* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answers to Biological Inquiry Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
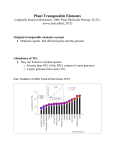
Answers to Biological Inquiry Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site Chapter 21 Figure 21.2 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: What are two reasons why the groups of species shown in (a) have variation in their total amount of DNA? ANSWER: One reason is that more complex species tend to have more genes. A second reason is that species vary with regard to the amount of repetitive DNA that is found in their genome. Figure 21.6 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: Based on their mechanism of movement, which type of TEs do you think would proliferate more rapidly in a genome, simple TEs (see Figure 21.5b) or retroelements? ANSWER: Retroelements. A single element can be transcribed into multiple copies of RNA, which can be converted to DNA by reverse transcriptase, and inserted into multiple sites in the genome. Figure 21.8 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: What is the advantage of a gene family? ANSWER: The overall advantage is specialization. When multiple copies of a gene are found in the genome, each copy can become specialized to suit the needs of particular cell types or particular stages of development. Figure 21.9 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: What genetic process explains the differences in protein abundance in liver cells versus muscle cells? ANSWER: Gene regulation. Genes that encode metabolic enzymes are highly expressed in liver cells, while those same genes are expressed in lower amounts in muscle cells. Conversely, genes that encode cytoskeletal and motor proteins are highly expressed in muscle cells, but less so in liver cells.