* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download US Foreign Policy
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Fragile state wikipedia , lookup
Great power wikipedia , lookup
Polarity (international relations) wikipedia , lookup
Legality of the Iraq War wikipedia , lookup
Foreign interventions by the United States wikipedia , lookup
International security wikipedia , lookup
World government wikipedia , lookup
New world order (politics) wikipedia , lookup
United States Department of State wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Security Council wikipedia , lookup
Collective security wikipedia , lookup
High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1953–1962) wikipedia , lookup
Counter-terrorism wikipedia , lookup
Salzburg Forum wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of United States foreign policy wikipedia , lookup
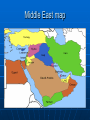
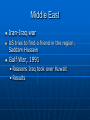
US Foreign Policy Ch 19 Topics History Governmental Structures Current Issues Goals in FP Trade: promoting and/or regulating Defense: National Security Promoting environment, human rights, good relations, cultural exchanges. America’s International Relations History 1800s: Small country expanding its influence 1900s: US becomes a world power Post-WWII: The UN and the Cold War: US is a superpower Post-Cold War: What are our goals? 1800s Beginnings: Isolationism 1820s: Monroe Doctrine Manifest Destiny and Expansion • War with Mexico 1846-48 • Oregon Treaty 1846 1900s: US becomes a world power The “new” Imperialism Spanish-American war and follow-up war in the Philippines Roosevelt Corollary to Monroe Doctrine Panama Canal US becomes a world power World War I • US stays out 1914-1917 • Joins 1917 • Ends Nov, 1918 Versailles Treaty • Wilson hopes for collective security through League of Nations 1920s and 30s: trend toward isolationism World War II • What countries are on what side? Axis Japan Italy Germany vs. Allies UK USSR US France China Post WWII Internationalism Free trade promoted in international organizations: Bretton Woods System • GATT • IMF http://www.imf.org/external/about/overview.htm • World Bank http://web.worldbank.org/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/EXTABOUTUS/0,,pagePK:5000 4410~piPK:36602~theSitePK:29708,00.html United Nations United Nations: www.un.org Purposes: Preamble • http://www.un.org/en/documents/ch arter/preamble.shtml Structures • General Assembly • Secretary General • Security Council: Purposes Who has power in it? • Economic and Social Council • International Court of Justice http://www.un.org/en/aboutun/structur e/index.shtml • Limitations of UN UN Security Council 15 countries 5 permanent countries with veto power: • US • UK • China • USSR • France UN US Ambassador to the UN :Susan Rice http://usun.state.g ov/ Cold War 1946-1991 US and allies vs. USSR and allies Ideological rivalry • Communism vs. Democracy and capitalism No direct war Lots of proxy wars Competition for influence and dominance around the world Arms race Space race Cold War terms and policies Containment NATO and Warsaw Pact Fighting the Cold War is the backbone of US Foreign Policy 19451991 Cold War Korean and Vietnam Wars Nuclear Deterrence and MAD Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962 Détente • Nixon in China 1970s Human Rights as a goal • UN Human Rights Declaration http://www.un.org/en/documents/udhr/ Cold War ends 1989, 1991 New Goals? Human Rights as a goal Internationalism/Multilateralism Combating terrorism Environment Nukes: Which countries have them? • • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_states_with_nuclear_weapons NPT http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nuclear_Non-Proliferation_Treaty Spreading Democracy Globalization Who makes foreign policy? Checks and balances in duties of branches of gov’t Industry Media Public The Executive Branch is #1 in foreign and military policy The President • Access to and control of information • Commander in Chief of the military Departments of State, Defense, Homeland Security Department of State: http://www.state.gov/ Foreign policy negotiations Embassies Economic Development Department of Defense http://www.defense.gov/ Robert Gates Army, Navy, Air Force, Marines Joint Chiefs CIA National Security Council: advises the president http://en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/United_States_Nati onal_Security_Council Department of Homeland Security • Cabinet department created after the 9/11 attacks for domestic U.S. security • Janet Napolitano http://www.dhs.gov/ Congress’s role in FP Oversight: hearings Appointments: hearings Appropriations: $$ Treaties Declaration of war Pass laws dealing with Foreign Policy Declaration of War: power shift from Congress to President Since WWII: Korea, Vietnam, Gulf War, Afghanistan, Iraq. How? Congressional Resolutions and President using power as Commander in Chief War Powers Act, 1973 • Pres can deploy • Congress must approve after or troops must return • Not very effective The Military Industrial Complex The relationship and influence of U.S. armed forces Defense industries on Government Mostly about: $$: Defense contracts http://www.sonyclassics.com/whywefight/main. html The News Media Reporting and investigation Agenda setting Influencing public opinion The Public Generally more interest in domestic over foreign affairs Influences FP through • • • • Elections Widespread resistance or protests Polls Work in nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) such as Amnesty International Middle East map Middle East World War I impacts • Britain and France in the region World War II impacts • Israel Cold War impacts • Conflicts seen through “cold war glasses” Iran’s Shah is overthrown • Islamic revolution • Americans taken hostage Middle East Iran-Iraq war US tries to find a friend in the region: Saddam Hussein Gulf War, 1991 • Reasons Iraq took over Kuwait • Results Afghanistan The Soviet Union’s “Vietnam” Results map: http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/a sia/af.htm 9/11 What were the motives behind the attacks? Who was responsible? Why did the US go to war with Afghanistan afterwards? Al Qaeda, Osama Bin Laden The Taliban The War on Terrorism War in Iraq Reasons for war? US attempted to get UN Security Council’s OK Congressional vote to allow the use of force US attacks in March, 2003 Bush Doctrine: preemptive strike Countries Read classmates’ reports on countries If no student reports, read NY Times topics pages on China Russia North Korea Iran Iraq Pakistan Afghanistan Al Qaeda Taliban Yemen Israel Palestinians







































![Afghanistan[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008230902_1-f21ca290603cca82ee4cbd5fb89e4c57-150x150.png)