* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cell division - 7 - Mugans Biology Page
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
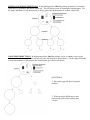
NAME___________________________ DATE___________________ HOUR___________________ BIOLOGY I MEIOSIS AND GAMETOGENESIS CELL DIVISION - 7 DIRECTIONS: The drawings below represent a cell going through meiosis. This cell has three pairs of homologous chromosomes. Use the shape and shade of each chromosome to follow where the chromosomes go as these cells divide. QUESTIONS 1. What is the purpose of Meiosis? 2. Why is Meiosis necessary for sexual reproduction? 3. What are tetrads? When do they form? 4. What is crossing over? When does it happen? SPERMATOGENESIS DIRECTIONS: In the drawings below label the primary spematocyte, secondary spermatocyte, spermatid, and mature sperm cell. This cell has two pairs of homologous chromosomes. Use the shape and shade of each chromosome to follow where the chromosomes go as these cells divide. OOGENESIS DIRECTIONS: In the drawings below label the primary oocyte, secondary oocyte, polar bodies, and the mature ovum. This cell has two pairs of homologous chromosomes. Use the shape and shade of each chromosome to follow where the chromosomes go as these cells divide. QUESTIONS: 1. How many egg cells does Oogenesis produce? 2. What causes the differences in size between the polar bodies and the other oocytes?