* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Overview – History and Structure
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
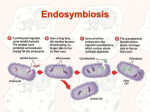
Cell Overview – History and Structure “A View of the Cell” Cytology: the study of cells Histologist: studies cells Organization - Atom - Molecule - __________________ - __________________ - Tissue - Organs - Systems - Organisms Important Figures in the Discovery of Cells 1. Anton van Leeuwenhoek (leave-in-hook) * Mid-1600s - Holland * Used hand lens microscope to observe pond water * Observed microscopic life 2. Robert Hooke * Mid-1600s - England * Used microscope to observe living tissues * Named chambers “_________” 3. German Cell Biologists a. Matthias Schleiden - Concluded that all _______ are made up of cells. b. Theodor Schwann - Concluded that all _____________ are made up of cells. 4. Rudolph Virchow * 1855 - Germany * New cells can only be produced from ____________ cells, confirmed by French scientist Louis Pasteur. 5. Watson and Crick * 1953 Watson & Crick proposed that ______ is composed of two strands of nucleotides held together by nitrogenous bases in the form of a _______________ __________. Cell Theory 1) All organisms are composed of one or more __________ 2) The cell is the basic unit of structure and functions of living things 3) All cells come from ________________ cells To Be a Cell - __________________: cell membrane, made of 2 layers of phospholipids - __________________: carbohydrate and water based solution that suspends all internal parts of the cell - __________________: produces proteins - _______: genetic material made of nucleic acids Two Types of Cells 1. Prokaryote: bacteria, archaebacteria 2. Eukaryote: protist, fungus, plant, animal Prokaryote - No nucleus - No organelles - Small - Simple - Plasma membrane, ribosome, cytoplasm, DNA - Typically unicellular - Ex. Archaebacteria Eukaryote - complex - contains 4 basic components plus organells. - multi-cellular organisms - many variations - organelles: small compartments that carry out specialized functions within a cell. Plasma Membrane - A flexible boundary between the cell and its environment maintains a balance of nutrients, etc - Selective permeability - A process in which a membrane allows some molecules to pass through while keeping others out Structure of Plasma Membrane A. Phospholipids o A double layer that creates water-soluble outsides surrounding water insoluble insides B. Transport Proteins o Span the entire membrane to regulate which molecules enter and which leave Major Organells - Nucleus – both plant and animal - Chloroplast - plants - Mitochondria – plant and animal - Centrioles - animal **Don’t forget the importance of the plasma membrane! - Organelles are membrane bound structures with particular (specialized) functions within eukaryote cells. 1. Nucleus = cell control! - Chromatin - Strands of genetic material (____) that contains the directions for making proteins. Forms chromosomes - Nucleolus, Nuclear Pores, and Nuclear Envelope - A prominent body within the nucleus, which makes the ribosomes 2. Chloroplast - Containing the green pigment, chlorophyll, these oval bodies capture light _________ and turn it into chemical __________ (____________________). 3. Mitochondria - Rod-shaped organelle with many inner folds, which breaks down sugar to release its stored _______________ for cell use (______ ______________) 4. Centrioles - Pairs of microtubles that plays an important role in cell division. Plant and Animal Cell Similarities - Cell membrane that surrounds the cell - Cytoplasm - Nucleus that houses DNA - Ribosomes for protein production - Mitochondria that breaks down food and creates energy for the cell. - Vacuoles for storage of food, water, and waste. Although plants have one large vacuoles compared to animals many small vacuoles. Plant and Animal Cell Differences - Plants contain a cell wall that surrounds the cell membrane and provides shape and support. - Plants contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis - Plant cells have a brick-like shape where as animal cells are more cylindrical. - Plants use chloroplasts to store energy in sugar; animal cells use mitochondria to release energy stored in food. Plants contain a cell wall that surrounds the cell membrane and provides shape and support. - Plants contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis - Plant cells have a brick-like shape where as animal cells are more cylindrical. - Plants use chloroplasts to store energy in sugar; animal cells use mitochondria to release energy stored in food. Endosymbiotic Theory Scientific explanation: - Origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts Endosymbiotic bacteria – bacteria that live within other cells and perform specific functions for host cells Endosymbiotic Theory – suggests critical stage in evolution of eukaryotic cells involved endosymbiotic relationships with prokaryotes Energy-producing bacteria reside in larger bacteria, eventually evolving into mitochondria Photosynthetic bacteria live within larger bacteria, leading to evolution of chloroplasts Support for endosymbiotic theory - Presence of numerous symbiotic relationships - Present-day mitochondria, chloroplasts, and centrioles contain their own DNA Similar to DNA of bacteria in size and character