* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mechanisms of Evolution Mechanisms of Evolution
Survey
Document related concepts
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
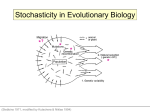
Mechanisms of Evolution • Directed evolution/Internal mechanisms “orthogenesis” etc. • Inheritance of acquired characteristics (“Lamarckism”) • Genetic drift • Neutral theory • Natural Selection • Higher level sorting Mechanisms of Evolution • Directed evolution/Internal mechanisms “orthogenesis” etc. • Inheritance of acquired characteristics (“Lamarckism”) • Genetic drift • Neutral theory • Natural Selection • Higher level sorting 1 Directed evolution • Favorable variations arise because they are directed to do so -- by unknown internal or external forces • a.k.a. - “orthogenesis”, “aristogenesis”, divine evolution, etc. Gryphaea, Jurassic Trueman (1922) 2 3 Inheritance of acquired characteristics (“Lamarckism”) Genetic drift • Genetic variants can become established (“fixed”) in a population by chance (esp. in small populations) 4 Neutralism • Genetic variants that do not affect fitness (“neutral” traits) can become established in populations due to mutation alone. Natural Selection Definition: The non-random and differential reproduction of different genotypes acting to preserve favorable variants and eliminate less favorable variants. 5 “3 unarguable observations and 2 inescapable conclusions” • Observations: – 1) There is variation – 2) At least some of it is inherited – 3) There is vast overproduction • Conclusions: – 1) There is a “struggle for existence”. – 2) On average, those individual organisms with traits that confer some advantage in this struggle will leave more offspring. Natural Selection -- Another way to remember it: VISTA • • • • • Variation Inheritance Selection Time Adaptation 6 Higher level sorting 7 8