* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of Flowers Test Review 2014 Answer Key
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
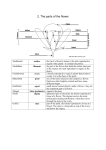
Parts of Flowers Test Review Name______TEACHER_______________________________________ Directions: Answer the following questions in the space provided on the right. 1) The structures that make up that outside of the flower and may be colored or contain nectar or perfume glands are _________. 1) Petals 2) ______ are flowering plants. 2) Angiosperms 3) The ______ is the part of the pistil that receives the pollen. 3) Stigma 4) One adaptation a cactus has to survive in the desert is it has _____ instead of leaves. 4) Needles 5) Narrow leaves on grasses that grow in the prairie minimize 5) Water _______ loss. 6) The female reproductive cells in a flowering plant are called _______ , or eggs. 6) Ovules 7) Some tropical plants have ______ to support them in the shallow soil. 7) Props 8) A _____ is the stalk that supports the anther. 8) Filament 9) Mosses and ferns, also known as epiphytes, live and grow on the top of other plants in order to receive _____. 9) Sunlight 10) The _____ is the female reproductive organ of the flower. It is made of the stigma, style and ovary. 10) Pistil 11) Many trees in the temperate deciduous forest have thick _____ to protect itself from the cold winters. 11) Bark 12) _____ occurs when the pollen unites with the ovules. 12) Fertilization 13) _____ on evergreen trees in the taiga help reduce water loss and aid in the shedding of snow. 13) Needles 14) The _____ connects the stigma to the ovary. 14) Style 15) Some plants in the taiga grow in clumps to conserve _____. 15) Heat 16) The male reproductive organ of the flower is the ______. 16) Stamen 17) The _____ is the part of the stamen where pollen develops. 17) Anther 18) The male reproductive cells in a flowering plant are the ______. 18) Pollen 19) Once pollination has occurred, the ovules become ______. 19) Seeds 20) Once a seed in formed in the ovary, the ovary changes into 20) Fruit ______. It will protect the seed until it is ripe, then aid in seed dispersal. 21) The ______ is the place where the flower and the stem meet. 21) ******* 22) _______ are special features that allow a plant or animal to 22) Adaptations live in a particular place or habitat. 23) When a seed does not germinate immediately after leaving 23) Dormancy the parent plant, it goes into a period of ______, or inactivity. 24) In order for a seed to come out of this dormancy state, 24) Moisture, Heat, Light, Fire conditions have to be ideal. Ideal conditions depend of the seed type but they include factors like ______, _______, and ______. 25) _______ means bending toward or away from a stimulus. 25) Tropism 26) _____ is a plant’s response to water. 26) Hydrotropism 27) _______ is a plant’s response to gravity. 27) Geotropism/Gravitropism 28) ______ is a plant’s response to light. 28) Phototropism