* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is an Organism??
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Taxonomy (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Simple living wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Acquired characteristic wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
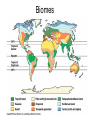
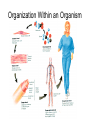
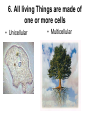
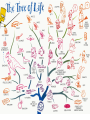
BIOLOGY • BIO = Latin for “LIFE” OLOGY = From the latin word LOGOS meaning the “STUDY OF” Section 2.1 5 Levels of Organization Biosphere Ecosystems Communities Populations Organism BIOSPHERE Biomes ECOSYSTEMS Communities Populations Section 2.1 What is an Organism?? Organization Within an Organism 6 CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Living things must possess all these characteristics in order to be considered alive 1. Organisms Use Energy • Every organism uses energy in a process called Metabolism – All the chemical reactions that take place inside an organism. Autotrophs Heterotrophs 2. Every living thing Responds to stimuli • Changes happen inside and outside of an organism and an organism needs to respond appropriately to stay alive. 3. LIFE IS ORGANIZED • We say that life struggles to keep things organized. Living things must use energy to stay organized • The natural tendency in nature is to become less organized. This is why dead things decompose 4. Living things GROW and DEVELOP • Growth involves adding more cells • Development involves changes in cell’s structure and function 5. Living Things Reproduce • The Individual doesn’t need it to survive • Species need reproduction to avoid extinction. – There are lots of ways to do it – Sexual vs. Asexual. What does the prefix mean? • Gene: short segment of DNA that contains instructions for a single trait. 6. All living Things are made of one or more cells • Unicellular • Multicellular Themes of Biology • Themes are very broad concepts that connect the enormous variety of life. • They are ways in which we study life (biology) 1.Diversity & Unity of Life • Diversity: There’re lots of different organisms in the world. • Unity: All of these different organisms have certain things in common – All have the Characteristics of Life – All have a genetic code These relationships can be shown with a “tree of life” model. Three Domains of Classification • 3 Categories of all living things – 1. Eubacteria – 2. Archae (2 forms of Bacteria) – 3. Eukarya (all living things besides bacteria belong to this group) • Another way to categorize living things is the “Kingdom” system –6 Kingdoms – Animalia – Plantae – Fungi – Protista – Monera – Archaea 2. Interdependence • Organisms & their environment interact • Ecology studies this • Ecosystems are communities of living things and their environments • Humans really interact with the environment 3.Evolution of Life • Changes can occur in a species over generations • New species can arise from drastic changes in a population of a species. • This explains the branches of the tree of life 4. Genetics • A species passes on traits from one generation to the next. 5. Homeostasis • All living things must have a way to maintain stable internal conditions. 6. Cellular Structure & Function • The cell is the basic unit of all life • The cell is the smallest structure considered living. • All cells come from pre-existing cells.