* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is pollination?
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
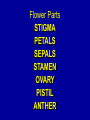
ENDURING UNDERSTANDING • Flowers depend on seed production and dispersal for their reproduction. LEARNING GOAL • I will dissect and mount the structures of simple flowers. • I will examine a variety of seeds to discover their dispersal mechanisms. • I will explain the function of flowers and pollination. • I will explain how seed-dispersal mechanisms contribute to a plant’s survival. • I will understand the origin of seeds by investigating the reproductive systems in flowers. PLANT REPRODUCTION READING QUESTIONS DISCUSSION POLLINATION REVIEW • What is the purpose of flowers? • What is pollination? • Why are there so many different colors and shapes of flowers? • What is a seed and what is its purpose? • Why is it not a good idea for all the seeds to grow directly under the parent plant? IMAGES • Let’s look at some POLLINATORS, FLOWERS, AND SEED-DISPERSAL MECHANISMS on the cdrom Plant Reproduction POLLINATION BEES SEXUAL REPRODUCTION FLOWERS SEEDS Flower Parts STIGMA PETALS SEPALS STAMEN OVARY PISTIL ANTHER SEED DIVERSITY • We know quite a bit about seeds, including where they come from, their basic parts, what happens when they start to germinate, and the roles played by the parts of the sprouting seed. There is a lot of similarity among seeds. But there is a lot of diversity in seeds as well. • In what ways are seeds different? SURVIVAL • The ultimate measure of an organism’s success is its survival until it reproduces. Survival depends on the organism’s ability to acquire the resources necessary to stay alive, including air, water, nutrients, energy, and space. Many Monera, animals, and protists can move to find the resources they need for survival. Plants can not. SURVIVAL • Plants have to use other strategies for acquiring resources. One important strategy for survival is growing in a location where there is little competition for resources. In many cases this means starting life some distance away from the parent plant. SEED DISPERSAL • Seeds are not rooted in the ground. This is the only time in a plant’s life that it can move. Seeds must have ways to get away from the parent plant. The features of seeds that allow them to move are called seed-dispersal mechanisms. • Have you seen examples of seed dispersal? • What kinds of features do the seeds have that allow them to move away from the parent plant? READING • Turn your book to page 46 and we will read “Seeds on the Move”. • We will do “Read and Sketch” to help us remember important information. SEED DISPERSAL • Has anyone ever had to remove stickers or burs from a cat or dog’s fur? • What do your socks look like after a walk through a field in the fall? • What happens to dandelions after they go to seed? What are the fluffy things that blow away? • What do squirrels do with all those acorns they collect in the fall? SEED HUNT • Today we are going to look for seeds in nature to see what kinds of features they have for getting around. We are going to take a walk around campus to look for seeds on plants that are growing there. SEED-COLLECTION BAGS SEED DIVERSITY • How many different seeddispersal features did you observe on seeds in our area? • What dispersal mechanism is used the most by plants in our area?