* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heredity Study Guide
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
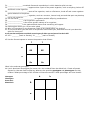
Heredity Study Guide 1. Why do cells need to produce new cells? 2. What is the result of mitosis? 3. __________ is the passing of traits from parents to offspring. 4. What trait appears in the first generation? 5. What trait appears in the second generation? 6. __________ are different forms of a characteristic. 7. What are alleles? 8. Instructions for an inherited trait are called _____. 9. Use a Punnett square to determine the possible genotypes of the offspring of a YY x Yy cross. 10. What does each parent give off to the offspring? 11. What does it mean when an organism is homozygous for a trait? 12. _________________ is a feature that has different forms in a population. 13. The process that produces sex cells is called ______________. 14. What cells are produced during asexual cell reproduction? 15. How are sex cells different from other human cells? 16. Where are genes located? 17. How many cells are produced during meiosis? 18. Who was Gregor Mendel? 19. Draw a picture a DNA model. Describe the shape of DNA. 20. DNA is made of subunits called _____________. 21. What is chromatin? 22. What are mutations? 23. To be copied, a DNA molecule splits where? 24. What letters represent the four bases in a DNA molecule? 25. Fill in the chart below: Stage of Mitosis Description Drawing of each stage Interphase prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis 26. What is a chromosome? 27. What is a homologous chromosome? 28. _______ ____________ is the life cycle of a cell. 29. Compare and contrast mitosis vs. meiosis. 30. For each picture below, write whether they going through sexual or asexual reproduction. BacteriumHydraStrawberry plantJellyfish- 31. _______ ________ a method of asexual reproduction in which bacteria splits into two. 32. _____________________: happens when a part of the parent organism, such as a hydra, pinches off and forms a new organism. 33. _____________________: parts of the organism, such as a flat worm, break off and a new organism grows identical to the parent. 34. _____________________: organism, such as a sea star, loses a body part and that part may develop into a new organism. 35. You can use a _____ ___________ to organize possible offspring combinations. 36. ________________ is an organism’s appearance. 37. ________________ is the entire genetic makeup of an organism. 38. _______________ is the mathematical chance that something will happen. 39. Homozygous alleles (ex. PP) are also called _________________. 40. Why is it important for chromosomes (DNA) to be copied before cell division? 41. If a child has blue eyes and both of her parents have brown eyes, what does this tell you about the allele for blue eyes? It tells you that each parent carried the recessive gene for blue eyes and passed it to their child. 42. XX = _______ (male or female); XY _______ (male or female) 43. Use the Punnett square to answer the question that follows: ? ? S SS SS Ss Ss s What is the unknown genotype? 44. Lisa is dominant homozygous for brown hair. Her husband Dean has blond hair. Create a Punnett Square for Lisa and Dean’s offspring. What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for their children? What percentage of the children will have brown hair? What percentage will have blonde? Genotypes= Phenotypes= Brown hair= Blonde hair= b B B b