* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download darwin natural selection notes
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
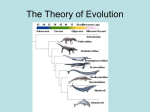
Darwin & Natural Selection Essential Question Activating Strategy How do scientists define and support the theory of evolution? Evolution is the process by which different kinds of living organisms are thought to have developed and diversified from earlier forms during the history of the earth. Major changes happen to the earth over billions of years. Scientists define the theory of evolution as organisms that possess heritable traits that enable them to better adapt to their environment. They are compared with other members of their species and will be more likely to survive, reproduce, and pass more of their genes on to the next generation. Scientists support this by making observations and collections of their studies. They do research that helps support and give more detail for the theory of evolution. What does the theory of Evolution state? The theory of evolution states that all things come from one organisms and they grow over time. Charles Darwin (1809-1882) - sailed on an English ship named the HMS Beagle - as a naturalist, he studied and collected a wide array of specimens along the 5 year journey - his observations and collections on the Galapagos islands were especially important - he found unique plant and animal species to those islands BUT there were a lot of similarities to species in other locations - these observations led Darwin to examine how species may change over time - over the next 20 years, Darwin continued his research and came up with idea of natural selection: organisms with a favorable variation survive, reproduce and then pass their favorable variation onto their offspring - published a book about evolution called “On the Origin of Species” in 1859 Natural Selection Usually, the population grows faster than the food supply, so only those that can get food best (the fittest individuals) will survive and then pass their traits on to the next generation. Over time, the offspring, of the survivors will make up a large part of the population and form a new species that has the adaptations that allowed them to survive. Evidence for Evolution 1. Adaptations = any variation that helps an organism survive - 2 kinds of adaptations: Structural & Physiological Darwin & Natural Selection STRUCTURAL Arise slowly over time (millions of years) Ex: a rose bush’s thorns to protect the bush from predators Ex: a porcupines quills to protect from predators Mimicry (resembling another species) Ex. A fly is yellow and black just like a yellow jacket which has a poisonous stinger Camouflage (blend in with surroundings), prevents the prey from being spotted PHYSIOLOGICAL Can arise quickly Changes in an organisms metabolic processes Ex: penicillin (created 50 yrs ago) no longer kills many strains of bacteria because they have evolved a physiological adaptation to prevent being killed by penicillin Ex: adaptations in insects to prevent being killed from pesticides Ex: adaptations in weeds to prevent being killed from herbicide 1. Fossils – show that life was simple and became more complex 2. Anatomy Homologous structures: body parts similar in structure that indicate a common evolutionary origin (ex. Forelimbs of birds and crocodiles) Analogous structures: body parts similar in function but do not have a common evolutionary origin (ex. Bird wing and moth wing) Vestigial Structures: body part with no or limited function; probably useful to an ancestor (ex. Eyes of a blind mole rat) 3. Embryology: similar embryo structures 4. Biochemistry: similar DNA (the more similar two organisms’ DNA sequences are, the more closely they are related!)