* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10 Day Lesson Plan - Joseph L. Anderson
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
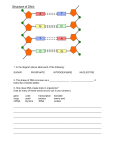
7th Grade Life Science Hampton Cove Middle School Ed-497 Chapter 5 DNA Lesson 1 J Anderson Standards: Alabama COS Standard 7th Grade Science: 10.) Identify differences between deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA-double helix, contains thymine; RNA-single stranded, contains uracil Identifying Watson and Crick as scientists who discovered the shape of the DNA molecule Questions: What is DNA? How does it work? Why does it matter? Objectives: Students will identify what forms the genetic code. Students will understand the replication of DNA. Students will understand the role of Watson and Crick in relation to the structure of DNA Vocabulary: Deoxyribonucleic Acid, DNA Replication Nitrogen Bases Transfer RNA Mutation Cancer Lesson Segments Segment 1: The Genetic Code (Day 1) Engage (15 min) Activation of Prior Knowledge Have students recall what DNA means Discuss the cell and the role of mtDNA in cellular reproduction How does DNA relate to genes? Read DNA Debut from Pearson Online Explore (15 min) What is a code? Have students complete the Roman Code Worksheet Explain (20 min) What Forms the Genetic Code? DNA has the genetic code It is present in the cell nucleus It is found in chromosomes Made of double helix structure (Spiral Staircase) 4 Bases, o Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine Side Structure o Deoxyribose (Sugar) o Phosphate Note that Bases form in pairs Adenine to Thymine Guanine to Cytosine Genes are a specific code sequence The order of nitrogen bases in a gene is the code to make a specific protein Segment 1: The Genetic Code (Day 2) Elaborate (40 min) What happened to the Romanovs? Have students read: Identifying the Tsar and His Family Have students complete Genetic Investigation Evaluate (10 min) Quiz: The Genetic Code Student will complete a quiz on the genetic code Students will grade their own papers Segment 2: DNA Replication (Day 3) Explain (15 min) Nitrogen Bases Students will be introduced to the concept of Nitrogen Base pair replication Adenine pairs with Thymine and Guanine pairs with Cytocine Using visuals (ppt or Pearson) teach the structure of DNA Deoxyribose sugar molecule, Phosphate molecule, and attached Bases DNA replication takes place in the cell nucleus The DNA molecule unwinds and separates allowing for bases to pair up with the DNA Two new identical DNA strands now exist. Elaborate (15 min) Cell Cycle Review 1. Interphase DNA replication 2. Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase 3. Cytokinesis Telophase Discussion about DNA replication use Pearson online text Evaluate (30 min) Students to complete DNA graphic activity worksheet Segment 3 DNA Modeling Laboratory (Day 4) Engage (50 min) Students will construct a 3 dimensional model of DNA Students will work in groups of 3 Students will complete a lab foldout to be put into lab note books Segment 4 (Day 5) Elaborate (50 min) Film: Cracking the Genetic Code Nova film on the human genome project Breaking the Roman Code During the Roman Empire Caesar would send secret messages using codes that were deciphered with a codex (Book) that held the key. Use the key below to decipher the message. ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ Z Y X WVU T S RQ P O N M L K J I HG F E D C BA GSRH CLWV RH MLG GSZG SZIW GL XIZXP _____ _____ __ ____ ______ ____ __ _____ Try cracking the following code! DSZTRHWRUUVIVGMZYLFGGSRHLXWV _______________________________________________ 1. Did the lack of spaces make cracking the code difficult? _______________________________________________ 2. How difficult would decoding be if there was missing or miss placed letters? _______________________________________________ 3. In What ways do you think that codes may relate to DNA? _______________________________________________ Identifying a Tsar and His Family Tsar Nicholas II of Russia Tsar Nicholas the II was Tsar (King) of Russia in the early 19th century. After World War I, The political stability of Russia was in an uproar. During this political unrest the King and his family disappeared and it has been a mystery for years as to their fate. What really happened to the Romanov’s? It was determined that the newly established soviet had taken the Romanov’s and executed them and the bodies of the Romanov’s were never found. In the late 1990’s a mass grave was discovered by a Russian forensic investigator. This investigator and top genetic scientists from Russia and elsewhere began the task of identifying all of the remains. The Forensic team began their investigation by extracting the mtDNA (mitochondrial DNA) from the bones. Because Tsar Nicholas was related the Royal family of Britain through Queen Victoria DNA from Prince Charles was used to compare with that of the mass grave. mtDNA is found as a result of the female relative in descendants. So both Prince Charles and Tsar Nicholas would have mtDNA from Queen Victoria. Other investigations were conducted after to verify the scientist’s findings. At the time if the first investigation the grave of Tsar Nicholas’ brother had not been identified; however, since then, the grave of the Tsar’s brother was found and their DNA was compared giving positive proof that the remains found were that of the Tsar himself. Mitochondrial DNA Resource: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nicholas_II_of_Russia Resource: http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/chromosome/MT Genetic Investigation: the Romanov/Wessex Analysis The following is a code from the mtDNA of Queen Victoria of England that was extracted from Prince Charles. Compare this mtDNA to that of the bodies found in the mass grave in the Ural region of Russia. QV/PC: AGCTAACTCTGGATAT Try to find Tsar Nicholas by matching the six Base code TCTGGA. The mitochondrial DNA of the mother will be present in both the sons and daughters of Nicholas and Alexandra but only the mitochondrial DNA of Queen Victoria will be in Tsar Nicholas. Some traits are passed by skipping generations. Match/Partial/None Body 1: TTAGGACTCGCCGTA _______________________ Body 2: TTAGAAGCCGCCAGA _______________________ Body 3: AGCTAGGCCGATCTG _______________________ Body 4: GATGCTTCTGGATTAG _______________________ Body 5: GCCGTTGAAGTCGTAC _______________________ Body 6 TTAGGAGACAGCCGAG _______________________ Body 7 TTGCCGTAGAGCAGTC _______________________ Which body is Tsar Nicholas? _________________________________ Can you identify the wife and children by comparing the codes of the other bodies? ___________________________________________________________ Chapter 5 DNA Explore Worksheet DNA Replication Name ________________ How does DNA replicate in the cell? We will explore this process during this activity. As DNA prepares to replicate the double helix begins to unwind much like the diagram below. As it unwinds new deoxyribose phosphate groups begin to form with the proper matching nitrogen bases. Complete the DNA segment replication below and answer the questions D-Ribose = Deoxyribose (orange) P = Phosphate (purple) D-Ribose P hydrogen bond A = Adenine (Red), C = Cytosine (green), G = Guanine (blue), T = Thymine (yellow) Color code your bases and side 1. When DNA replicates, how many DNA molecules result in the process? 2. The nitrogen bases always pair in certain ways, why is this important? 3. Where does this replication take place? 4. What are the sides of the DNA molecule made from? 5. What kind of bond keeps the DNA nitrogen bases together? Laboratory: DNA Model Name _________________ In this exercise you will create a three dimensional model of Deoxyribonucleic Acid or DNA. You will use various model pieces that represent the components of the double helix and the nitrogen bases that form the molecule Kit parts 10 red (Phosphate molecules) 12 black (Deoxyribose molecules) 20 yellow tubes (bonds) 6 white (hydrogen bonds) 3 red tubes (Adenine) 3 blue tubes (Thymine) 3 green tubes (Guanine) 3 grey tubes (Cytosine) 1 black 4 prong stand 1 long grey tube Construct one side of the DNA 1. Connect 1 phosphate molecule to a deoxyrobose molecule using the yellow tubes. Continue constructing by alternating phosphate and deoxyribose so there are 6 deoxyrobise and 5 phosphates. 2. Complete the other side of the DNA using the same procedure. 3. Add the nitrogen bases to the sides pairing blue and red with a white hydrogen bond in between and green and grey with a white hydrogen bond in between. 4. Now connect the long grey tube to the stand and slip the tube through the hydrogen bonds. As you do this the model will begin to curl into the shape of the double helix. 5. In your notebooks, answer the following questions. What is the shape of the DNA molecule? What forms the side structure of DNA? Draw the DNA molecule in your note book and label each component. Can you imagine how DNA unwinds and separates to replicate itself? Describe the process of replication in your notebook. Quiz: DNA, The Genetic Code Name________________________ 1. Chromosomes contain Genes that are coded in the ________ molecule. 2. Gene codes determine which specific ________ that are made. 3. The series patterns of Nitrogen Bases make up the __________. 4. Adenine pairs of matches with ___________. 5. Guanine matches with ____________. 6. ______________ and ___________ make up the sides of DNA. 7. DNA is formed as a __________ _________ which is like a spiral staircase. 8. Genes can be made up of hundreds to millions of _________. 9. The length of a DNA that codes for a specific protein is called a _________. 10. Cytosine always pairs with ________, and Thymine always pairs with _______. Word Bank: Adenine, Bases, Code, Cytosine, DNA, Double Helix, Gene, Guanine, Proteins, Thymine, Quiz: DNA, The Genetic Code Name________________________ Key 1. Chromosomes contain Genes that are coded in the DNA molecule. 2. Gene codes determine which specific Proteins that are made. 3. The series patterns of Nitrogen Bases make up the Genetic Code. 4. Adenine pairs of matches with Thymine. 5. Guanine matches with Cytosine. 6. Sugar and phosphate make up the sides of DNA. 7. DNA is formed as a Double Helix which is like a spiral staircase. 8. Genes can be made up of hundreds to millions of Nitrogen Bases. 9. The length of a DNA that codes for a specific protein is called a Gene. 10. Cytosine always pairs with Guanine, and Thymine always pairs with Adenine. Word Bank: Adenine, Bases, Code, Cytosine, DNA, Double Helix, Gene, Guanine, Proteins, Thymine, Quiz: DNA, The Genetic Code Name________________________ Chapter 5 Section 2 Protein Synthesis Standard: Alabama 7th Grade Science: 10.) Identify differences between deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Examples: - DNA-double helix, contains thymine; - RNA-single stranded, contains uracil Objectives: How Do Cells Make Proteins? Lesson 1 (Day 1) Bell Ringer (5 Min) Before Activity Quick Write: Predict the difference between DNA and RNA (Pretest) (Honors Students write a paragraph) (Regular Students write a sentence) (Inclusion Oral discussion with cues) Engage (10 Min) Have Students Read Dinosaur Chicken. ( 5th Hour Read to students) Explain (30 Min) Students read fact sheet on RNA (5th hour Read fact sheet to students) Students to read Pearson Text online or in book section 5.2 (5th Hour Students best readers) (ELL Student additional help with words) Evaluate (10 Min) After Activity RNA Jeopardy (Honors& Regular) (Oral review for 5th hour students) Quiz: DNA, The Genetic Code Name________________________ Home Work Assignment Pearson HW Chapter 5 Elaborate activity Lesson 2 (Day 2) Explain (10 Min) Review Pearson Elaborate with Students Read section on Pearson Text if no internet (Additional help for 5th Hour as needed) Explore (45 Min) Lab Activity (Protein Synthesis) Explain group responsibilities and activities 6 Groups 5 each (adjust group size for smaller classes) Assist Inclusion and ELL learners as needed (Collaborative Assistant) See Lab Handouts DNA Laboratory Day 3 Explore (55 Min) DNA extractions lab Homework Assignment: 4 questions from lab sheet What is DNA? How was DNA extracted from the Strawberries? What did the DNA look like? How was DNA preserved? Graphic Organizer (3 versions for Honors, Regular and Inclusion classes) The first section will be given to each class as an example. Honors will generate their own headings and subtitles while regular classes will be given the headings Quiz: DNA, The Genetic Code Name________________________ in each section. The inclusion class will be taken through the entire graphic in class using the text as a reference. Alternative Assessment Day 4 Bell Ringer (10 Min) Before Activity Quick Write: Describe Protein Synthesis (Honors write a paragraph using graphic organizer) (Regular, write a paragraph using graphic organizer) (Inclusion, write a sentence using text and paraphrasing) Rubric (10 Min) Honors: Cover rubric criteria for protein synthesis poster Regular: Cover instructional rubric for protein synthesis paper Inclusion: Cover instructional rubric for protein synthesis paper (Using text as resource) Research Activity (30 min) Honors: Use internet access to find two sources for poster and take notes. Start poster working in groups of 2 – 3 some students working alone. Regular: Use Internet to find sources for paper and take notes. Start paper using Microsoft Word Times New Roman or Arial font size 12 with Name and period in header. Practice Quiz (5 min) Assign Practice quiz as homework Quiz: DNA, The Genetic Code Name________________________ Formative Assessment 5.2 (Day 5) Review Practice Quiz (10 min) Quiz (15 min) Assign appropriate quiz for honors regular and inclusion classes Trade papers and grade Project work (15 min) Pass out study guide for test (Homework for next day) Vocabulary Bingo/Jeopardy (15 min) Given definitions students fill in blanks with term or answer with a question. i.e. Contains all the genes necessary for life. What is DNA? Assessment work (Day 6) Review Study Guide (20 min) Review in class Project work (35 min) Collect project/papers from band members (test on Monday next) Vocabulary Test Test (10 min) Project Presentations (45 min) students will evaluate collaborative peers Papers Students will turn in there papers to website Begin Chapter 6 if time allows Chapter 5 Test Test (30 min) Begin Chapter 6 RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) Fact Sheet __________________________________________________________ In the last few days we have explored the fundamental workings of the DNA molecule. We have talked of Replication and Protein Synthesis. But what does it all mean and why RNA? During cell reproduction we have found that the DNA unwinds and separates. It has also been learned that two identical DNA strands are formed for each daughter cell to have all the information it needs to carry out cell functions. RNA plays a critical role in protein production. Before we examine the process further, we must know the fundamental difference between DNA and RNA. RNA does not have two sides as DNA. There is a slight difference in the sugar phosphate structure. RNA has one base that is different than DNA. This base replaces thymine and is called uracil. RNA also comes in two different types, messenger and transfer. Messenger RNA is made in the cell nucleus as a polymerase unwinds and copies a specific gene on a DNA molecule. Free Nucleotides attach in the process creating the RNA molecule which is then sent from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm for protein Synthesis. It is in the cytoplasm that the Ribosome begins the process of protein production using transfer RNA to code for Amino Acids. There are twenty possible Amino Acid combinations. There are more possibilities than Amino Acids to the three base sequences. Some combinations may code for the same amino acid or some codes may mean begin or stop the sequence. By: J Anderson Resources for images are in creative commons licensure. Text facts are from Wikipedia and Pearson text. Protein Synthesis (LAB) In this activity each lab group will act as a portion of the process by which RNA is made Group 1 (DNA polymerase) Sends instructions for DNA to unwind at a gene location and copies the gene to mRNA using nucleotides from Group 3 Group 2 (DNA) Receives instruction to unwind and provides the gene code for Group 1 to copy Group 3 (Nucleus) Provides nucleotides to Group 1 for construction of mRNA Group 4 (Cytoplasm) Contains the building blocks for tRNA and instructs the ribosome to read the mRNA code from Group 1 and build proteins. Group 5 (Ribosome) Reads mRNA and requests tRNA from the cytoplasm for protein synthesis. Conducts Protein synthesis and releases the protein upon a stop command Group 6 (Protein Chain) Receives Amino Acids from the Ribosome to construct a protein There will be five members per group. Each group will work as a team to follow instructions for the production of a protein. Protein Synthesis (LAB) Group 1 (Polymerase) Instructions Sends instructions for Group 2 DNA to unwind at a gene location and copies the gene to mRNA using nucleotides from Group 3 1. Select 1 person to direct this activity who will be group member 1. 2. Send a group member 2 to group 1 and ask the DNA to unwind and read a gene sequence 1A1, return to group 1. 3. Wait for group 2 to report that the gene on the DNA is ready to copy. 4. Send group member 3 to request nucleotides for mRNA construction from group 3 and return to group. 5. Wait for group 3 to send word that nucleotides are available for the process 6. Send group member 4 to group 2 and ask for the DNA gene sequence and return to group 1. 7. Wait for the DNA sequence. 8. Send group member 5 to group 3 to request the specified nucleotides, return to group 1. 9. Construct the mRNA sequence and send the mRNA to group 4 via group member 1, return to group 1. 10. Repeat these steps for genes 2A1, 1B1, and 2B1 Glue or tape nucleotides together to form mRNA Protein Synthesis (LAB) Group 2 (DNA) Instructions Receives instruction to unwind and provides the gene code for Group 1 to copy 1. Select one group member to direct this activity, who will be group member 1. 2. Wait for instructions from group 1. 3. Unwind the requested gene sequence and send group member 2 to group 1 to report the sequence for the requested gene is ready to be copied, return to group 2. 4. Wait for group 1 instructions. 5. Group member 3 copies the sequence and gives to group member 4. 6. Group member 4 checks the sequence and gives to group member 5. 7. Group member 5 takes the code sequence to group 1 and gives to group 1 member 1. 8. Rewind the DNA and wait for further instructions Seq: 1A1 (TTT GTG GAA GCT TCC AAA GGT TAA AAT TAG CTT CCC ATT) Seq: 2A1 (TTG ATA GGG TTC CGT TAC GCT TCC AAA GGT TAA TCC ATC) Seq: 1B1 (TTT GTG GAA GCT TCC AAA TAC GCT TCC AAA GGT TAA ACT) Seq: 2B1 (GAA GCT TCC AAA TAC GCT TCC TAA AAT TAG TAA TCC ATC) Protein Synthesis (LAB) Group 3 (Nucleus) Instructions Provides nucleotides to Group 1 for construction of mRNA 1. Select one group member to direct this activity, who will be group member 1. 2. Wait for instructions from group 1. 3. Identify the number of nucleotides required for the specified Gene. Group members 2 through 5 report available nucleotides to group member 1 4. Group member 1 takes a message to group 1 member 1, that nucleotides are ready. Return to group 3. 5. Wait for instructions from group 1. 6. Group member 1 takes nucleotides to group 1 member 1, for mRNA construction, return to group 3 7. Wait for further instructions. 8. Provide for nucleotides to the cytoplasm group 4 as required same procedure as for group 1 9. Wait for instructions Cut nucleotides and leave a strip for group 1 or 4 to glue Protein Synthesis (LAB) Group 4 (Cytoplasm) Instructions Contains the building blocks for tRNA and instructs the ribosome to read the mRNA code from Group 1 and build proteins. 1. Select one group member to direct this activity, who will be group member 1. 2. Wait for mRNA from group 1. 3. Member 1 provide mRNA to Group 5 member 1, inform members 2 through 5 that tRNA production is to begin. Return to group 4. 4. Provide various tRNA amino acids groups upon request Note: when constructing the tRNA the code must be opposite what is listed for tRNA to match up with mRNA Protein Synthesis (LAB) Group 5 (Ribosome) Instructions Reads mRNA and requests tRNA from the cytoplasm for protein synthesis. Conducts Protein synthesis and releases the protein upon a stop command 1. Select one group member to direct this activity, who will be group member 1 2. Wait for instructions from group 4 to read mRNA and begin protein synthesis 3. Upon instructions member 2 read mRNA first code and member 3 request tRNA from group 4, return to group 5. 4. Receive tRNA and member 4 is to release Amino Acid to Group 6; member 5 return tRNA to group 4 both members return to group 5. 5. Request next tRNA sequence by repeating process 3 and 4 until a stop code 6. upon a stop code member 1 send a message to group 6 to release the protein to the teacher and return to group. 7. wait for further instructions Cut Amino Acids from tRNA Protein Synthesis (LAB) Group 6 (Protein Chain) Instructions Receives Amino Acids from the Ribosome to construct a protein and then release it upon a stop code. 1. Select one group member to direct this activity, who will be group member 1. 2. Wait for Amino Acids 3. Upon Receipt of Amino Acid member 2 begins process and passes Amino Acid through to member 5 who holds it until the next Amino Acid comes. 4. Upon receipt of next Amino Acid member 3 passes it to member 5 who connects the link. 5. Repeat these steps rotating through 2, 3, and 4 as receivers until a stop code; member 5 hands the completed protein chain to group member 1 who takes it to the teacher and then returns to the group. 6. Wait for further instructions. Staple or glue Amino Acids together. Protein Synthesis (LAB) Make 1 copy per class for group 2 Protein Synthesis (LAB) Make 1 copy per class for group 2 Protein Synthesis (LAB) Make 1 copy per class for group 2 Protein Synthesis (LAB) 2B1 Make 1 copy per class for group 2 Protein Synthesis (LAB) Make 5 copies for group 3 Protein Synthesis (LAB) Make 5 copies for group 3 Protein Synthesis (LAB) Make 5 copies for group 3 Protein Synthesis (LAB) Make 5 copies for group 3 Protein Synthesis (LAB) Make 5 copies for group 3 Protein Synthesis (LAB) Make 7 copies for group 4 Name ________________________________ Protein Synthesis ________ Period Is about … 1 2 3 4 5 6 So what? What is important to understand about this? Name ________________________________ ________ Period Protein Synthesis (Honors) Is about … The process of making proteins by reading the DNA code in the cell nucleus producing RNA and using that in the cytoplasm to make proteins with the ribosomes. 1 DNA to Unwind 2 The polymerase directs the transcription of mRNA 3 mRNA leaves the Nucleus and goes to the cytoplasm DNA unwinds at a specific gene location Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine are the same in RNA mRNA attaches to the ribosome Directed by the Polymerase molecule Thymine is replaced by Uracil Ribosome begins the process of tranlastion The mRNA code is opposite of the DNA Ribosome has entry, code, and exit areas 4 tRNA with groups of three nucleotides and an Amino acid pair in the ribosome with mRNA 5 tRNA Stop Code 6 Many ribosomes can read an mRNA at the same time creating many copies of the same protein If match tRNA moves to code area signaling the release of an Amino Acid The protein (polypeptide chain) is released to be used by the cell. Students may get more information from the internet The ribosome now moves and the next tRNA is in the entry position This process may continue for several copies of that protein. This sheet is used to organize their information for the poster. New tRNA comes in as empty tRNA goes out until a stop code occurs. So what? What is important to understand about this? Genetic codes for specific traits are passed on through DNA replication and by protein synthesis with mRNA and tRNA Name ________________________________ ________ Period Protein Synthesis Is about … mRNA is made in the nucleus. Then it is read by a ribosome in the cytoplasm where tRNA helps make proteins. 1 DNA Unzips 4 2 At a certain gene location tRNA pairs with mRNA in the ribosome. tRNA moves to position and starts an Amino Acid chain The ribosome now moves and the next tRNA joins its Amino Acid More tRNA comes in creating a long chain of Amino Acids. 5 mRNA is made in the nucleus Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine are the same in RNA Thymine is replaced by Uracil mRNA is a single strand Process continues until a stop code is read The protein (Amino Acid chain) is released 3 mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to the cytoplasm 6 mRNA joins with a ribosome. This process may continue creating several copies of the same protein. Research more information on the internet So what? What is important to understand about this? Genetic codes for specific traits are passed on through DNA replication by protein synthesis with mRNA and tRNA Practice Quiz 1. DNA must __________________ for the codes to be read and mRNA to be Made 2. RNA is different from DNA in that the _________ molecule is different and Thymine is replaced by __________. 3. The RNA nucleotides are opposite to the DNA _____________. 4. mRNA is made in the Cell __________. 5. tRNA is made in the ________________. 6. mRNA must travel to the cytoplasm and join with a ___________ to begin protein synthesis. 7. tRNA carries ________ _________ attachments to the ribosomes. 8. When the tRNA code matches the mRNA code in the ribosome a _________ is made between amino acids. 9. Once the tRNA reads a stop code the _________ chain is released to be used by the cell. 10. A Protein that is made was the result of one ________ being translated from the DNA in the nucleus. Word Bank: Cytoplasm, Gene, Link, Nucleus, Nitrogen Bases, Protein, Ribosome, Sugar, Uracil, Unzip Extra Credit: Intelligent Behavior a. What molecule performs a similar function to the ribosomes in the nucleus during mRNA translation? b. A long chain of amino acids is known as a protein, a short protein chain is known as what? c. Metacognition is the process of: d. What is effective listening? e. What is important about collaboration?: Practice Quiz KEY 1. DNA must unzip for the codes to be read and mRNA to be Made 2. RNA is different from DNA in that the sugar molecule is different and Thymine is replaced by uracil. 3. The RNA nucleotides are opposite to the DNA nitrogen bases. 4. mRNA is made in the cell nucleus. 5. tRNA is made in the cytoplasm 6. mRNA must travel to the cytoplasm and join with a ribosome to begin protein synthesis. 7. tRNA carries amino acids attachments to the ribosomes. 8. When the tRNA code matches the mRNA code in the ribosome a link is made between amino acids. 9. Once the tRNA reads a stop code the protein chain is released to be used by the cell. 10. A Protein that is made was the result of one gene being translated from the DNA in the nucleus. Word Bank: Cytoplasm, Gene, Link, Nucleus, Nitrogen Bases, Protein, Ribosome, Sugar, Uracil, Unzip Extra Credit: Intelligent Behavior a. What molecule performs a similar function to the ribosomes in the nucleus during mRNA translation? b. A long chain of amino acids is known as a protein, a short protein chain is known as what? c. Metacognition is the process of: d. What is effective listening? e. What is important about collaboration?: Practice Quiz Honors 1. DNA must __________________ for the codes to be read and ________ to be Made 2. RNA is different from DNA in that the _________ molecule is different and ________ is replaced by __________. 3. The RNA ____________ are opposite to the DNA _____________. 4. mRNA is made in the Cell __________. 5. tRNA is made in the ________________. 6. mRNA must travel to the cytoplasm and join with a ___________ to begin protein synthesis. 7. tRNA carries ________ _________ attachments to the ribosomes. 8. When the tRNA code ________ the mRNA code in the Ribosome a link is made between amino acids. 9. Once the _____ reads a stop code the _________ chain is released to be used by the cell. 10. A Polypeptide (protein) that is made was the result of one ________ being translated from the DNA in the nucleus. Word Bank: Cytoplasm, Gene, Link, Nucleus, Nucleotides, Matches, mRNA Nitrogen Bases, Polypeptide, Ribosome, Sugar, Thymine, tRNA, Uracil, Unzip Extra Credit: Intelligent Behavior a. What molecule performs a similar function to the ribosomes in the nucleus during mRNA translation? b. A long chain of amino acids is known as a protein, a short protein chain is known as what? c. Metacognition is the process of: d. What is effective listening? e. What is important about collaboration?: Practice Quiz Honors KEY 1. DNA must unzip for the codes to be read and mRNA to be Made 2. RNA is different from DNA in that the Sugar molecule is different and Thymine is replaced by Uracil. 3. The RNA Nucleotides are opposite to the DNA Nitrogen Bases. 4. mRNA is made in the cell Nucleus. 5. tRNA is made in the Cytoplasm. 6. mRNA must travel to the cytoplasm and join with a Ribosome to begin protein synthesis. 7. tRNA carries amino acid attachments to the ribosomes. 8. When the tRNA code matches the mRNA code in the Ribosome a link is made between amino acids. 9. Once the tRNA reads a stop code the polypeptide chain is released to be used by the cell. 10. A Polypeptide (protein) that is made was the result of one Gene being translated from the DNA in the nucleus. Word Bank: Cytoplasm, Gene, Link, Nucleus, Nucleotides, Matches, mRNA Nitrogen Bases, Polypeptide, Ribosome, Sugar, Thymine, tRNA, Uracil, Unzip Extra Credit: Intelligent Behavior a. What molecule performs a similar function to the ribosomes in the nucleus during mRNA translation? b. A long chain of amino acids is known as a protein, a short protein chain is known as what? c. Metacognition is the process of: d. What is effective listening? e. What is important about collaboration? Practice Quiz ELL/501/IEP 1. _____ must unwind for the codes to be read and mRNA to be Made 2. _____ is different from DNA in that the Sugar molecule is different and Thymine is replaced by Uracil. 3. The RNA nucleotides form with Uracil replacing _____________. 4. mRNA is made in the cell __________. 5. tRNA is made in the ________________. 6. mRNA must _______ to the cytoplasm and join with a ribosome to begin protein synthesis. 7. tRNA carries ________ ________ to form the protein chains. 8. When the tRNA code matches the _______ code in the ribosome a link is made between amino acids. 9. Once the tRNA reads a _____ _______ the protein chain is released to be used by the cell. 10. A Protein that is made is the result of ________ ___________. Word Bank: Cytoplasm, mRNA, Nucleus, Nitrogen Bases, Protein, Protein Synthesis, Ribosome, RNA, Stop Code, Sugar, Thymine, Travel, DNA Extra Credit a. How many types of RNA are there for protein synthesis? b. What does RNA stand for? c. What does the m stand for in mRNA? d. What does the t stand for in tRNA? Practice Quiz ELL/501/IEP 1. DNA must unwind for the codes to be read and mRNA to be Made 2. RNA is different from DNA in that the Sugar molecule is different and Thymine is replaced by Uracil. 3. The RNA nucleotides form with Uracil replacing Thymine. 4. mRNA is made in the cell Nucleus. 5. tRNA is made in the Cytoplasm. 6. mRNA must travel to the cytoplasm and join with a ribosome to begin protein synthesis. 7. tRNA carries Amino Acids to form the protein chains. 8. When the tRNA code matches the mRNA code in the ribosome a link is made between amino acids. 9. Once the tRNA reads a Stop Code the protein chain is released to be used by the cell. 10. A Protein that is made is the result of Protein Synthesis Word Bank: Cytoplasm, mRNA, Nucleus, Nitrogen Bases, Protein, Protein Synthesis, Ribosome, RNA, Stop Code, Sugar, Thymine, Travel, DNA Extra Credit e. How many types of RNA are there for protein synthesis? f. What does RNA stand for? g. What does the m stand for in mRNA? h. What does the t stand for in tRNA? 5.2 Quiz _____Period Name__________________ Q-R 1. mRNA travels from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where________ _________ occurs. 2. RNA is different from DNA in that DNA has a double helix and RNA has a single _________. 3. In the RNA copy of DNA guanine pairs with cytosine and adenine pairs with _______. 4. __________ RNA is made in the cell nucleus. 5. __________ RNA is made in the cytoplasm. 6. DNA must unwind for the gene sequence to be read and ______ to be made. 7. tRNA carries amino acid attachments to the ___________ where a polypeptide chain begins. 8. A protein that is made is the result of one gene being __________ from the DNA in the cell nucleus. 9. Once the tRNA reads a stop code the protein is __________ to be used by the cell. 10. When the tRNA code pairs with the mRNA code in the ribosome a link is made between ____________. Word Bank: Amino acids, messenger, mRNA, protein synthesis, released, ribosomes, strand, transfer, translated, thymine, uracil Extra Credit: Intelligent Behavior Thinking about how we think is a process known as what? 5.2 Quiz _____Period Name__________________ Q – R Key 1. mRNA travels from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where protein synthesis occurs. 2. RNA is different from DNA in that DNA has a double helix and RNA has a single strand. 3. In the RNA copy of DNA guanine pairs with cytosine and adenine pairs with uracil. 4. Messenger RNA is made in the cell nucleus. 5. Transfer RNA is made in the cytoplasm. 6. DNA must unwind for the gene sequence to be read and mRNA to be made. 7. tRNA carries amino acid attachments to the ribosomes where a polypeptide chain begins. 8. A protein that is made is the result of one gene being translated from the DNA in the cell nucleus. 9. Once the tRNA reads a stop code the protein is released to be used by the cell. 10. When the tRNA code pairs with the mRNA code in the ribosome a link is made between amino acids. Word Bank: Amino acids, messenger, mRNA, protein synthesis, released, ribosomes, strand, transfer, translated, thymine, uracil Extra Credit: Intelligent Behavior Thinking about how we think is a process known as what? Metacognition 5.2 Quiz _____Period Name__________________ Q-H 1. mRNA travels from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where________ _________ occurs. 2. RNA is different from DNA in that DNA has a double helix and RNA has a single _________. 3. In the RNA copy of DNA guanine pairs with cytosine and adenine pairs with _______. 4. The __________ instructs the DNA to unwind and translate ___________ into mRNA. 5. __________ RNA is made in the cytoplasm. 6. DNA must unwind for the polymerase to read the _____ sequence. 7. tRNA carries amino acid attachments to the ___________ where a polypeptide chain begins. 8. Once the ribosome senses a tRNA stop sequence the protein is __________ to be used by the cell. 9. A ____________ is the result of several amino acids that have linked in the ribosome. 10. When the tRNA code pairs with the mRNA code in the ribosome a link is made between ______ _______. Word Bank: Amino acids, gene, messenger, mRNA, nucleotides, polypeptide (Protein), polymerase, protein synthesis, released, ribosomes, strand, transfer, translated, thymine, uracil Extra Credit: Intelligent Behavior Working with peers to accomplish a task or solve a problem is known as what? 5.2 Quiz _____Period Name__________________ Q-H 1. mRNA travels from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where Protein Synthesis occurs. 2. RNA is different from DNA in that DNA has a double helix and RNA has a single strand. 3. In the RNA copy of DNA guanine pairs with cytosine and adenine pairs with uracil. 4. The polymerase instructs the DNA to unwind and translate nucleotides into mRNA. 5. Transfer RNA is made in the cytoplasm. 6. DNA must unwind for the polymerase to read the gene sequence. 7. tRNA carries amino acid attachments to the ribosome where a polypeptide chain begins. 8. Once the ribosome senses a tRNA stop sequence the protein is released to be used by the cell. 9. A Polypeptide (protein) is the result of several amino acids that have linked in the ribosome. 10. When the tRNA code pairs with the mRNA code in the ribosome a link is made between amino acids. Word Bank: Amino acids, gene, messenger, mRNA, nucleotides, polypeptide (Protein), polymerase, protein synthesis, released, ribosomes, strand, transfer, translated, thymine, uracil Extra Credit: Intelligent Behavior Working with peers to accomplish a task or solve a problem is known as what? Collaboration 5.2 Quiz _____Period Name__________________ Q-I 1. _____ must unwind for the codes to be read and mRNA to be Made 2. _____ is different from DNA in that the Sugar molecule is different and Thymine is replaced by Uracil. 3. The RNA nucleotides form with Uracil replacing _____________. 4. mRNA is made in the cell __________. 5. tRNA is made in the ________________. 6. mRNA must _______ to the cytoplasm and join with a ribosome to begin protein synthesis. 7. tRNA carries ________ ________ to form the protein chains. 8. When the tRNA code matches the _______ code in the ribosome a link is made between amino acids. 9. Once the tRNA reads a _____ _______ the protein chain is released to be used by the cell. 10. A Protein that is made is the result of ________ ___________. Word Bank: Amino Acid Cytoplasm, mRNA, Nucleus, Nitrogen Bases, Protein, Protein Synthesis, Ribosome, RNA, Stop Code, Sugar, Thymine, Travel, DNA Extra Credit: Working toward a task or goal until success is achieved is known as what intelligent behavior? 5.2 Quiz _____Period Name__________________ 1. DNA must unwind for the codes to be read and mRNA to be Made 2. RNA is different from DNA in that the Sugar molecule is different and Thymine is replaced by Uracil. 3. The RNA nucleotides form with Uracil replacing Thymine. 4. mRNA is made in the cell nucleus. 5. tRNA is made in the cytoplasm. 6. mRNA must travel to the cytoplasm and join with a ribosome to begin protein synthesis. 7. tRNA carries amino acids to form the protein chains. 8. When the tRNA code matches the mRNA code in the ribosome a link is made between amino acids. 9. Once the tRNA reads a Stop code the protein chain is released to be used by the cell. 10. A Protein that is made is the result of Protein Synthesis. Word Bank: Amino Acid Cytoplasm, mRNA, Nucleus, Nitrogen Bases, Protein, Protein Synthesis, Ribosome, RNA, Stop Code, Sugar, Thymine, Travel, DNA Extra Credit: Working toward a task or goal until success is achieved is known as what intelligent behavior? Perseverance Chapter 5 Study Guide 1. Deoxyribonucleic acid is also known as DNA 2. Rosalind Franklin used x-ray crystallography to photograph DNA 3. The Structure of DNA was found by Crick and Watson 4. The back bone or sides of DNA are made from sugar and phosphate molecules 5. The rungs or nitrogen bases are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, and Thymine 6. Nucleotides are found in the cell nucleus 7. DNA replication occurs in the cell nucleus and two new DNA molecules result 8. The two new DNA molecules then go to daughter cells in meiosis. 9. The structure of DNA is a double helix. 10. During protein synthesis DNA unwinds at a specific gene location 11. RNA translation copies the DNA code and proceeds to the cytoplasm as mRNA 12. mRNA joins with the ribosome where tRNA pairs with matching codes of mRNA to form amino acid chains. 13. Amino Acid chains are also known as polypeptide chains if they are short and proteins if they are long. 14. RNA differs from DNA in that it is a single strand, has uracil instead of thymine and has a different sugar. There are two types, messenger and transfer. 15. Protein synthesis is the process by which DNA provides information via mRNA to create a protein in the cytoplasm via tRNA and mRNA with amino acid chains. Chapter 5 Test Period _____ DNA & Protein Synthesis Name ____________________ T-H-1 1. Rosalind Franklin first photographed DNA by using … a. X-Ray Symmetry b. Crystallization c. X-Ray Crystallography d. Infrared Photography 2. The structure of DNA was determined by the biochemists… a. Pasteur and La Chatélier b. Holmes and Watson c. Watson and Crick d. Franklin and Edison 3. The structure of DNA was determined to be… a. Double Hyperbola b. Single Strand c. Double Helix d. Trigonal 4. Chemically DNA sides are made from … a. Sodium and Chromate b. Potassium and Nitrate c. Nitrogen and Oxygen d. Phosphate and Deoxyribose 5. When DNA replicates the molecule splits down the middle … a. Two identical copies that migrate to the daughter cells b. Two different copies that are part of meiosis c. No copies each goes to a daughter cell d. Two similar copies that are part of meiosis 6. The Nitrogen Bases in DNA form … a. Genes that are coded in groups of three b. Genes that are coded in groups of four c. Protein that form chains from amino acid d. Amino Acid that form from tRNA 7. The Nitrogen Bases form pairs where… a. Guanine matches Uracil and Adenine matches Thymine b. Cytosine matching Uracil and Guanine matches Thymine c. Adenine matches Thymine and Guanine matches Cytosine d. Guanine matching Cytosine and Adenine matches Uracil 8. RNA is different from DNA in that … a. It forms a single strand and contains uracil not adenine b. It forms a single strand and contains uracil not guanine c. It forms a single strand and contains uracil not cytosine d. It forms a single strand and contains uracil not thymine 9. Protein synthesis results in the formation of a. Polypeptide chains from the ribosome in the cytoplasm b. A single amino acid from tRNA in the cytoplasm c. Polymerase molecules the match with mRNA and tRNA d. Translation of DNA into mRNA in the nucleus 10. mRNA is formed from … a. the polymerase instructing the DNA to unzip at a specific gene location b. the matching of nucleotides in the cytoplasm c. the polymerase instructing the RNA to unwind in the ribosome d. Nitrogen bases that contain thymine Match the following terms with their definition 11. Deoxyribonucleic Acid a. Transfer Ribonucleic Acid 12. Polypeptide b. Messenger Ribonucleic Acid 13. Amino Acid c. The molecule that holds genes within a chromosome to form proteins 14. Polymerase d. a short chain of amino acids 15. mRNA e. The enzyme that instructs DNA to form mRNA 16. Uracil f. one of twenty, single molecule proteins 17. Ribose g. The nitrogen base found only in the mRNA and tRNA molecules 18. tRNA h. The sugar found in RNA molecules True or False 19. RNA forms a double strand before leaving the nucleus and traveling to the cytoplasm. a. True b. False 20. DNA is translated into RNA in the nucleus by the ribosome. a. True b. False Chapter 5 Test Period _____ DNA & Protein Synthesis Name ____________________ T - H – 1 Key 1. Rosalind Franklin first photographed DNA by using … a. X-Ray Symmetry b. Crystallization c. X-Ray Crystallography d. Infrared Photography 2. The structure of DNA was determined by the biochemists… a. Pasteur and La Chatélier b. Holmes and Watson c. Watson and Crick d. Franklin and Edison 3. The structure of DNA was determined to be… a. Double Hyperbola b. Single Strand c. Double Helix d. Trigonal 4. Chemically DNA sides are made from … a. Sodium and Chromate b. Potassium and Nitrate c. Nitrogen and Oxygen d. Phosphate and Deoxyribose 5. When DNA replicates the molecule splits down the middle … a. Two identical copies that migrate to the daughter cells b. Two different copies that are part of meiosis c. No copies each goes to a daughter cell d. Two similar copies that are part of meiosis 6. The Nitrogen Bases in DNA form … a. Genes that are coded in groups of three b. Genes that are coded in groups of four c. Protein that form chains from amino acid d. Amino Acid that form from tRNA 7. The Nitrogen Bases form pairs where… a. Guanine matches Uracil and Adenine matches Thymine b. Cytosine matching Uracil and Guanine matches Thymine c. Adenine matches Thymine and Guanine matches Cytosine d. Guanine matching Cytosine and Adenine matches Uracil 8. RNA is different from DNA in that … a. It forms a single strand and contains uracil not adenine b. It forms a single strand and contains uracil not guanine c. It forms a single strand and contains uracil not cytosine d. It forms a single strand and contains uracil not thymine 9. Protein synthesis results in the formation of a. Polypeptide chains from the ribosome in the cytoplasm b. A single amino acid from tRNA in the cytoplasm c. Polymerase molecules the match with mRNA and tRNA d. Translation of DNA into mRNA in the nucleus 10. mRNA is formed from … a. the polymerase instructing the DNA to unzip at a specific gene location b. the matching of nucleotides in the cytoplasm c. the polymerase instructing the RNA to unwind in the ribosome d. Nitrogen bases that contain thymine Match the following terms with their definition 11. Deoxyribonucleic Acid c a. Transfer Ribonucleic Acid 12. Polypeptide d b. Messenger Ribonucleic Acid 13. Amino Acid f c. The molecule that holds genes within a chromosome to form proteins 14. Polymerase e d. a short chain of amino acids 15. mRNA b e. The enzyme that instructs DNA to form mRNA 16. Uracil g f. one of twenty, single molecule proteins 17. Ribose h g. The nitrogen base found only in the mRNA and tRNA molecules 18. tRNA a h. The sugar found in RNA molecules True or False 19. RNA forms a double strand before leaving the nucleus and traveling to the cytoplasm. a. True b. False 20. DNA is translated into RNA in the nucleus by the ribosome. a. True b. False Chapter 5 Test Period _____ DNA & Protein Synthesis Name ____________________ T-R–1 1. Wet DNA was first photographed using X-Ray Crystallography by… a. Watson and Darwin b. Crick and Darwin c. Edison d. Franklin 2. The structure of DNA that was photograph by Rosalind Franklin was determined by… a. Pasteur and La Chatélier b. Holmes and Watson c. Watson and Crick d. Franklin and Edison 3. The structure Identified by Watson and Crick was determined to be… a. Like a funnel b. A spiral staircase c. An hour glass d. A stepping stone 4. Chemically DNA sides are made from Sugar and … a. Sodium b. Potassium c. Phosphorous d. Phosphate 5. When DNA replicates the molecule splits down the middle with … a. Two identical copies b. Two different copies c. No copies each goes to a daughter cell d. Two similar copies 6. The Nitrogen Bases in DNA form the… a. Genetic malformation b. Genetic Code c. Protein before the Nitrogen Bases separate d. Amino Acid chain 7. The Nitrogen Bases pair with Adenine matching Thymine and… a. Guanine matching Uracil b. Cytosine matching Uracil c. There is no such match d. Guanine matching Cytosine 8. RNA is different from DNA in that Thymine is replaced by… a. Guanine b. Cytosine c. Uracil d. Adenine 9. Protein synthesis results in the formation of an Amino Acid… a. Bond b. Chain c. Separation d. Translation 10. mRNA leaves the nucleus and joins with the ribosome in the … a. Cytoplasm b. Nucleus c. Golgi Apparatus d. Endoplasmic Reticulum Match the following terms with their definition 11. Deoxyribonucleic Acid a. A phosphorous based molecule in the sides of DNA 12. Amino Acid b. A sugar molecule in the sides of DNA 13. Ribosome c. The molecule that holds genes within a chromosome to form proteins 14. Cytoplasm d. Single simple proteins that form a short or long chain 15. Phosphate e. The portion of the cell outside of the nucleus 16. Uracil f. The enzyme in the cytoplasm that translates mRNA with tRNA 17. Ribose g. The nitrogen base found only in the mRNA and tRNA molecules 18. Deoxyribose h. The sugar found in RNA molecules True or False 19. Protein synthesis takes place in the nucleus only a. True b. False 20. DNA is replicated while RNA is translated a. True b. False Chapter 5 Test Period _____ DNA & Protein Synthesis Name ____________________ T - R – 1 Key 1. Wet DNA was first photographed using X-Ray Crystallography by… a. Watson and Darwin b. Crick and Darwin c. Edison d. Franklin 2. The structure of DNA that was photograph by Rosalind Franklin was determined by… a. Pasteur and La Chatélier b. Holmes and Watson c. Watson and Crick d. Franklin and Edison 3. The structure Identified by Watson and Crick was determined to be… a. Like a funnel b. A spiral staircase c. An hour glass d. A stepping stone 4. Chemically DNA sides are made from Sugar and … a. Sodium b. Potassium c. Phosphorous d. Phosphate 5. When DNA replicates the molecule splits down the middle with … a. Two identical copies b. Two different copies c. No copies each goes to a daughter cell d. Two similar copies 6. The Nitrogen Bases in DNA form the… a. Genetic malformation b. Genetic Code c. Protein before the Nitrogen Bases separate d. Amino Acid chain 7. The Nitrogen Bases pair with Adenine matching Thymine and… a. Guanine matching Uracil b. Cytosine matching Uracil c. There is no such match d. Guanine matching Cytosine 8. RNA is different from DNA in that Thymine is replaced by… a. Guanine b. Cytosine c. Uracil d. Adenine 9. Protein synthesis results in the formation of an Amino Acid… a. Bond b. Chain c. Separation d. Translation 10. mRNA leaves the nucleus and joins with the ribosome in the … a. Cytoplasm b. Nucleus c. Golgi Apparatus d. Endoplasmic Reticulum Match the following terms with their definition 11. Deoxyribonucleic Acid c a. A phosphorous based molecule in the sides of DNA 12. Amino Acid d b. A sugar molecule in the sides of DNA 13. Ribosome f c. The molecule that holds genes within a chromosome to form proteins 14. Cytoplasm e d. Single simple proteins that form a short or long chain 15. Phosphate a e. The portion of the cell outside of the nucleus 16. Uracil g f. The enzyme in the cytoplasm that translates mRNA with tRNA 17. Ribose h g. The nitrogen base found only in the mRNA and tRNA molecules 18. Deoxyribose b h. The sugar found in RNA molecules True or False 19. Protein synthesis takes place in the nucleus only a. True b. False 20. DNA is replicated while RNA is translated a. True b. False Chapter 5 Test Period _____ DNA & Protein Synthesis Name ____________________ T–I–1 1. The structure of DNA was determined by… a. Crick and La Chatélier b. Watson and Crick c. La Chatélier and Crick d. Franklin and Watson 2. The DNA structure is … a. Like a funnel b. A spiral staircase c. An hour glass d. A stepping stone 3. The Nitrogen Bases in DNA are … a. Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine b. Histamine, Fluorine, Chlorine, and Adenine c. Histamine, Fluorine, Chlorine and Thymine d. Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Uracil 4. RNA is different from DNA in that it is a… a. Bond where histamine replaces thymine b. Chain the forms from Amino Acids c. Separation from one side to the other d. Single Strand where uracil replaces thymine 5. mRNA leaves the nucleus and joins with the ribosome in the … a. Cytoplasm to match with tRNA and form a protein b. Nucleus to match with tRNA and form a ribose c. Cytoplasm to match with DNA and for tRNA d. Nucleus to match with tRNA and form a Nucleotide Match the following terms with their definition 6. DNA a. A phosphorous based molecule in the sides of DNA 7. Amino Acid b. The sugar found in RNA molecules 8. Ribose c. The molecule that holds genes within a chromosome to form proteins 9. Uracil d. Single simple proteins that form a short or long chain 10. Phosphate e. The Nitrogen Base that replaces Thymine in tRNA and mRNA Chapter 5 Test Period _____ DNA & Protein Synthesis Name ____________________ T – I – 1 Key 1. The structure of DNA was determined by… a. Crick and La Chatélier b. Watson and Crick c. La Chatélier and Crick d. Franklin and Watson 2. The DNA structure is … a. Like a funnel b. A spiral staircase c. An hour glass d. A stepping stone 3. The Nitrogen Bases in DNA are … a. Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine b. Histamine, Fluorine, Chlorine, and Adenine c. Histamine, Fluorine, Chlorine and Thymine d. Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Uracil 4. RNA is different from DNA in that it is a… a. Bond where histamine replaces thymine b. Chain the forms from Amino Acids c. Separation from one side to the other d. Single Strand where uracil replaces thymine 5. mRNA leaves the nucleus and joins with the ribosome in the … a. Cytoplasm to match with tRNA and form a protein b. Nucleus to match with tRNA and form a ribose c. Cytoplasm to match with DNA and for tRNA d. Nucleus to match with tRNA and form a Nucleotide Match the following terms with their definition 6. DNA c a. A phosphorous based molecule in the sides of DNA 7. Amino Acid d b. The sugar found in RNA molecules 8. Ribose b c. The molecule that holds genes within a chromosome to form proteins 9. Uracil e d. Single simple proteins that form a short or long chain 10. Phosphate a e. The Nitrogen Base that replaces Thymine in tRNA and mRNA Alternative Assessment Protein Synthesis Rubric Honors Class Organization Facts Neatness Resources Vocabulary 1 Project is not well organized The steps of protein synthesis are not clear and missing considerable facts The presentation is not neat and does not meet expectations Resources are not provided Little or no vocabulary words were used 2 Project somewhat organized with The steps of protein synthesis are somewhat clear and missing some facts 3 Project is Organized 4 Project is well organized The steps of protein synthesis are clear have the minimum facts The presentation is somewhat neat and meets some expectations Resources are not well documented Some vocabulary words were used The presentation is neat and meets expectations The Steps of protein synthesis are clear and include additional facts From Resources. The presentation is clearly neat and exceeds expectations Resources exceed expectations Vocabulary words were used in addition to new terms learned from resources Resources are document and acceptable An acceptable amount of vocabulary word were used In addition the above rubric, students should be aware not plagiarize sources. Paragraphs should be in your own words. Each area will be scored based upon 4 points for a total of 20 points. This will be averaged for a score of 100. Project due for presentation on Thursday April 11. Protein Synthesis Paper Rubric Write a one page paper double spaced with 1 inch margins. The topic is protein synthesis. The grading criteria are as follows: Correct spelling of vocabulary. General facts should be correct. No less than one paragraph preferably 2 No less than two resources, not from your text (1 can be Wikipedia) List resources after your paragraph using just the URL This project will be graded as a Test Protein Synthesis Paper Rubric Inclusion Class Write a one page paper double spaced with 1 inch margins. The topic is protein synthesis. The grading criteria are as follows: Correct spelling of vocabulary. General facts should be correct. One paragraph. This project will be graded as a Test