* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download key stage 2 year group : t - Aldingbourne Primary School
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
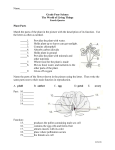
KEY STAGE 2 YEAR GROUP : 3 /4 TERM : SUMMER CYCLE B THEME : LIFE CYCLES KEY VOCABULARY : habitat, environment, features, identify, producers, consumers, food chains, keys, relationships, Expressions : making generalisations and comparisons LEARNING GOALS ACTIVITIES TIME ALLOCATION To identify and assign locally Collect plants from the school grounds. Observe features. 2 ½ hours occurring plants to groups Show children a simple key and how to use it using a key Introduce Venn diagrams as a way of organising the information Ask children to locate data and answers questions about information in Venn diagrams and keys To know that a plant has Discuss the fact that plants are grown for food and look at some examples of 2 hours different parts which are all vegetables to show the importance of plants that have been grown well. ( + 4 weeks of necessary for it to grow well Revise parts of a plant and what each part is for. observations) To make careful observations Investigate the growth of a plant with no leaves ( use 2 plants and remove and measurements of plants leaves from one ) by measuring plants at intervals over a period of weeks. growing Describe differences in how the plants grew – relate to function of leaves. To use results to draw conclusions To know that water is taken Use celery to and water containing dye to show movement of water. 1 hour in through the roots and transported to other parts of the plant via the stem To know that plants need Investigate growing a seedling using different amounts of watering. 2 hours water for growth – but not an ( + 2 weeks of unlimited amount observations ) To make accurate measurements To know that plants need Show children a plant that has been grown in the dark or some grass that has 1 hour light for healthy growth been covered. Ask children to suggest investigations to show that plants grow well in the Varies light. To know that flowering plants Revise the fact that plants have fruits and seeds which will produce new 1 ½ hours reproduce To know that seeds can be dispersed in a variety of ways To consider conditions that might affect germination and plan how to test them To make careful observations and comparisons and use them to draw conclusions To know that insects pollinate flowers To know the male and female parts of a flower and that the seeds of a plant are formed after pollination takes place. plants. Draw examples. Look at a selection of fruits with seeds eg. apple, tomato, cherry, strawberry; and some seed cases such as wheat, poppy, dandelion, ash. Make drawings. Talk about the different ways that seeds are dispersed. Try growing some unusual seeds eg avocado, maize ( sweetcorn ) Ask children what seeds need in order to germinate and how they could investigate this. Ensure a valid test is set up – varying one factor and using sufficient seeds. Discuss and evaluate results Explain the role of insects in pollination, using examples of flowers that attract bees and other insects. Use school grounds to observe this if possible. Dissect flowers to see stigma, stamen and style. Look at pollen grains from different plants. Label drawings and learn names of parts. INVESTIGATION Are plants able to grow without soil? Do all plants have leaves ? All plants absorb the same amount of water – investigate. Do plants grow best in the dark ? USEFUL DOCUMENTS : 2 hours 2 hours (+ 2 weeks of observations ) 1 ½ hours 2 hours