* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Agents of Evolution - rosedale11universitybiology
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
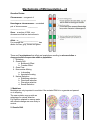
Mechanisms of Microevolution – v3 Genetics Review Chromosome – a segment of __________________________ Homologous chromosomes – a matched pair of chromosomes, __________ _______________ Gene - a section of DNA on a chromosome that has instructions to _________________________ Allele – a ____________________ For example the _______________ has alleles for blue, grey, brown and green. There are 5 mechanisms that affect real populations resulting in microevolution or changes to allele frequencies within a population. 1. Mutations 2. Genetic Drift a. Bottleneck Effect b. Founder Effect 3. Gene Flow 4. Non-random Mating a. In-breeding b. Assortative mating 5. Natural Selection a. Stabilizing selection b. Directional selection c. Disruptive selection d. Sexual Selection 1. Mutations Mutations are only important to evolution if the mutated DNA is in a gamete and passed on to offspring. The new mutation may provide an advantage for natural selection. Ex) Daphnia adapted to warmer water with climate change are more likely to survive. 2. Genetic Drift Genetic drift is defined as chance changes in allele frequencies due to a small population size. The smaller the population the less likely all of the alleles in the parent gene pool will be reflected in the offspring gene pool. a) The Bottleneck Effect The bottleneck effect is a reduction in alleles in a population resulting from a disaster that drastically reduces population size. Example: earthquakes, volcanoes b) The Founder Effect The founder effect occurs when a few individuals separate from a large population and establish a new one. Their allele ratios can be very different and some alleles can be missing in the new population. 3. Gene Flow Gene flow is the gain or loss of alleles from a population by the movement of individuals or gametes. This could result from immigration or emigration. 4. Non-Random Mating In-breeding or mating between closely related partners results in fewer heterozygotes and more homozygotes. ex. Purebred dogs are homozygous for many traits. Assortative mating is where a similar partner is chosen like toads choosing a same size partner, or dog breeding. 5. Natural Selection Natural selection is the process by which individuals with favorable traits that make them better suited for their environment are more likely to survive to reproductive age and leave more offspring. Mechanisms of Microevolution – v3 Chromosome – a segment of __________________________ Homologous chromosomes – a matched pair of chromosomes, __________ _______________ Gene - a section of DNA on a chromosome that has instructions to _________________________ Allele – a _________________________ For example the _______________ has alleles for blue, grey, brown and green. There are 5 mechanisms that affect real populations resulting in _________________ or changes to ______________________________________________ 1. ______________________ 2. Genetic Drift including a. _______________________ b. _____________________ 3. __________________ 4. Non-Random Mating including a. _____________________ b. _____________________ 5. _______________________ a. Stabilizing selection b. Directional selection c. Disruptive selection d. Sexual Selection 1. Mutations Mutations are only important to evolution if the mutated DNA is in a _________ ___________________________________________________ The new mutation ___________________________________ for natural selection. Ex) Daphnia adapted to warmer water with climate change are more likely to survive. 2. Genetic Drift Genetic drift is defined as ___________ _______________________________ _________________________________ The smaller the population the less likely all of the alleles in the parent gene pool will be reflected in the offspring gene pool. 2a) The Bottleneck Effect The bottleneck effect is a reduction in _________________ in a population resulting from a _________________ that _______________________ population size. Example: earthquakes, volcanoes 2b) The Founder Effect The founder effect occurs when a ________________________________________ and establish a new one. Their allele ratios can be very different and some ____________________________________ in the new population. 3. Gene Flow Gene flow is the _____________________ ___________ from a population by the movement of individuals or gametes. This could result from _________________ or __________________________. 4. Non-Random Mating In-breeding or mating between closely related partners __________________________________________. ex. Purebred dogs are homozygous for many traits Assortative mating is where a ____________ _________________________________ like toads choosing a same size partner, or dog breeding. 5. Natural Selection Natural selection is the process by which individuals with _______________________ ,that make them better suited for their environment, are more likely to ______________ ______________________. Watch the video The Making of the Fittest and answer the following questions. 1. Describe the habitat of the rock mouse. 2. Who are rock mouse predators? 3. In your own words describe what changes occurred in the rock mouse population and why the changes occurred. 4. Which mechanism of microevolution was most important?