* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Theories and Models - MrD-Home
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Sodium hydroxide wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Alkaline earth metal wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
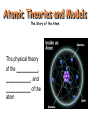
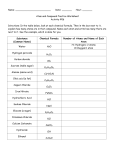
Atomic Theories and Models The Story of the Atom The physical theory of the _________, __________, and __________ of the atom John Dalton Law of Conservation of Mass Subatomic Particles (Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons) Subatomic Particles Name Symbol Relative Mass (Atomic Mass Unit, AMU) Electric Charge Location in the Atom Note: 1 atomic mass unit = 1.66053886 × 10-27 kg = one-twelfth of the mass of the nucleus of a carbon-12 atom. Atomic Number (Z) Proton number • The number of __________ found in the nucleus of an atom • Atoms have no overall electric charge (i.e. charge of atom is zero) Atomic Number= = • If a proton ( ) is added to an element’s nucleus, a _______ element will be produced. • e.g. 1 19 + 1 9 F p Mass Number (A) Atomic mass number or nucleon number • The number of nucleons (________________________) in an atomic nucleus Mass Number= Atomic Mass Average mass of an element’s isotopes • Since most of the mass of an atom is concentrated in the __________ and ___________ located in the nucleus, the atomic mass is ________________ to the mass number. • Recall, mass number = • Atomic Mass Mass Number # of neutrons = • If a neutron ( ) is added to an element’s nucleus, a heavier version of the _________ element (isotope) will be produced. • e.g. 19 + 1 9 0 F n Isotopes • Atoms having the same _________________ but different _______________ (because different number of __________). • E.g. Hydrogen isotopes Hydrogen-1 (hydrogen) Hydrogen-2 (deuterium) Hydrogen-3 (tritium) Ions • Most atoms are capable of either _________ or ________ electrons. • A few elements, like hydrogen, are able to do both! • They can do this by ____________ electrons from, or ________ electrons to, other atoms. • Atoms that have gained or lost electrons are called ______. Ions (continued…) An ion is an electrically __________ atom (or groups of atoms): i) ____________ - charged ion: when electron(s) is/are added to a neutral atom (i.e. there are _______ electrons than protons). _____________ tend to gain electrons and become negatively charged. ii) ___________ - charged ion: when electron(s) is/are removed to a neutral atom (i.e. there are ________ electrons than protons). ________ tend to gain electrons and become negatively charged. Ions (continued…) Chemical Equations Depict the kind of _________ and ________ and their relative amounts in a reaction. 2 Al(s) + 3 Br2(l) Al2Br6(s) The numbers in the front are called _____________. The letters (s), (g), and (l) are the physical states of compounds. Chemical Equations Symbolic equation: 2 Al(s) + 3 Br2(l) ---> Al2Br6(s) Balancing Chemical Equations Example: CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O Example: CH4 + O2 CO2 + H 2O The chemical equation for the reaction of methane and oxygen is ______ yet properly balanced because the atoms of the elements on the product side do not ______ the atoms of each element on the reactant side of the equation. The _________________________, which states that matter can neither be ________ nor __________ in an ordinary chemical reaction, must be upheld when writing a chemical equation. This chemical equation is ___________. Balancing Chemical Equations Example: CH4 + O2 CO2 + Rewrite and balance the equation below. H2O Balancing Chemical Equations Balancing the following equations using atomic models. 1. K+ Cl2 KCl (draw) 2. N2 + H2 NH3 (draw) 3. Fe + Cl2 FeCl3 (draw) 4. Zn + HCl ZnCl2 + H2 (draw) Balancing Chemical Equations 1. K+ Cl2 KCl 2. Ba + Br2 BaBr2 3. N2 + H2 NH3 4. H2 + O2 H2O 5. Na + N2 Na3N 6. NaCl + F2 NaF + Cl2 7. AgNO3 + MgCl2 AgCl + Mg(NO3)2 8. CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O 9. ZnO + HCl ZnCl2 + H2O 10. I2 + NaBr NaI + Br2 Write the word equations below as chemical equations and balance. 1. Zinc and lead (II) nitrate yield zinc nitrate and lead. 2. Potassium chlorate when heated yields potassium chloride and oxygen gas. 3. Copper and sulfuric acid yield copper (II) sulfate and water and sulfur dioxide. 4. magnesium chloride + ammonium nitrate magnesium nitrate + ammonium chloride 5. iron (III) chloride + potassium hydroxide potassium chloride + Iron (III) hydroxide 6. sodium nitrate (heated) sodium nitrite + oxygen 7. potassium phosphate + magnesium chloride magnesium phosphate + potassium chloride 8. mercury (II) hydroxide + hydrogen phosphate (phosphoric acid) mercury (II) phosphate + water 9. carbon dioxide + carbon carbon monoxide 10. ammonium chloride + sodium nitrite sodium chloride + nitrogen + water On a separate piece of paper, write the following equations and balance them. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. zinc + hydrochloric acid (HCl) zinc chloride + hydrogen calcium oxide + water calcium hydroxide mercury (II) oxide mercury + oxygen hydrogen + chlorine hydrogen chloride aluminum + chlorine aluminum chloride iron (II) oxide + carbon iron + carbon monoxide aluminum + copper (II) sulphate aluminum sulphate + copper aluminum + tin (IV) chloride aluminum chloride + tin (II) chloride sodium hydroxide + hydrogen bromide sodium bromide + water sulphuric acid + sodium hydroxide sodium sulphate + water silver nitrate + sodium chloride silver chloride + sodium nitrate 12. calcium hydroxide + nitric acid calcium nitrate + water 13. hydrochloric acid (HCl) + magnesium hydroxide magnesium chloride + water 14. phosphoric acid (H3PO4) + magnesium hydroxide magnesium phosphate + water 15. carbon dioxide + calcium hydroxide calcium carbonate + water 16. hydrochloric acid (HCl) + magnesium oxide magnesium chloride + water 17. hydrochloric acid (HCl) + magnesium magnesium chloride + hydrogen 18. carbon + oxygen carbon dioxide