* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is the difference between Autotrophs and heterotrophs?
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
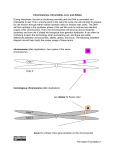
genetics 1. Normal cell has 2N number of chromosomes and a gamete has a haploid number; egg is larger 2. meiosis 3. Diagram showing gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross 4. genes- chemical factors that determine traits allele- different forms of a gene 5. homozygous- two identical alleles for a particular trait (T,T) heterozygous- two different alleles for the same trait (T,t) 6. P is parent, F1 is first generation, F2 is second generation 7. The dominant traits covers/masks the recessive trait. 8. 9. a. TT x tt b. Tt x tt c. Tt x Tt a. separation of alleles during gamete formation b. independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes c. result of the cytoplasm not dividing evenly d. chromosome that is not a sex chromosome e. two different alleles for the same trait f. two identical alleles for a particular trait g. gene located on the X or Y chromosome 10. Male= XY Female= XX 11. 1 12. Crossing over- process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis translocation- part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another nondisjunction- error in meiosis in which homologous chromosomes fail to separate 13. replication- copying process where cell duplicates its DNA transcription- process in which part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA is copied into a complementary sequence in RNA translation- decoding of mRNA message into a polypeptide chain 14. Deoxyribose molecule, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base 15. adenine-thymine cytosine-guanine 16. Refer to foldable 17. Refer to the diagram in the book on pages 304-305 18. threonine, alanine, stop 19. 20 20. Page 304 protein synthesis