* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download thermodynamics, heat and mass transfer
Survey
Document related concepts
Solar water heating wikipedia , lookup
Radiator (engine cooling) wikipedia , lookup
Thermoregulation wikipedia , lookup
Building insulation materials wikipedia , lookup
Insulated glazing wikipedia , lookup
Heat exchanger wikipedia , lookup
Heat equation wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic insulation wikipedia , lookup
Copper in heat exchangers wikipedia , lookup
Vapor-compression refrigeration wikipedia , lookup
Cogeneration wikipedia , lookup
R-value (insulation) wikipedia , lookup
Solar air conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Thermal conduction wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthermia wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
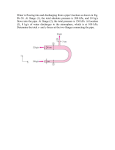
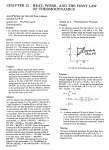
THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER TUTORIAL NO: 3 FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS (CM) 1. During the working stroke of an engine the heat transferred out of the system was 150 kJ/kg of working substance. The internal energy also decreased by 400 kJ/kg of working substance. Determine the work done and state whether it is work done on or by the engine. 2. Air in a closed vessel of fixed volume 0.14 m3 exerts a pressure of 10 bar at 2500C. If the vessel is cooled so that the pressure falls to 3.5 bar, determine the final temperature and heat transfer. 3. A storage tank contains air at the same temperature as the surroundings (350C). Suddenly it begins to rain, and the surrounding temperature drops to 200C. The tank was initially at a pressure of 200 kPa, and the tank volume is 10 m3. (a) What is the final pressure in kilopascals in the tank after the air cools in the tank to the temperature of the surroundings? (b) How much heat transfer in kilojoules occurred to or from the air during the cooling? [R = 287 J/kg K, CV = 718 J/kg K] 4. A cylinder contains 1 m3 of a gas at 100 kPa and 1000C. The gas is compressed to a volume of 0.25 m3, the final pressure being 600 kPa. Determine: (a) the mass of gas (b) the value of index n for compression (c) change in internal energy of the gas. [R = 287 J/kg K, CV = 718 J/kg K] 5. Ethane initially at 35 kPa with a volume of 0.12 m3 is compressed frictionlessly in a cylinder until its volume is halved in such a manner that its pressure and volume are linearly related, P = a + b V. The final pressure is 80 kPa, and the change in internal energy of ethane is 3.22 kJ. Determine the heat transfer. 6. Air (2 kg) is contained in a vertical frictionless piston-cylinder device shown in Figure P3.6. The mass of the piston is such that the air has a pressure and temperature of 10.0 MPa and 75.50C. There is a heat transfer to the cylinder until the piston reaches some stops, at which point the total volume is 0.04 m3. There is an additional heat transfer to the air until the pressure is 15.0 MPa. Determine the total heat transfer and the total work, and show the process on a P-v diagram. [R = 287 J/kg K, CV = 718 J/kg K] 7. Shaft work (500 kJ/kg) is transferred to the air-filled frictionless piston-cylinder device shown in Figure P3.7. Determine the heat transfer (kJ/kg). The initial and final states of the air are T1 = 2000C, P1 = 400 kPa and T2 = 2500C, respectively. [CP = 1.005 kJ/kg K] THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT & MASS TRANSFER 5 TUTORIAL NO. 3 Figure P3.6 Figure P3.7 8. 1 kg of air can be expanded between two states as it does 20 kJ of work and receives 16 kJ of heat. A second kind of expansion can be found between the same initial and final states which requires a heat input of only 9 kJ. What is the change of internal energy in the first expansion, and what is the work done by the air in the second expansion? 9. The following table gives data, in kJ, for a system undergoing a thermodynamic cycle consisting of four processes in series. For the cycle, kinetic and potential energy effects can be neglected. Determine: (a) the missing table entries, each in kJ. (b) whether the cycle is a power cycle or a refrigeration cycle. Process 1-2 2-3 3-4 4-1 U ----670 --- 360 Q ----0 ---- W - 610 230 920 0 10. A gas is held in a cylinder behind a piston undergoes a cycle composed of three process: Process 1 – 2: an adiabatic compression process. For this process W1-2 = - 58 kJ. Process 2 – 3: an expansion during which heat is added and work is done on the piston. Q2-3 = 253 kJ; and W2-3 = 95 kJ. Process 3 – 1: a cooling of the gas while the piston is stationary to bring the gas to its initial state. Determine the net heat transfer and heat transfer of process 3 – 1. ANSWER 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. – 449.8 kJ/kg 8. – 4 kJ, 13 kJ 9. 610 kJ, 0, 900 kJ, - 920 kJ, - 360 kJ 10. 37 kJ, - 216 kJ 250 kJ/kg 183 K, - 228 kJ 190.3 kPa, - 243.7 kJ 0.934 kg, 1.292, 435.54 kJ – 0.23 kJ 1201 kJ, 200 kJ THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT & MASS TRANSFER 6 TUTORIAL NO. 3