* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Processes Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
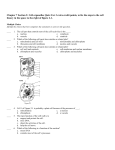
Cell Processes Review Modified True/False ____ 1. You can't see the cells in your body because most of them are very small. ____________________ ____ 2. A cell makes a copy of its DNA during the stage of the cell cycle called mitosis. ____________________ ____ 3. Cell repair helps replace damaged cells when a bone is broken. ____________________ ____ 4. The cell theory states that cells are produced from nonliving cells. ____________________ ____ 1. Which of the following is not absorb by a human cell? a. carbon dioxide b. oxygen c. water d. food ____ 2. Which of these is arranged from smallest to largest level of organization? a. organs, tissues, cells, organ systems b. molecules, atoms, elements, compounds c. atoms, organs, cells, organ systems d. compounds, cells, tissues, organs ____ 3. The stage of the cell cycle that follows mitosis is called a. telophase. b. cytokinesis. c. metaphase. d. interphase. ____ 4. Which organelles release chemicals that break down large food particles into smaller ones? a. endoplasmic reticulum b. Golgi bodies c. vacuoles d. lysosomes ____ 5. Which organelle is the control center of a cell? a. chloroplast b. nucleus c. ribosome d. mitochondrion ____ 6. Which of the following best describes the function of mitochondria? a. They store energy from food molecules. b. They produce nucleic acids that release energy. c. They convert energy from food molecules into energy the cell can use. d. They store energy from sunlight. ____ 7. The process by which plants and some other cells make their own food is known as a. cellular respiration. b. photosynthesis. c. diffusion. d. homeostasis. ____ 8. The regular cycle of growth and division that cells undergo is called a. replication. b. the cell cycle. c. mitosis. d. interphase. ____ 9. What is the function of a cell wall? a. to protect and support the cell b. to perform different functions in each cell c. to prevent water from passing through it d. to prevent oxygen from entering the cell ____ 10. Mitosis is the stage of the cell cycle during which a. the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei. b. the cell’s DNA is replicated. c. the cell divides into two new cells. d. the cell’s cytoplasm divides. ____ 11. What forms around the chromatids during mitosis? a. two new nuclei b. two new chromosomes c. two new cells d. two new DNA molecules ____ 12. Which of these is not a function of cell division? a. repair b. growth c. respiration d. reproduction ____ 13. During what stage of the cell cycle does replication occur? a. mitosis b. interphase c. prophase d. cytokinesis ____ 14. Many substances move through cell membranes from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration in the process of a. DNA replication. b. diffusion. c. reproduction. d. cellular respiration. ____ 15. What is the function of a cell membrane? a. to perform different functions in each cell b. to control which substances enter and leave the cell c. to support the cell d. to form a hard outer covering for the cell ____ 16. In which order does mitosis occur? a. prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase b. prophase, anaphase, metaphase, telophase c. telophase, anaphase, metaphase, prophase d. metaphase, telophase, anaphase, prophase ____ 17. What are chromatids? a. doubled rods of centromeres b. identical strands of chromosomes c. identical daughter cells d. pigments that absorb the energy in sunlight ____ 18. Which organelles store food and other materials needed by the cell? a. mitochondria b. chloroplasts c. vacuoles d. ribosomes ____ 19. Which cellular structure contains thin strands of DNA known as chromotin? a. golgi apparatus b. cell membrane c. mitochondria d. nucleus ____ 20. Which of the following scientists made the observation while looking at cork under his microscope, that the empty space looked like tiny rectangular rooms, or cells? a. Schwann b. Leeuwenhoek c. Hooke d. Virchow ____ 21. At the end of mitosis, chromosomes provide each daughter cell with a. an exact copy of the parent’s genetic material. b. four times the amount of the parent’s genetic material. c. twice the amount of the parent’s genetic material. d. half the parent’s genetic material. Cell Processes Test Answer Section MODIFIED TRUE/FALSE 1. ANS: OBJ: BLM: 2. ANS: T Tell what cells are. knowledge F, interphase PTS: 1 STA: SC.6.L.14.2 DIF: L1 TOP: c_ch01_039 PTS: OBJ: STA: BLM: 3. ANS: 1 DIF: L2 Identify the events that take place during the three stages of the cell cycle. SC.6.L.14.3 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.4.2.2 | MA.6.A.3.6 TOP: c_ch02_036 comprehension F, division PTS: STA: BLM: 4. ANS: 1 DIF: L2 SC.6.L.14.3 | SC.6.L.14.4 comprehension F, living OBJ: Summarize the functions of cell division. TOP: PH_EN_SC_MGS_2010_X_56543 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: Describe how scientists first observed cells and developed the cell theory. STA: SC.6.N.3.1 | SC.6.L.14.2 TOP: c_ch01_038 BLM: knowledge MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: STA: BLM: 2. ANS: OBJ: STA: BLM: 3. ANS: OBJ: STA: BLM: 4. ANS: OBJ: STA: BLM: 5. ANS: OBJ: STA: BLM: 6. ANS: OBJ: A PTS: 1 DIF: L2 OBJ: Tell what cells are. SC.6.L.14.2 TOP: PH_EN_SC_MGS_2010_FL_0015 comprehension D PTS: 1 DIF: L2 Distinguish among the levels of organization in many-celled organisms. SC.6.L.14.1 | LA.6.2.2.3 | MA.6.A.3.6 TOP: PH_EN_SC_MGS_2010_FL_0014 comprehension B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 Identify the events that take place during the three stages of the cell cycle. SC.6.L.14.3 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.4.2.2 | MA.6.A.3.6 TOP: c_ch02_029 comprehension D PTS: 1 DIF: L2 Describe the functions of cell structures and organelles. SC.6.N.3.4 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.2.2.3 TOP: c_ch01_026 comprehension B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 Describe the functions of cell structures and organelles. SC.6.N.3.4 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.2.2.3 TOP: c_ch01_008 comprehension C PTS: 1 DIF: L2 Describe the functions of cell structures and organelles. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. STA: SC.6.N.3.4 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.2.2.3 TOP: c_ch01_009 BLM: comprehension ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: Identify cell processes that maintain homeostasis, such as extracting energy from food, getting rid of waste, and reproducing. STA: SC.6.N.2.1 | SC.6.L.14.3 | LA.6.2.2.3 TOP: PH_EN_SC_MGS_2010_FL_0018 BLM: knowledge ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 OBJ: Identify the events that take place during the three stages of the cell cycle. STA: SC.6.L.14.3 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.4.2.2 | MA.6.A.3.6 TOP: c_ch02_030 BLM: comprehension ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: Describe the functions of cell structures and organelles. STA: SC.6.N.3.4 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.2.2.3 TOP: c_ch01_023 BLM: knowledge ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: Identify the events that take place during the three stages of the cell cycle. STA: SC.6.L.14.3 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.4.2.2 | MA.6.A.3.6 TOP: c_ch02_010 BLM: knowledge ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: L2 OBJ: Identify the events that take place during the three stages of the cell cycle. STA: SC.6.L.14.3 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.4.2.2 | MA.6.A.3.6 TOP: c_ch02_027 BLM: comprehension ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: L2 OBJ: Summarize the functions of cell division. STA: SC.6.L.14.3 | SC.6.L.14.4 TOP: PH_EN_SC_MGS_2010_FL_0020 BLM: comprehension ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: Identify the events that take place during the three stages of the cell cycle. STA: SC.6.L.14.3 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.4.2.2 | MA.6.A.3.6 TOP: c_ch02_024 BLM: knowledge ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 OBJ: Identify cell processes that maintain homeostasis, such as extracting energy from food, getting rid of waste, and reproducing. STA: SC.6.N.2.1 | SC.6.L.14.3 | LA.6.2.2.3 TOP: PH_EN_SC_MGS_2010_X_56965 BLM: comprehension ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: Describe the functions of cell structures and organelles. STA: SC.6.N.3.4 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.2.2.3 TOP: c_ch01_007 BLM: knowledge ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: L2 OBJ: Identify the events that take place during the three stages of the cell cycle. STA: SC.6.L.14.3 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.4.2.2 | MA.6.A.3.6 TOP: PH_EN_SC_MGS_2010_FL_0021 BLM: comprehension ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 OBJ: Identify the events that take place during the three stages of the cell cycle. STA: SC.6.L.14.3 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.4.2.2 | MA.6.A.3.6 TOP: c_ch02_026 BLM: comprehension ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: Describe the functions of cell structures and organelles. STA: SC.6.N.3.4 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.2.2.3 TOP: c_ch01_025 BLM: knowledge ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: STA: BLM: 20. ANS: OBJ: STA: BLM: 21. ANS: OBJ: STA: BLM: Describe the functions of cell structures and organelles. SC.6.N.3.4 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.2.2.3 TOP: PH_EN_SC_MGS_2010_FL_0019 knowledge C PTS: 1 DIF: L2 Describe how scientists first observed cells and developed the cell theory. SC.6.N.3.1 | SC.6.L.14.2 TOP: PH_EN_SC_MGS_2010_FL_0016 comprehension A PTS: 1 DIF: L2 Identify the events that take place during the three stages of the cell cycle. SC.6.L.14.3 | SC.6.L.14.4 | LA.6.4.2.2 | MA.6.A.3.6 TOP: ls01a_64 comprehension