* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Space Science Unit 2 Lesson 2 Worksheet 1. Which of Kepler`s laws
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Heliosphere wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Streaming instability wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
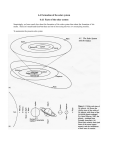
Space Science Unit 2 Lesson 2 Worksheet 1. Which of Kepler’s laws does the diagram below illustrate? Second Law (near perihelion, a planet sweeps out an area that is short & wide, near aphelion, long & narrow). 2. At what point in Earth’s orbit is Earth farthest from the sun? aphelion 3. “The orbit of a planet or other body around the sun is an ellipse, and the sun is one focus of the ellipse.” This is explaining which of Kepler’s laws? First Law 4. What type of force makes a body follow a curved path? Centripetal 5. What force caused a solar nebula to collapse toward the center, making the center of a star dense and hot? gravity 6. Which diagram below, A or B, will have the greater gravitational force? Why? B, The objects are closer together. A. B. 7. What is the process in which energy is released as the nuclei of small atoms combine to form a larger nucleus? Nuclear fusion 8. What is an effect of centripedal force? Objects move in a circular motion. 9. At what point in Earth’s orbit is Earth closest to the sun? Perhelion 10. What is a rotating cloud of gas and dust that forms into stars and planets? Solar nebula 11. What type of disk do planets form in? Protoplanetary disk 12. What are planetesimals? Large bodies that collided to form planets. 13. Which diagram below, A or B, will have the greater gravitational force? Why? A, Higher masses A. B. 14. Which of Kepler’s laws does the diagram below illustrate? Third, The square of the orbital period is proportional to the cube of the planet’s average distance from the sun. 15. How can the following sequence be fixed to show the proper formation of our solar system? protostellar disk nuclear fusion sun solar nebula planetesimals planets solar nebula protostellar disk nuclear fusion sun planetesimals planets 16. What is the law of universal gravitation? States that all objects in the universe attract each other through gravitational force. 17. As a solar nebula contracts, it begins to rotate faster and faster eventually flattening out into what type of disk? Protostellar disk 18. What type of planets form from the merger of rocky planetesimals? terrestial planets 19. What type of planets formed in the outer disk, have rocky or metallic cores and deep atmospheres of gas and ice? gas giants 20. What is an orbit? The path that a body follows as it travels around another body in space.