* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download time: - 90 minutes
Survey
Document related concepts
Temperature wikipedia , lookup
Thermal expansion wikipedia , lookup
Second law of thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Thermal radiation wikipedia , lookup
Thermal comfort wikipedia , lookup
Countercurrent exchange wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Thermoregulation wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer wikipedia , lookup
R-value (insulation) wikipedia , lookup
Thermal conduction wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic insulation wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
Adiabatic process wikipedia , lookup
Vapor-compression refrigeration wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Examination Papers ME-228
Re Exam Ist 1427
QUESTION(1) Answer the following.
1. What is difference between saturated liquid, saturated vapor and superheated
vapor?
2. What happens to temperature and pressure during boiling process?
3. Which process needs more energy, complete vaporization of 1kg of saturated
liquid at 1bar pressure or complete vaporization of 1kg of saturated liquid at 8
bar pressure? Why?
4. Which process needs ore energy, complete vaporization of 1kg of saturated
liquid at 100oC temperature complete vaporization of 1kg of saturated liquid
at 200oC temperature? Why?
QUESTION(2) Differentiate between:
1.Closed and open systems
2.Adiabatic and isothermal process
3.Heat and temperature
4.Isolated and closed systems
5.Intensive and extensive properties
6.Heat and work
QUESTION(3)
A tank whose volume is unknown is divided into two parts by a separating partition. One
side of the tank contains 0.01 m3 of refrigerant 134a that is saturated at 0.8 MPa, while
the other side is evacuated. The partition is removed and tank fills the entire volume of
the tank. If the final state of the refrigerant is 25 oC and 200 kPa, determine the volume of
the tank.
QUESTION(4)
(a) Air at 4.18 kg/m3 enters a nozzle that has an inlet to exit area ratio of 2:1 with a
velocity of 120 m/s and leaves with 380 m/s. Determine the density of the air as it leaves
the nozzle.
(b)A vacuum gage connected to a chamber reads 24 kPa at a location where
atmospheric pressure is 92 kPa. Determine the absolute pressure in the chamber.
© Determine change in the internal energy change and the enthalpy of nitrogen as it is
heated from 600 K to 1000 K using
(i) constant value of Cp and Cv
(ii) Average value of Cp and Cv
QUESTION(5) Complete the table
T,oC
220
190
P,kPa
400
u,kJ/kg
1825
phase
Saturated vapor
2000
4000
3040
THERMAL ENGINEERING
FOR CIVIL ENGINEERING STUDENTS
ME-228
TIME: - 90 MINUTES
(A) A tank whose volume is unknown is divided into two parts by a separating partition.
One side of the tank contains 0.01 m3 of refrigerant 134a as a saturated liquid at 0.8 MPa.
The other side is evacuated. The partition is removed and tank fills the entire volume of
the tank. If the final state of the refrigerant is 25 oC and 200 kPa, then
(1) The initial temperature of the refrigerant is --------------0C
(2) The initial specific volume of the tank is -------------m3/kg
(3) The mass of the refrigerant is ------------kg
(4) The final condition of the refrigerant is ------------------------(5) The final specific volume of the refrigerant is ----------------- m3/kg
(6) The volume of the full tank is ----------------------- m3
(12 marks)
(B) Complete the table
T,oC
?
220
110
?
P,kPa
400
?
?
4000
v,m3/kg
?
?
?
?
u,kJ/kg
1825
?
?
3650
liquid
water
water
R-134a
R-134a
Quality, x
?
1
0.5
?
(12 marks)
© A 20m3 tank contains nitrogen at 250C and 800 kPa. Some nitrogen escapes the tank
through a leakage. The leakage is stopped. The final temperature and pressure of the
nitrogen in the tank is 200C and 600 kPa respectively.
(1)The initial mass of the nitrogen is -----------kg
(2)The final mass of the nitrogen is -------------kg
(3)The mass of nitrogen that leaked is ----------kg.
(6 marks)
(D) 5 kgs of hydrogen are heated from 400 K to 100 K
(1)Using constant values of Cp and Cv,
(a) the change in internal energy of hydrogen is -------kJ
(b) change in enthalpy of hydrogen is --------------kJ.
(2) Using average values of Cp and Cv,
(a) the change in internal energy of hydrogen is -------kJ
(b) change in enthalpy of hydrogen is --------------kJ.
(4 marks)
(E) Fill in the blanks.
(1 mark each)
(a) The pressure gage connected to a tank reads 400 kPa at a location where
barometer reads 760 mm of mercury. The absolute pressure in the tank is ---kPa.
(b) The vacuum gage on a tank reads 35 kPa at a location where barometer reads
760 mm of mercury. The absolute pressure in the tank is ----kPa.
(c) A 800 L rigid tank contains 10kg of oxygen at 250C. The pressure in the tank is
------------kPa. If the atmospheric pressure is 97 kPa, then the reading of the
pressure gage attached to the tank is _____kPa.
(d) The difference in the open system and closed system is that the --------- crosses
the boundaries of the open system.
(e) A tank contains a gas at 100 kPa. It is heated so that the temperature changes by
100C. The corresponding change in Kelvin scale is ------------__
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
THERMO-FLUID GROUP
SUBJECT:-THERMO FLUIDS FOR CIVIL ENGINEERING
DAY: - MONDAY DATE:- _08-01-2007 TIME:-04PM-0530PM
(1) A frictionless piston cylinder device initially contains 200L of saturated liquid
refrigerant-134-a. The piston is free to move and its mass is such that it maintains a
constant pressure of 800kPa on the refrigerant. The refrigerant is now heated until its
temperature rises to 500C. Calculate work done during the process.
(2) A steam power plant receives heat from the furnace at a rate of 280GJ/h. Heat losses
to the surrounding air from the steam as it passes through the components of the power
plant is 8GJ/h. The waste heat transferred to the cooling water is 145 GJ/h. (GJ = 109J)
Determine (a) The net power output of the plant.
(b) The thermal efficiency of the plant.
(3) Air enters an adiabatic nozzle steadily at 300 kPa, 200oC and 30 m/s. It leaves at 100
kPa and 180 m/s. The inlet area of the nozzle is 80 cm2.
Find (a) The mass flow rate through the nozzle.
(b) Temperature at the exit of the nozzle.
(c) The area of the nozzle at its exit.
(4) Steam enters an adiabatic turbine at 10MPa and 5000C at a rate of 3 kg/s and leaves at
200kPa. The power output of the turbine is 2MW. Neglect the changes in kinetic and
potential energy
(a) Determine the temperature of the steam at the exit.
(b) Draw P-v and T-v diagram of the process showing the inlet and the exit states.
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
THERMO-FLUID GROUP
SUBJECT:-THERMO FLUIDS FOR CIVIL ENGINEERING
(1) Air enters a nozzle steadily at 2.21 kg/m3 and 30 m/s and leaves at 0.762 kg/m3 and
180 m/s. If the inlet area of the nozzle is 80 cm2 , determine the mass flow rate and the
exit area of the nozzle.
(2) A frictionless piston cylinder device initially contains 200L of saturated refrigerant134a. The piston is free to move and its mass is such that it maintains a pressure of
800kPa on the refrigerant. The refrigerant is now heated until its temperature rises to
500C. Calculate work done during the process.
(3) A steam power plant receives heat from the furnace at a rate of 280GJ/h. Heat losses
to the surrounding air from the steam as it passes through the components of the power
plant is 8GJ/h. The waste heat transferred to the cooling water is 145GJ/h. Determine the
net power out put of the plant and the thermal efficiency of the plant.
(4) (1) Air enters an adiabatic nozzle steadily at 300 kPa, 200oC and 30 m/s. It leaves at
100 kPa and 180 m/s. The inlet area of the nozzle is 80 cm2. Find the mass flow rate
through the nozzle, temperature at the exit of the nozzle and the area of the nozzle at its
exit.
(5)Air is heated in a circular duct by a 15 KW electric heating system placed inside the
duct. Air enters the duct at 100 kPa and 170C with a mass flow rate of 150 m3/ min. If the
heat lost from the duct to the surroundings is at a rate of 200 J/s, determine the exit
temperature of the air.
(6) Steam enters an adiabatic turbine at 10MPa and 5000C at a rate of 3 kg/s and leaves at
200kPa. If the power out put of the turbine is 2MW, determine the temperature of the
steam at the exit. Neglect the changes in kinetic and potential energy.
SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION
THERMAL ENGINEERING ME-228
TIME: - 90 MINUTES
Use constant properties of gases at 300K
QUESTION (1)
Answer the following
(a) What is the difference between work transfer and heat transfer?
(b)Classify the following processes as heat or work. Give reasons.
-Temperature rise of a gas in a cylinder when it is compressed by the
piston.
-Heating of a room when an electric iron is plugged in.
-Solar heating of a room.
-Heating of an insulated room by burning candles.
(c)Write the statement of First law of thermodynamics.
QUESTION (2)
(i)Nitrogen at an initial state of 300 K, 150 kPa and 0.2 m3 is compressed by an
adiabatic process to a final pressure of 800 kPa. Find the total work done.
(ii) Air at a flow rate of 4.2 kg/m3 leaves a diffuser that has an exit to inlet area ratio of
2:1 with a velocity of 120 m/s. It enters the diffuser with a velocity of 380 m/s find the
density of the air as it enters the diffuser.
QUESTION (3)
.
A mass of 15kg of air in a piston cylinder device is heated from 250C to 770C by passing
current through a resistance heater inside the cylinder. The pressure inside the cylinder is
kept constant at 300kPa during the process and a heat transfer of 60KJ occurs from the
device to the surroundings. Determine the electrical energy supplied.
QUESTION (4)
Liquid water at 300 kPa and 20oC enters a mixing chamber a rate of 1.8 kg/s where it is
mixed with superheated steam at 300 kPa and 300oC. If the mixture leaves the mixing
chamber at 60oC, determine the mass flow rate of the super heated steam.
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
THERMO-FLUID GROUP
SUBJECT:-THERMO FLUIDS FOR CIVIL ENGINEERING
Final Examination (IInd Semester1428)
TIME[ 08 am to 11 am]
NOTE:-1 DO ALL QUESTIONS.
2 WRITE WITH PEN ONLY AND NOT WITH PENCIL
QUESTION(1)
An air conditioning unit heats and humidifies air at 10 kPa, 200C and 50 percent relative
humidity to 350C and 60 percent relative humidity.
(i)
Find the change in wet bulb temperature of air
(ii)
Find the change in dew point temperature of air
(iii)
Find the change in specific volume of air
(iv)
Find the change in specific humidity of air
(v)
Find the change in specific enthalpy of air
(vi)
If the flow rate through the air conditioner is 75 kg/min, find the heat added.
(vii)
If the C.O.P of the air conditioner is 4.5, find the power required fot this
process
(viii)
Show the process on psychometric chart.
QUESTION (2)
A store house 10m x 10m x 5m has the roof and the floor made of such material that the
heat transfer through these is negligible. Its four wall are made of concrete
W
{k 2
} of thickness 150 mm. The wall is insulated from outside as well as
m 0 C
W
inside. The outside insulation is a plaster { k 0.03
} of thickness 30 mm
m 0 C
W
whereas the inner side insulation is a fiber glass board { k 0.035
}of thickness 5
m 0 C
mm. The outside temperature is 350C and the inside temperature is 50C. The outside and
W
W
inside heat transfer coefficients are ho 15 2 0
and hi 25 2 0 .
m C
m C
Find the total thermal resistance of the walls.
Find the rate of heat transfer to the store room.
Find the interface temperatures at all layers of a wall.
An air conditioner is used to maintain the inside temperature as 50C, and
the C.O.P of the air conditioner is 4.5, find the power consumed.
Question #1
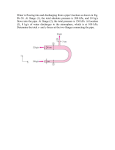
A house has a composite wall of wood, fiberglass insulation, and plaster board, as
indicated in Fig. 1. On a cold winter day the convection heat transfer coefficients are h o
= 60 W/m oC, and hi = 30 W/m2 oC. The total wall surface area is 350 m2. The thermal
conductivities of the wall are kP = 0.22 W/m oC, kb = 0.038 W/m oC, and ks = 0.12 W/ m
o
C as shown in the figure(1). Assuming heat transfer through the wall to be one
dimensional and steady and neglect the radiation heat transfer, determine:
ithe total thermal resistance of the wall, including inside and outside
convection effects for the prescribed conditions.
iithe rate of heat transfer through the wall
iiithe temperature at the interface between the plaster board and the glass fiber
blanket and also between the glass fiber blanket and the plywood siding
(assume perfect contact),
ivdraw the electrical analogy circuit of the wall,
vdraw the temperature profile through the wall.
Marks (10)
Figure (1)
SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION
THERMAL ENGINEERING ME-228
TIME: - 90 MINUTES
ASSUME THE DATA IF THE SAME IS NOT GIVEN
QUESTION (1)
(a) Write the two atatements of second law of thermodynamics.
(b) An automobile engine consumes fuel at a rate of 20Litres/hour and delivers a
power of 60 KW.The fuel has a density of 800kg/m3 and a heating value of
44,000KJ/kg. Determine the efficiency of the engine.
QUESTION (2)
(a) Write an expression for the isentropic efficeincy of a compressor in terms of
enthalpy changes. Show the actual and isentropic compression process on hs diagram.
(b) Air is compressed by an air compressor from 95 kPa and 270C to 600 kPa and
2770c.Determine the isentropic efficiency of the compressor. Take Cp=1.005KJ/kg-K,
R=0.287 KJ/kg-K.Assume no changes in kinetic and potential energy.
QUESTION (3)
(a) Write the steady flow energy equation with units as kJ/kg. What are the varoius
terms in it.
(b) Show the isentropic and actual process of expansion hs plots.
(c) Steam at 3 MPa and 4000C enters an adiabatic nozzel steadily with a velocity of
40m/s and leaves at 2.5 MPa and 300m/s. Determine exit temperature and area ratio of
the nozzel.
________________________________________