* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Navigational Tool Background
Survey
Document related concepts
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Reflecting instrument wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
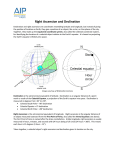
Navigational Tool Background Astrolabe: The astrolabe is a navigational instrument which helps the Navigant’s at Sea to find there Latitude. An astrolabe was often made of metal with a map of the stars and the zodiac circle on the other side. The sun or a star showed a certain point on the astrolabe which allowed the Navigator to determine the ships positions and during the day even the time. Cross-Staff: A cross-staff is inspired by the Kamal which was used by the Arab Navigators. The cross-staff is made of a long staff normally 36 inches long and 4 smaller cross pieces which move up and down the long staff. The navigator holds the cross-staff to the eye and moves one of the four cross pieces forth and back until the two ends focus on the horizon and a celestial’s body. The altitude he can read on the appropriate scale. The cross-staff is much simpler than the astrolabe. The table of declination: Is a navigational system similar to the longitude and latitude system on earth. Declination is one of two coordinates. Therefore you imagine the space is as round as the earth. The second coordinator is either the right ascension or an hour angle. Declination is measured in degrees, north or south of the celestial equator. That means the equator has a declination of O degree, the north pole a declination of plus 90 degrees and the south pole a declination of minus 90 degrees. Since you can use the solar system as well as stars to determine your position explorers invented a so called table of declination of the sun, which includes the average of a leap circle over four years. The solar system is much more changing over the years due to earth rotation and the several seasons of the year. The stars are much more fixed and lie nearly always in the same constant direction when viewed from the earth. All these navigational tools should allow me to make my journey as fast as possible and find the Spicy Islands . Compass: A compass is an instrument to navigate based on the magnetic poles, the North Pole and the South Pole. Wherever you are the compass shows you the direction toward the pole. On the surface of the compass you find the cardinal points of the magnetic field like North, South, East and West. Often Compasses are build with a magnetized bar or needle turning freely to point in the Northern or Southern direction. Together used with a other navigational tools you can determine your longitude and latitude at sea. Image of a Compass