Europe – U.S. gains a lot of Europeans’ trust – Soviets felt the plan was Economic Imperialism U.S. Policies to Fight the Cold War • Truman Doctrine – “It must be the policy of the U.S. to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or [foreign] pressures” -Harry S. Truman – Provide support for nations resisting Communism – Provide Aid (Military, weapons, money) – Quickly used to help Greece, Turkey George Kennan [“X Article”]: CONTAINMENT Goals Means Actual Application 1. Restoration of the balance of power Encouragement of selfconfidence in nations threatened by Soviet expansion. Long-term program of U.S. economic assistance [Marshall Plan] 2. Reduction of Soviet ability to project outside power. Exploitation of tensions in international communism. Cooperation with communist regimes; [supporting Titoism in Yugoslavia] George Kennan [“X Article”]: CONTAINMENT Goals Means Actual Application 3. Modification of the Soviet concept of international relations. Negotiating settlement of outstanding differences. Using “carrots & sticks’; containing Germany with an embrace and Russia at arms length. Failures of US Strategy • Soviet Union tests an Atomic Weapon (1949) • Soviet Union tests a Hydrogen Bomb (1953) • Failure to overthrow Fidel Castro in Cuba (Bay of Pigs incident in 1961) • By 1962, the US created a “Quarantine Zone” around the Caribbean in order to prevent the Soviets from delivering Nukes to Castro’s Communist government • It was a 13-day stand-off in the sea with both sides threatening M.A.D. (Mutually Assured Destruction) Failures of US Strategy • One of the biggest failures of Containment was when China’s civil war ended and Mao Zedong started the People’s Republic of China a communist country. • Mao then began to turn his attention, with the help of the Soviet Union, to fixing some of the domestic issues that had plagued China for almost a century (starvation, lack of infrastructure, lack of modernization, disparate peoples and lands, etc.) National Defense Budget [1940-1964] Korean War [1950-1953] Korean War [1950-1953] Kim Il-Sung Syngman Rhee “Domino Theory” The Shifting Map of Korea [1950-1953] -Both sides continue to arm the Korean border so that the possibility of renewed warfare remains a threat even today. -The most militarized location on the planet = 38th parallel. Korean Peninsula at Night: Present Day Questions (Due Monday) • What was the policy of Containment? • How did Containment get the U.S. embroiled in foreign wars/conflicts? • Was the U.S. in support of North or South Korea? Explain why. • Was the U.S. in support of North or South Vietnam? Explain why. • Is there a belief system today that you believe must be stopped even if it involves invading foreign nations? • Explain the Truman Policy. How does it encourage getting into other nations’ affairs? • Explain the Marshall Plan. Did it work? Vietnam: The Long-lasting “limited war” • Ho Chi Minh had been trying to free his nation from French rule from 1941-1950 • In 1950, North Vietnamese declared the independence of Vietnam and the creation of the Communist Government. • In 1950, Minh met with Mao Zedong and Josef Stalin to address recognizing the nation and providing support from foreign attack Vietnam: The Long-lasting “limited war” • By 1954, U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower agreed to fund the government in South Vietnam to prevent all of Vietnam from falling to Communism. • The South Vietnamese leader Ngo Ding Diem refused to hold free elections – Objective observers: “Ho Chi Minh would have won easily.” • By 1963, President Lyndon Johnson inherited a smallscale war from President Kennedy. Johnson decided to commit U.S. troops to try and defend South Vietnam. • By 1966, 365,000 US troops were in the Vietnam War • The Viet Cong (Ho’s supporters were called Viet Cong) were successful at killing US troops and escaping. Ho Chi Minh’s military success is now considered one of the greatest military strategies used in Guerilla War • By 1973 a growing anti-war movement in the US protested the cost and the growing number of US casualties. A ceasefire was reached between the North and South Vietnam. • However, in 1975 the North Vietnamese troops overran the South Vietnamese army and reunited the two parts of Vietnam. The Unforeseen Benefit of the Cold War The Space Race • With competition for superior technology, the two superpowers also competed for outer space as well. • The Soviets launched the first space satellite in 1957 – Sputnik created fears in the US that the Soviets would control space and the Space Race began. • The US responded and launched their own satellite a few months later. • During the 60s the Science and Technology race continued until the United States reached the moon with a manned spacecraft in 1969.