* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Civil War Vocabulary- Chapters 21, 22, and, 23
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
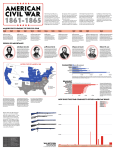
Civil War Vocabulary- Chapters 21, 22, and, 23 1. Abolitionist- one who took action against slavery, with the intent to “abolish” or outlaw it. 2. Missouri Compromise- 1820- a compromise between states passed to regulate slavery of the western territories of the United States. Object of the compromise was to balance the number of slave-states and free-states. The boundary line was drawn at the 36/30degree parallel. 3. Racism- the belief that one person is less “human” than another person, biased based on skin color, language, or culture. 4. Wilmot-Proviso- A proposal made in 1846- to prohibit slavery in the territory added to the U.S. as a result of the Mexican-American War. 5. Compromise of 1850- the agreement made in order to admit California in the Union as a free-state. This arrangement allowed for the New Mexico and Utah territories to decide whether they would be slave-territories or not. 6. Fugitive Slave Act- This was a federally mandated order that if a slave ran away to the North, then the owner of the slave had the right to go retrieve the run-away . Also, a $1,000 fine would be given to anyone who did not turn in a known fugitive. 7. Uncle Tom’s Cabin- an anti-slavery novel by Harriet Beecher Stowe. Revealed the horrors of slavery to many Northerner who read it. 8. Popular Sovereignty- the idea that the government’s authority should come from the people. 9. Kansas-Nebraska Act- This act repealed the Missouri Act. This act allowed people in the territories of Kansas and Nebraska to decide whether they would allow slavery to be accepted in the territory. 10. “Bleeding Kansas”/Bloodshed in Kansas- Border war between slavery and anti-slavery states. John Brown came into Kansas to fight against slavery. The tension for fighting started because many neighboring states were pro-slavery and Kansas was divided. 11. John Brown- an abolitionist who believed armed fighting was the only way to end slavery. Commanded forces in Kansas and raided at Harper’s Ferry’s. 12. Dred Scott Supreme Court Case- Supreme Court ruling on slavery and the rights of slaves as they travel from free to slave states. Conclusions from the ruling: 1. African-Americans were not U.S. citizens. 2. The federal government had no power to regulate slavery in any territory (it becomes a states-rights issue) acquired subsequent to the creation of the U.S. 13. Secede/secession- to withdraw from an organization or alliance. 14. Confederate States of America (Confederacy)- made up of 11 states that seceded from that Union. The Southern states were: South Carolina, Mississippi, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, North Carolina, and Tennessee. 15. Anaconda Plan- Union Gen. Winfield Scott’s plan for surrounding and over-taking the Confederacy through blockades of Southern ports to isolate and “strangle” the Confederate states by the Union. 16. Gettysburg Address- Address given on the Battlefield of Gettysburg, in memoriam of those who died fighting for the freedoms of others. 17. Emancipation Proclamation- The order issued by President Lincoln through a speech presented in January 1, 1863 by President Lincoln declaring that the slaves in the confederate states to be free. 18. 13th Amendment- Ratified in 1865- abolishing slavery 19. 14th Amendment- 1868- granting citizenship to anyone born in the U.S and guaranteeing all citizens equal protection under the law. 20. 15th Amendment- 1872- declaring that the states cannot deny anyone the right to vote because of race or color, or because the person was once a slave. 21. Reconstruction- The time period after the Civil War in which the Southern states were rebuilt and brought back into working order in the union. 22. Freedmen’s Bureau- Agency established by Congress at the end of the Civil War to help protect newly freed Black Americans. 23. Black codes- laws passed in 1855-1865, in the former Confederate states to limit the rights and freedoms of African Americans. Civil War Categories Place each vocabulary word in the appropriate category: Leads to the Civil War: Abolitionist Missouri Compromise RacismWilmot-Proviso Compromise of 1850 Uncle Tom’s Cabin Popular Sovereignty Kansas-Nebraska Act Bleeding Kansas”/Bloodshed in Kansas John Brown Dred Scott Supreme Court Case Secede/secession Black codes Takes place during the Civil War: Fugitive Slave Act Confederate States of America (Confederacy) Anaconda PlanGettysburg AddressEmancipation Proclamation Black codes After the Civil War ends: 13th Amendment 14th Amendment- 1868 15th Amendment- 1872 Reconstruction Freedmen’s Bureau