* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C3 Revision Question Booklet
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Fluorochemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Biological aspects of fluorine wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Sodium hydroxide wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Acid strength wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Sodium hypochlorite wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
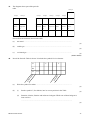
Barnard Castle School Chemistry Department GCSE Chemistry C3 Revision Questions Name ………………………………….. Teacher …………………………… Barnard Castle School 1 1. Use the periodic table on the Data Sheet to help you to answer these questions. (a) Write the symbol for helium. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Write the name of an element in Group 4. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Write the name of the element which has a relative atomic mass of 64. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (d) Write the name of the element with the next highest atomic number after Te (tellurium) in the periodic table. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 4 marks) 2. The periodic table on the Data Sheet may help you to answer this question. (a) Newlands and Mendeleev both designed periodic tables in which the elements were put in the order of their relative atomic masses. When the elements are put in this order a few of them are placed incorrectly when compared with a modern periodic table. (i) Give one example of a pair of elements that would be placed incorrectly if they were in the order of their relative atomic masses. ......................................................... and .......................................................... (1) (ii) Explain why placing these two elements in the order of their relative atomic masses would not be correct. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) In the modern periodic table the elements are put in order of their atomic (proton) numbers. Explain how the positions of the elements in the periodic table are linked to the electronic structure of their atoms. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 4 marks) Barnard Castle School 2 3. Chemical tests can be used to identify compounds. (a) List A gives the names of four compounds in solution. List B gives tests and the result of the tests. Draw a straight line from each compound in List A to its test and test result in List B. The first one has been done for you. List A Name of compound in solution List B Test and result of the test Calcium chloride Add barium chloride solution and dilute hydrochloric acid. A white precipitate formed. Lithium sulphate Do the flame test. Yellow flame produced. Potassium carbonate Add silver nitrate solution and dilute nitric acid. A white precipitate formed. Sodium nitrate Add hydrochloric acid. Carbon dioxide gas given off. (2) (b) State what you would see when sodium hydroxide solution reacts with copper sulphate solution. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) (i) Name one instrumental method which can be used to help in the identification of substances. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Suggest one advantage of the instrumental method you have named. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 6 marks) Barnard Castle School 3 4. A student carried out a titration to find the concentration of a solution of hydrochloric acid. The following paragraph was taken from the student’s notebook. I filled a burette with hydrochloric acid. 25.0 cm3 of 0.40 mol/dm3 potassium hydroxide was added to a flask. 5 drops of indicator were added. I added the acid to the flask until the indicator changed colour. The volume of acid used was 35.0 cm3. (a) What piece of apparatus would be used to measure 25.0 cm3 of the potassium hydroxide solution? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Name a suitable indicator that could be used. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Calculate the number of moles of potassium hydroxide used. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Moles of potassium hydroxide = ............................................ mol (2) (d) Calculate the concentration of the hydrochloric acid. The equation for the reaction is: KOH + HCl KCl + H2O ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Concentration of hydrochloric acid = ........................................ mol/dm3 (2) (Total 6 marks) Barnard Castle School 4 5. A chemist used a titration to investigate a solution used to unblock drains. AQ A ‘X ’ LIQUID DRAIN OPENER tough on blocks 25 cm3 of a diluted solution of Drain Opener was put into a beaker. The graph shows how the pH of this solution changed as hydrochloric acid was slowly added. 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 pH 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 (a) 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Volume of hydrochloric acid in cm 3 40 45 What volume of hydrochloric acid was needed to neutralise the Drain Opener solution? Volume = ...............................................cm3 (1) Barnard Castle School 5 (b) Which of the following best describes Drain Opener solution? Draw a ring around your answer. neutral strong acid strong alkali weak acid weak alkali (1) (c) Which of the following would be best for accurately measuring the volume of hydrochloric acid added? Draw a ring around your answer. beaker burette measuring cylinder pipette Give a reason for your choice. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 4 marks) 6. The diagram shows some of the elements in Groups I and 7 of the Periodic Table. 0 Group 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Li F Na Cl K Br I (a) The elements in Group 1 have similar chemical properties. Describe one chemical reaction which shows that lithium, sodium and potassium react in the same sort of way. You should say what you would react them with and what substances would be produced. What you would react them with .......................................................................................................................... Substances produced .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (3) Barnard Castle School 6 (b) All the elements in Group 7 react with hydrogen. Fluorine reacts in the dark, explosively, at very low temperatures. Chlorine reacts explosively in sunlight, at room temperature. Bromine, in light, only reacts if heated to about 200°C. Suggest the conditions needed for hydrogen and iodine to react. Give reasons for your answer. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Hydrogen and chlorine react to produce hydrogen chloride. Balance the symbol equation for the reaction. H2 + Cl2 HCl (1) (d) Use your understanding of atomic structure to explain the trend in reactivity in the Group 7 elements. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) 7. (a) A student had forgotten to label which of two test tubes contained a solution of aluminium nitrate. Describe a chemical test using sodium hydroxide solution to show which test tube contained nitrate ions. Give the result of this test. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) Name an instrumental method of analysis that might be used to detect a drug in the urine of an athelete. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) Barnard Castle School 7 (c) Describe how advances in technology have assisted in the development of instrumental methods for the detection and identification of elements and compounds. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) 8. A student wanted to find out how much of a substance, to the nearest 0.1 gram, dissolves in 15cm³ of water. His plan for the experiment is shown below, but the descriptions of some of the steps have been missed out. 1 Grind the substance in a pestle and mortar. 2 3 4 Add the 0.1 gram of the substance to the water in the test tube. 5 YES 6 Examine to see if all the substance is dissolved. NO 7 The missing steps in his plan are written below, but not in the correct order. (a) A Shake thoroughly for some time. B Measure out 0.1 gram of the substance. C Record the amount of substance added. D Measure out 15cm³ of water into a test tube. Write the letters A, B, C and D in the boxes in his plan, in the correct order. (4) (b) How would you know that the substance had dissolved? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Barnard Castle School 8 9. Many soft drinks contain citric acid. INGREDIENTS: CARBONATED WATER, SUGAR, CITRIC ACID, ACIDITY REGULATOR (E331), FLAVOURINGS, PRESERVATIVE (E211) (a) Citric acid is a weak acid. (i) What is meant by a weak acid in terms of its ionisation in water? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Describe and give the results of an experiment which would show that citric acid is a weaker acid than hydrochloric acid of the same concentration. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Citric acid behaves as an acid. Explain why, using the ideas of Arrhenius and of Bronsted-Lowry. To gain full marks in this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) Barnard Castle School 9 10. Chemical tests are used to identify compounds. (a) What colour is produced by sodium compounds in flame tests? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Chemical tests are carried out on these substances. ammonium chloride potassium nitrate copper bromide copper nitrate magnesium sulphate zinc carbonate Complete each sentence by choosing the correct substance from the box. You may use each substance once or not at all. The substance which (i) reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce carbon dioxide gas is ............................................................................................................................ (1) (ii) in solution reacts with sodium hydroxide solution to form a blue precipitate is ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) in solution reacts with barium chloride solution, in the presence of dilute hydrochloric acid, to form a white precipitate is ............................................................................................................................ (1) (c) State what you see when sodium chloride solution reacts with silver nitrate solution in the presence of dilute nitric acid. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 5 marks) Barnard Castle School 10 11. A leaflet listed the effects of hard water: HOW HARD WATER COSTS YOU HARD CASH Hard water causes: Blocked showers, burnt out immersion heaters Scale build up inside water pipes Higher water heating cost Extra soap required to get a lather Describe how softening the hard water could save money. ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 3 marks) 12. One definition of an element is: “A substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical methods.” The table shows some of the “substances” which Antoine Lavoisier thought were elements. He divided the “substances” into four groups. He published these groups in 1789. The modem names of some of the “substances” are given in brackets. Acid-making elements Gas-like elements Metallic elements Earthly elements sulphur light cobalt mercury lime (calcium oxide) magnesia (magnesium oxide) phosphorus caloric (heat) copper nickel charcoal (carbon) oxygen gold azote (nitrogen) iron platina (platinum) silver barytes (barium sulphate) argilla (aluminium oxide) hydrogen lead tin silex (silicon dioxide) manganese tungsten zinc (a) Name one “substance” in the list which is not a chemical element or compound. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) Barnard Castle School 11 (b) Name one “substance” in the list which is a compound. (i) .......................................................................................................................... (1) Suggest why Lavoisier thought that this “substance” was an element. (ii) .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Dimitri Mendeleev devised a Periodic Table of the elements in 1869. A modem version of this table is shown on the Data Sheet. Give two ways in which Mendeleev’s table is more useful than Lavoisier’s. 1 ................................................................................................................................. ..................................................................................................................................... 2 ................................................................................................................................. ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 5 marks) 13. (a) Complete each sentence about water by choosing the correct words from the box. Each word may be used once or not at all. calcium (i) chloride chlorine hydroxide nitrate oxygen Hardness in water is caused by dissolved ........................................ ions. (1) (ii) Some ........................................ dissolved in water is essential for aquatic life. (1) (iii) The use of artificial fertilisers can result in many natural waters being contaminated with dissolved ........................................ ions, which can have harmful effects on babies. (1) Barnard Castle School 12 (b) The diagram shows part of the water cycle. Wind Cloud Sun Rain Lake Sea River Describe what is happening in the water cycle. To gain full marks you should write down your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use correct scientific words. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (c) This label has been taken from a bottle of carbonated mineral water. Sparkling Mineral Water MINERAL ANALYSIS TYPICAL VALUES mg/l Calcium 35.0 Magnesium 5.3 Sodium 22.0 Potassium 2.2 Chloride 38.0 Sulphate 22.0 Nitrate Fluoride Carbonated Natural Mineral Water Barnard Castle School 34.0 LESS THAN 0.1 2 LITRE e 13 (i) The bar chart shows the amounts of some of the ions in this mineral water. 40 30 Amount of ions in 20 mg per litre 10 0 Calcium Sodium Chloride Sulphate Nitrate Complete the bar chart to show the amount of nitrate ions given on the label. (1) (ii) Describe how water is carbonated. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 9 marks) 14. The idea of a periodic table of the elements was started by John Newlands about 140 years ago. He wrote down the elements he knew about in order, starting with the lightest atoms. Then he arranged them into seven groups, like this: Barnard Castle School 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 H Li Be B C N O F Na Mg Al Si P S Cl K Ca 14 (a) Write down three differences between the groups in Newlands’ periodic table and the groups in the modern periodic table (up to the element Ca, which is calcium). ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) Suggest one reason why this part of Newlands’ table was different from the modern one. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Dimitri Mendeléev later developed the periodic table of the elements. He arranged the elements according to their properties and their relative atomic masses. The diagram shows where Mendeléev put tellurium (Te) and iodine (I) in his table because of their properties. (The diagram uses present day symbols and the atomic numbers of the elements have been added to Mendeléev’s table.) GROUP 6 GROUP 7 16 O 8 19 F 9 32 S 16 35.5 Cl 17 80 Br 35 128 Te 52 (i) 127 I 53 What is wrong with this arrangement of tellurium and iodine in terms of their relative atomic masses? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) Barnard Castle School 15 (ii) Explain why this is not a problem in the modern periodic table. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) 15. The table shows some properties of four Group 7 elements. Element Reaction with hydrogen Boiling point in ºC Melting point in ºC State at room temperature Fluorine – 218 – 188 Chlorine – 34 – 101 Bromine + 59 –7 Reacts if heated Iodine + 185 + 114 Reacts if heated strongly (a) Description Product gas Explosive reaction in dim light Hydrogen fluoride gas Explosive reaction in sunlight Hydrogen chloride Hydrogen iodide What is the state at room temperature of: (i) bromine; ............................................... (ii) iodine? .................................................. (2) (b) Which one of the four elements is most reactive? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Name the compound formed when hydrogen reacts with bromine. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 4 marks) Barnard Castle School 16 16. The symbol equation shows the reaction between methane and oxygen. CH4 methane + 2O2 oxygen CO2 + carbon dioxide 2H2O water The structural formulae in the equation below show the bonds in each molecule involved. H H C H + 2 [O = O] O = C = O + 2 [H – O – H] H In the three stages shown at (i), (ii) and (iii) below, calculate the net energy transfer when the formula mass (1 mole) of methane reacts with oxygen. (i) Write down the bonds broken and the bonds formed during the reaction. Bonds broken Bonds formed number number type type (4) (ii) Calculate the total energy changes involved in breaking and in forming each of these bonds. Total energy change in breaking bonds Total energy change in forming bonds (4) Barnard Castle School 17 (iii) Describe, as fully as you can, what the above figures in (ii) tell you about the overall reaction. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 10 marks) 17. Rainwater falling on limestone rocks can form caves. Rain Limestone Cave Lake (a) Complete the sentences by choosing the correct words from the box. acidic hard alkaline reacts dissolves soft tastes You may use each word once or not at all. Rainwater is an ....................... solution which ....................... with limestone. The solution formed in the lake is known as ....................... water. One advantage of drinking the water from the lake is that it ....................... better than rainwater. (4) Barnard Castle School 18 (b) Samples of water were tested by shaking with soap solution. The results are shown in the table. Water sample (50 cm3) (i) Volume of soap solution to form a lather in cm3 lake 15 boiled lake 3 rain 1 What is seen when only 10 cm3 of soap solution is shaken with 50 cm3 of water from the lake? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Why did the rainwater need only 1 cm3 of soap solution to form a lather? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Why did the water from the lake need 15 cm3 of soap solution to form a lather? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iv) Explain why boiled water from the lake needed only 3 cm3 of soap solution to form a lather. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 9 marks) 18. (a) The diagram shows the electronic structure of a particular element. x x x x In a similar way, show the electronic structure of another element from the same group in the periodic table and name the element you select. Name of element selected .......................................................................................... (4) Barnard Castle School 19 (b) The element lithium gives a moderate reaction with cold water, releasing hydrogen and forming a solution of lithium hydroxide. Describe how sodium is similar to and how it is different from lithium in its chemical reaction with cold water. Explain any similarity or difference in terms of their atomic structure. Similarity. .................................................................................................................. Reason. ...................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... Difference. ................................................................................................................. Reason. ...................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (5) Total 9 marks) 19. Four labels have come off four bottles. Aluminium sulfate solution Ammonium sulfate solution Al2(SO4)3(aq) (NH4)2SO4(aq) Magnesium sulfate solution Sodium sulfate solution MgSO4(aq) Na2SO4(aq) Describe and give the results of the chemical tests that you would do to identify which bottle contained which substance. ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... Barnard Castle School 20 ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... (Total 6 marks) 20. Chemical tests can be used to identify compounds. The table shows the results of some tests carried out on three solutions, A, B and C. Solution Flame Test A Yellow B Brick-red C Hydrochloric acid is added Sodium hydroxide solution is added Silver nitrate solution is added Carbon dioxide gas produced White precipitate insoluble in excess sodium hydroxide solution White precipitate Dark green precipitate Use the information in the table to identify solutions A, B and C. Give the name of: (a) solution A; ................................................................................................................... (2) (b) solution B; ................................................................................................................... (2) (c) the metal ion in solution C. ......................................................................................... (1) (Total 5 marks) Barnard Castle School 21 21. The diagram shows a simplified flow diagram of a water treatment works which supplies drinking water. Water from reservoir Simplified flow diagram of water treatment Filtration Sampling Chlorination and stabilisation To homes Storage (a) Explain the purpose of: (i) filtration ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (ii) chlorination. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Samples of the treated water must be tested at regular intervals. (i) Suggest why. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Suggest how the use of ICT and/or data logging equipment could help with this testing. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Drinking water can also be produced using distillation. Explain why this process is expensive. ..................................................................................................................................... Barnard Castle School 22 ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (d) In some parts of the country the water supplied to homes is hard water. (i) Name one ion that can make water hard. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Explain how hard water can affect central heating systems. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (iii) State one advantage of hard water. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 11 marks) 22. Washing powders are a mixture of substances. The substances in a box of Kleenkwik washing powder are shown. Detergent Bleach Perfume Soap Sodium phosphate Supersoap (a) Which substance in the washing powder gives clothes a pleasant smell? .................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) What does a bleach do? .................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Sodium phosphate removes the hardness in water. (i) What is hard water? ......................................................................................................................... Barnard Castle School 23 ......................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Why should the hardness be removed? ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Give another method which removes the hardness in water. ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... (1) (d) Circle the chemical which is used to make detergents. carbonic acid hydrochloric acid sulphuric acid (1) (Total 6 marks) 23. The symbol equation shows the decomposition of water. 2H2O 2H2 + O2 An energy level diagram for this reaction is shown below. energy (kJ) x (1856 kJ) y (1370 kJ) hydrogen + oxygen (products) z water (reactant) Explain the significance of x, y and z on the energy level diagram in terms of energy transfers that occur in the reaction. You should make specific reference to the bonds broken and formed and to the nett energy transfer (energy transferred to or from the surroundings). ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... Barnard Castle School 24 ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... (Total 6 marks) 24. A sample of water taken from a lake was found to contain sulphuric acid. A student carried out a titration to find the concentration of the sulphuric acid in this sample. 25.0 cm3 of the sulphuric acid solution was neutralised exactly by 34.0 cm3 of a potassium hydroxide solution of concentration 0.2 mol dm–3. The equation for the reaction is: 2KOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq) K2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(1) (a) Describe the experimental procedure for the titration carried out by the student. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (b) Calculate the number of moles of potassium hydroxide used. ..................................................................................................................................... Number of moles = ........................... (2) (c) Calculate the concentration of the sulphuric acid in mole per cubic decimetre (mol dm–3). ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Concentration = .................. mol dm–3 (3) (Total 9 marks) Barnard Castle School 25 25. The label shows the ions present in the bottle of spring water. This water is temporarily hard. Composition mg/litre calcium Ca2+ magnesium Mg 2+ potassium K + SPRING WATER WITH FIZZ (a) sodium Na+ – chloride Cl – fluoride F nitrate NO3 – sulphate SO4 2– hydrogencarbonate HCO 3 – 35 15 1 12 10 1 2 6 179 Name the compound that would be present in the greatest amount if this water were evaporated to dryness. ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) (i) What is hard water? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) State one advantage of hard water. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Describe an experiment that would show that this water is temporarily hard. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) Barnard Castle School 26 (d) This hard water may be softened as shown. 2+ Ca and Mg in water 2+ Ca 2+ and Mg2+ in solid Na + on solid Na + in water Before After What name is given to this process? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 10 marks) 26. (a) This label has been taken from a bottle of vinegar. es or preserva dditiv tive a s no MALT VINEGAR Pur eM r alt Vinega Vinegar is used for seasoning foods. It is a solution of ethanoic acid in water. In an experiment, it was found that the ethanoic acid present in a 15.000 cm3.sample of vinegar was neutralised by 45.000cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution, of concentration 0.20 moles per cubic decimetre (moles per litre). Barnard Castle School 27 The equation which represents this reaction is CH3COOH + NaOH CH3COONa + H2O Calculate the concentration of the ethanoic acid in this vinegar: (i) in moles per cubic decimetre (moles per litre); ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... Concentration =................................... moles per cubic decimetre (2) (ii) in grams per cubic decimetre (grams per litre). Relative atomic masses: H = 1; C = 12; O = 16. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... Concentration = .................................. grams per cubic decimetre (2) (b) The flow diagram shows some reactions of ethanoic acid. Sodium ethanoate + water Alkali B Sodium ethanoate + Ester C Sodium Ethanoic acid Ethanol + catalyst D gas A + water Sodium carbonate Carboxylic acid salt E + water + carbon dioxide Give the name of: (i) gas A, ............................................................................................................................ (1) Barnard Castle School 28 (ii) alkali B, ............................................................................................................................ (1) (iii) ester C, ............................................................................................................................ (1) (iv) catalyst D, ............................................................................................................................ (1) (v) carboxylic acid salt E. ............................................................................................................................ (1) (Total 9 marks) 27. The symbol equation below shows the reaction when methane burns in oxygen. CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O An energy level diagram for this reaction is shown below. x Energy level methane + oxygen (reactants) y z carbon dioxide + (products) water (a) Which chemical bonds are broken and which are formed during this reaction? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) Barnard Castle School 29 (b) Explain the significance of x, y and z on the energy level diagram in terms of the energy transfers which occur when these chemical bonds are broken and formed. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (Total 9 marks) 28. John Newland produced a periodic table in 1866. The first 21 elements in his table are shown in the diagram. Column 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 H Li Be B C N O F Na Mg Al Si P S Cl K Ca Cr Ti Mn Fe Use the periodic table on the Data Sheet to help you to answer these questions. (a) In which two columns of Newland’s periodic table do all the elements have similar properties? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) The modern periodic table is arranged in a different order to Newland’s table. (i) What order is used in the modern periodic table? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Argon has a higher relative atomic mass than potassium. Explain why. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Describe the changes in the number of electrons in the atoms of elements in the period which begins with potassium and ends with krypton. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 5 marks) Barnard Castle School 30 29. Use the Periodic Table of Elements on the Data Sheet to help you to answer this question. Francium (Fr) is a very rare element. It is estimated that there is only 25 g of francium in the Earth’s crust. Francium is radioactive and has a half-life of only a few minutes. Mendeleev predicted the existence of francium in the 1870s but the element was not discovered until 1939. (a) Explain why Mendeleev was able to predict the existence of francium in the 1870s. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Suggest why there is not much experimental evidence for the properties of francium. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) (i) If you could react francium with water, how would the reaction compare with that of sodium with water? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Explain the reason for your answer. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Barnard Castle School 31 30. This label has been taken from a bottle of household ammonia solution. Smith’s Household Ammonia Solution Ideal for all household cleaning tasks! Nothing shifts grease like Smith’s does! Household ammonia is a dilute solution of ammonia in water. It is commonly used to remove grease from ovens and windows. (a) The amount of ammonia in household ammonia can be found by titration. 25.0 cm3 of household ammonia is placed in a conical flask. Describe how the volume of dilute nitric acid required to neutralise this amount of household ammonia can be found accurately by titration. Name any other apparatus and materials used. To gain full marks you should write down your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use correct scientific words. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (4) Barnard Castle School 32 (b) In an experiment, it was found that 25.0 cm3 of household ammonia was neutralised by 20.0 cm3 of dilute nitric acid with a concentration of 0.25 moles per cubic decimetre. The balanced symbol equation which represents this reaction is NH3(aq) + HNO3(aq) NH4NO3(aq) Calculate the concentration of the ammonia in this household ammonia in moles per cubic decimetre. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... Concentration = ............................. moles per cubic decimetre (2) (c) The salt, ammonium nitrate, is formed in this reaction. Describe, and give the result of, a chemical test which shows that ammonium nitrate contains ammonium ions. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) 31. The table shows the properties of four elements from Group VII of the Periodic Table. Element Proton Electronic Boiling Melting State at Number structure point (ºC) point (ºC) 20ºC Fluorine 2.7 –188 –218 –34 –101 Chlorine 17 Bromine 35 2.8.18.7 +59 –7 Iodine 53 2.8.18.18.7 +185 +114 (a) gas Reaction with hydrogen Ease Product Explosive reaction hydrogen in dull light fluoride Explosive reaction hydrogen in sunlight chloride solid React if heated hydrogen bromide React if heated strongly hydrogen iodide Complete the spaces in the table. (4) (b) Comment briefly on the trend in melting points for these four elements. ..................................................................................................................................... Barnard Castle School 33 ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Explain, in as much detail as you can: (i) why the reactions of these elements with hydrogen are similar. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (ii) why their reactivity with hydrogen decreases from fluorine to iodine. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 9 marks) 32. This label has been taken from a packet of SuperClean. Sodium percarbonate is a powerful stain removing chemical. The formula of sodium percarbonate can be represented as Na2C2O6 (a) (i) Calculate the number of moles of sodium percarbonate in the 50 g packet. Relative atomic masses: C = 12; O = 16; Na = 23. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... Number of moles = ..................................... (2) Barnard Castle School 34 (ii) Calculate the concentration of the sodium percarbonate solution, in moles per cubic decimetre, when 50 g of sodium percarbonate is dissolved in 6 litres (dm3) of water. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... Concentration = ....................moles per cubic decimetre (1) (b) When sodium percarbonate acts as a stain removing chemical, it decomposes to produce oxygen. The equation which represents the decomposition of sodium percarbonate is 2Na2C2O6 2Na2CO3 + 2CO2 + O2 (i) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen produced from 50 g of sodium percarbonate. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... Number of moles = ..................................... (1) (ii) Calculate the volume of oxygen, at room temperature and pressure, produced from 50 g of sodium percarbonate. 1 mole of any gas at room temperature and pressure has a volume of 24 dm3. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... Volume of oxygen = ............................ dm3 (2) (Total 6 marks) 33. Some substances dissolve in water. The solubility of a substance is the number of grams that will dissolve in 100 grams of water. The diagram below shows how the solubilities of two substances, potassium nitrate and sodium chloride, vary between 0 – 100°C. Barnard Castle School 35 250 potassium nitrate 200 150 Solubility (grams) 100 50 sodium chloride 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Temperature (°C) (a) How much potassium nitrate dissolves in 100 grams of water at 60°C? ........................................ grams (1) (b) Describe what happens to the solubilities of potassium nitrate and sodium chloride between 0 – 100°C. Answer in as much detail as you can. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (5) (Total 6 marks) Barnard Castle School 36 34. Many hydrocarbons are used as fuels. An energy level diagram is shown for the combustion of the hydrocarbon methane. Energy (kJ) CH 4 (g) + 2O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2H 2 O(I) Describe and explain why the line rises and then falls to a lower level. ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... (Total 4 marks) 35. (a) Choose from the names of elements in the box the answers to the questions which follow. aluminium carbon chlorine copper helium iron magnesium sodium Give the name of: (i) an alkali metal ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) a halogen ........................................................................................................................... (1) Barnard Castle School 37 (iii) a noble gas ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) The alkali metals are in Group 1 of the Periodic Table. The elements in Group 1 have a number of similar properties. (i) Describe one chemical property which they have in common. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Describe one physical property which they have in common. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 5 marks) 36. The balanced equation for the combustion of ethane is shown using structural formulae. 2H (a) H H C C H H C + 7O O 4O C O + 6H O H Complete the table to show the number of bonds broken and made when two molecules of ethane react with seven molecules of oxygen. Type of bond Number of bonds broken Number of bonds made C –– C C –– H OO CO H –– O (2) (b) The combustion of ethane is a strongly exothermic process. Draw a labelled energy level diagram showing the endothermic and exothermic parts of the overall reaction. Indicate the activation energy on the diagram. (4) (c) Explain, in terms of particles and the activation energy of a reaction, how a catalyst is able to increase the rate of reaction. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) Barnard Castle School 38 37. You will find the information on the Data Sheet helpful when answering this question. This equation shows the reaction between ethene and oxygen. C2H4 + 3O2 2CO2 + 2H2O The structural formulae in the equation below show the bonds in each molecule involved. H H C C + H H 3 [O = O] 2[O = C = O] + 2[H – O –H] Use the three stages shown at (a), (b) and (c) below to calculate the nett energy transfer when the formula mass (1 mole) of ethene reacts with oxygen. (a) Write down the bonds broken and the bonds formed during the reaction. (Some have already been done for you.) Bonds broken Bonds formed Number Type Number Type 4 [C – H] 4 [C = O] 1 [C = C] (2) (b) Calculate the total energy changes involved in breaking and in forming all of these bonds. (Some have already been done for you.) Total energy change in breaking bonds Total energy change in forming bonds [4 × 413] = 1652 4 × [805] = 3220 [1 × 612] = 612 Total = Total = kJ kJ (4) Barnard Castle School 39 (c) Describe, as fully as you can, what the figures in (b) tell you about the overall reaction. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) 38. The electronic structures of five elements, V, W, X, Y and Z are shown below. (a) (i) V W X Y Z 2.1 2.6 2.8.4 2.5 2.8.6 Write the letters of the two elements which belong to the same group in the Periodic Table .................................................................................................. (ii) To which group do they belong? ..................................................................... (2) (b) Write the letters of two elements that are gases ........................................................ (1) (c) Lithium, sodium and potassium are the first three elements in Group 1 of the Periodic Table. (i) Lithium reacts with cold water to produce lithium hydroxide and hydrogen. Describe how the reaction between sodium and water is (A) similar and (B) different to that between lithium and water. (A) Similar ........................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................... (B) Different ..................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (ii) Potassium is much more reactive than lithium. Explain this in terms of their electronic structures. .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 9 marks) Barnard Castle School 40 39. The diagram shows part of the periodic table. Group 0 Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6 23 24 27 28 31 sodium magnesium aluminium silicon phosphorous sulphur 11 12 13 14 15 32 16 Group 7 35 40 chlorine argon 17 18 Choose from the elements shown in the table: (a) one metal .................................................................................................................... (1) (b) a noble gas ................................................................................................................. (1) (c) a coloured gas ............................................................................................................ (1) (Total 3 marks) 40. Part of the Periodic Table is shown. It includes the symbols for six elements. C Li F Na (a) Ca Ha log en s Al ka li m eta ls K Write the symbol for carbon. ..................................................................................... (1) (b) (i) Put the symbol Cl, for chlorine, into its correct position in the Table. (1) (ii) Bromine, chlorine, fluorine and iodine are halogens. Which one of these halogens is least reactive? ........................................................................................................................... (1) Barnard Castle School 41 (c) The alkali metals form Group 1 in the Periodic Table. Write the symbol of the most reactive alkali metal shown in the Table above. .................................................................................................................................... (1) (d) Write the symbol for an element which is in the same Group as sodium. .................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 5 marks) 41. These are the electronic structures of the atoms of three different elements. 2.8.1 element A (a) 2.8.8 element B 2.8.8.1 element C Identify elements A and B. Element A is ............................... Element B is ............................... (2) (b) (i) Why is element C more reactive than element A? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Why is element B unreactive? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Barnard Castle School 42 42. Methane and oxygen react together to produce carbon dioxide and water. CH 4 + 2O 2 CO 2 + 2H2 O 818 kJ of energy is given out to the surroundings for each formula mass (mole) of methane that reacts. The methane gas will not burn in oxygen until a flame is applied, but once lit it continues to burn. (a) Explain why energy must be supplied to start the reaction but it continues by itself once started. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (b) Sketch an energy level diagram for the reaction and indicate on the diagram the nett energy released. Energy Time (3) (Total 7 marks) Barnard Castle School 43 43. Complete the table which shows some of the physical properties of bromine, chlorine and iodine. Melting point Boiling point in °C in °C Physical state at 23 °C Colour of vapour Bromine –7 58 ................................. ................................. Chlorine –101 –34 ................................. greenish 114 183 ................................. ................................. Iodine (Total 2 marks) Barnard Castle School 44