* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Science 10 Enriched
Survey
Document related concepts
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
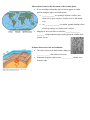
Science 10 E 12.1 EVIDENCE FOR CONTINENTAL DRIFT Name: Date: Block: (Reference: pp. 506 - 517 of BC Science 10) • Early maps of the world caused Wegener, in the early 20th century, to propose the continental drift theory. the theory that ____________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ THE MAIN EVIDENCE SUPPORTING THE CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY Wegener based his conclusions on three main pieces of evidence: 1. THE JIGSAW PUZZLE FIT _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uGcDed4xVD4 The original supercontinent was named _______ by Wegener. pan means all and gaea means Earth 2. MATCHING GEOLOGICAL STRUCTURES AND ROCKS __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. FOSSIL EVIDENCE __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Examples: ________________fossils, a small fresh water reptile, are found only in southeastern South America and southwestern Africa. Land dwelling ________________ and _______________fossils have been found on the different continents in the southern hemisphere. _______________ fossils, a fern, are found from South America and Africa to Australia, India and Antarctica. CLIMATE EVIDENCE FOR CONTINENTAL DRIFT Work by many scientists added support to the evidence for continental drift that Wegener had collected. Evidence of ___________ in parts of the world that are now tropical, such as parts of India and Africa. Paleoglaciation: ____________________ _________________________________ ______ ___________, which form from the decomposition of living things (usually tropical swamp material), in Antarctica . HOW CAN CONTINENTS MOVE? • Wegener’s evidence for continental drift did not explain how entire continents could change locations. • In Wegener’s time, scientists did not know that the surface of Earth is broken into large, movable slabs of rock called __________ __________. New scientific equipment allowed scientists to measure the slow but steady drift of Earth’s tectonic plates. Observations related to the movement of the tectonic plates It was noted that earthquakes and volcanoes appear in certain patterns along the edges of tectonic plates. ______________ are openings in Earth’s surface, that, when active, spew out gases, chunks of rock, and melted rock. An ________________ is a sudden, ground-shaking release of built-up energy at or under Earth’s surface. Mapping of the ocean floor revealed the _____-__________ ________, a long mountain range running down the middle of the Atlantic Ocean. Evidence from ocean rock and sediments The rocks closest to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge were _______________ than other ocean rocks. Sediments along the ridge became _____________ farther away from the ridge. Evidence from paleomagnetism Like a bar magnet, Earth has north and south magnetic ______ and a ____________ ________. Iron and other magnetic metals in rocks also usually align with these field lines. Earth’s magnetic field is not unchanging, however. It not only changes in strength from time to time but, over thousands of years, its direction can completely reverse, a process known as _____________ __________________. scientists think that Earth’s magnetic field is produced by the motion of _______ _____ in the planet’s interior. normal polarity: when Earth’s magnetic poles are ___________ to its geographic poles, as they are now. A compass needle would point in the general direction of the geographic _______ Pole. reverse polarity: when Earth’s magnetic poles reverse so that they are ____________ to Earth’s geographic poles. A compass needle would point in the general direction of the geographic ________ Pole. Paleomagnetism: _________________________ _________________________________________ rocks along the ridges show a pattern of stripes in the direction that iron-based minerals are pointing on the sea floor. The pattern, called ___________ ___________, occurs on both sides of the ridge and corresponds with reversing magnetic fields SEA FLOOR SPREADING: AN EXPLANATION • Hess suggested that magma rose to form new rock at certain places. Magma: ____________________________________ Like other fluids, it rises and falls due to ____________ differences (convection). The convection currents of magma formed a ______________ ___________where they broke through Earth’s crust. sea floor spreading: ___________________________ ___________________________________________ Like a “new crust” conveyer belt Magnetic striping of basalt rock shows long stripes of new rock moving away from ocean ridges and also reveals the direction of Earth’s magnetic field at that time. • Wilson combined the concepts of sea floor spreading and paleomagnetism to explain continental drift. He suggested that chains of volcanic islands, such as the ______________ ____________, were formed when a tectonic plate passed over a stationary _____ ______. hot spot: ______________________________ ______________________________________ He thought that continents must break up at certain areas, move across Earth’s surface, and then rejoin. This explained the formation of ____________ and _______ _______ and the cause of _______________ and ___________ eruptions. This also gave a reason for the movement of ___________ ________ and helped explain the transformation of rocks from one type to another in the rock cycle. • Later named the ________ _________ _________, the unifying theory of geology.