* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA SAMITI : NEW DELHI
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
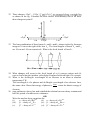
SET - 1 HSB COACHING CENTRE 9210846949 www.hsbsolutions.jimdo.com SAMPLE PAPER - V PHYSICS FOR CLASS XII General Instructions: (a) All questions are compulsory (b) There are 30 questions in total. Qns. 1 to 8 carry 1 mark each. Qns. 9 to 18 carry 2 marks each, Qns. 19 to 27 carry 3 mark each and Qns. 28 to 30 carry 5 marks each. (c) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question of 2 marks, one question of 3 marks and all three questions of 5 marks each. You have to attempt only one of the given choices in such questions. (d) Use of calculators is not permitted. (e) You may use the following physical constants wherever necessary. c = 3 x 108 ms-1 h = 6.6 x 10-34 Js e = 1.6 x 10-19C µo = 4π x 10-7 TmA-1 1/4πεo = 9 x 109 N m2C-2 Avogadro number NA = 6.023 x 1023 mol-1 Mass of the neutron = 1.675 x 10-27 kg Boltzmann constant, k = 1.38 x 1023 J K-1 1 In each of the diodes shown, forward resistance is 50 Ω. Then find current through the 100 Ω resistor in the given circuit. 150 Ω D1 50 Ω D2 6V 100 Ω 2 3 4 5 A convex lens and a concave lens of same focal length are combined in contact. What would be the resulting focal length? What orientation will a freely suspended magnetic needle have at (i) geographic south and (ii) magnetic south pole of the earth? What is the power factor of a pure inductor? Compare the velocities of X – rays of wavelength 1 Ả and red light of wave length 6000 Ả in vacuum. 6 In photo electric emission from the surface of a metal, when the wave length of incident light is λ, the maximum kinetic energy of photo electron is E and the number of emitted electrons is N. If now the intensity is doubled, keeping λ fixed, what will be the effect on kinetic energy and number of photo electrons emitted? 7 Calculate the ratio of energy of electron in the fourth and fifth orbits of hydrogen atom. 8 Why is the base region of transistor thin and lightly doped ? 9 A 80 µF capacitor is charged by a 50 V battery. The capacitor is disconnected from the battery and then connected across another uncharged 320 µF capacitor. Calculate the charge on the second capacitor. 10 A potential difference V is applied to a copper wire of diameter D and length l. What is the effect on the drift velocity of electrons when: (i) doubling V (ii) doubling l (iii) doubling D? 11 For what value of unknown resistance X, the current flowing through the galvanometer would be zero in the circuit shown below. 1Ω 6Ω 6Ω B G X 1Ω 1Ω 6Ω A C D 1Ω 12 State Ampere’s circuital law in magnetism and use it to find the magnetic field inside a current carrying toroidal solenoid. 13 The reactance of an inductor is 20 Ω. What does it mean? What would be its reactance, if the frequency of the a c is doubled? What opposition does the inductor offer to the flow of a d c? 14 State Lenz’s law in electromagnetic induction and explain how it supports law of conservation of energy. 15 Which part of the electromagnetic radiation: (i) is used for satellite communication (ii) has is frequency range 4 x 1014 Hz to 7 x 1014 Hz (iii) produce intense heating effect (iv) used for purification of water. 16 An equiconvex lens has a power of 5 D. If it is made of glass of refractive index 1.5, calculate the radius of curvature of each surface. OR Draw a labelled ray diagram of an astronomical telescope used in the normal adjustment position. Two astronomical telescopes T1 and T2 have the same magnifying power. The ratio of aperture of their objectives is 3:2. Which one of these two produces image of greater intensity? 17 When a deuteron of mass 2.0141 u and negligible kinetic energy is absorbed by a lithium (3Li6) nucleus of mass 6.0155 u, the compound nucleus disintegrates spontaneously into two alpha particles, each of mass 4.0026 u. Calculate the energy in joules carried by each alpha particle. ( 1 u = 1.66 x 10-27 kg) 18 Give reasons for the following: (i) Long distance radio broadcasts use short-wave bands. (ii) Satellites are used for long distance TV transmission. 19 A metallic square loop ABCD of size 15cm and negligible resistance is moved at a uniform velocity of v m/s in a uniform magnetic field of 2T. The field lines being normal to the plane of the paper. The loop is connected to an electrical network of resistances each of resistance 2 Ω. Calculate the speed of the loop for which 2mA current flows in the loop. 20 An electric kettle has two windings. When one of them is switched on , the water begins to boil in 15 min. and other is switched on in 30 min. In how much time will the water in the kettle begin to boil if the two windings are switched on (i) in series (ii) in parallel. 21 A large vessel is filled with a liquid of dielectric constant k. Two vertical plates touch the liquid. The dimensions of plates are a and b ,the distance between them is d. The plates have been charged by applying the voltage V 0 and then disconnected from the source. To what height will the liquid rise. 22 Three charges -2µC , +22µ -2µ as shown in the fig. Calculate the total electric field intensity due to all these three charges at point P. P 1m A -2µC B 1m 22µC C -2µC 1m 23 The lens combination of three lenses L1 and L2 and L3 shown in the fig. forms an image at 30 cm to the right of the lens L3 . The focal lengths of lenses L1 and L2 are 10 cm and -10 cm respectively. What is the focal length of lens L3. 24 What changes will occur in the focal length of a (i) concave mirror and (ii) convex lens when the incident violet light is replaced with red light. Give reason. 25 What is the de-Broglie wavelength of an electron in an atom at absolute temperature T K. The wavelength λ of a photon and de-Broglie wavelength of an electron have the same value. Show that energy of photon is 2mc times the kinetic energy of h electron. 26 state radioactive decay law and establish the relation between decay constant and half life period of a radio active substance. OR Write the nuclear decay equations for: (i) α – decay of 88 Ra 226 (ii) α – decay of 94 Pu 242 (iii) β- – decay of 15 P 32 (iv) β- – decay of 83 Bi 210 (v) β+ – decay of 6 C 11 (vi) β+ – decay of 43 Tc 97 27 Define the term Modulation . Name three different type of modulations used for a message signal, using sinusoidal continuous carrier wave. Explain the meaning of any one of these. 28 Explain the method of obtaining a n – type semiconductor from a sample of intrinsic semi conductor. Draw the energy band diagram of the n – type semi conductor. A semiconductor has equal electron and hole concentration of 6 x 10 8/m3. On doping with certain impurity, electron concentration increases to 9 x 1012/m3. (i) Identify the new semiconductor obtained after doping. (ii) Calculate the new hole concentration. OR What is an AND gate? Write its truth table and Boolean expression for its output. Draw the logic symbol With the help of a neat circuit diagram, explain the realization of an AND gate using semiconductor diodes. Write the truth table for the following combination of four NOR gates arranged as shown in figure. A B Y 29 With the help of a suitable diagram, describe Young’s double slit experiment for obtaining interference pattern. Write an expression for the fringe width of the pattern. Represent graphically the variation of intensity in the pattern. What will be the effect on interference fringes obtained in Young’s double slit experiment, if (i) source of light of longer wavelength is used (ii) distance between two slits be increased to larger extent (iii) two slits are illuminated by different sources of light of same λ (iv) if the distance of the source and the double slit is increased? OR Differentiate between plane polarized and un polarized light. Describe a method to get a plane polarized light by reflection. Discuss the intensity of transmitted light when a polaroid sheet is rotated between two crossed polaroids? What is the Brewster angle for air to glass transition? (Refractive index of glass=√3.) 30 Two circular coils X and Y having radii R and R/2 respectively are placed in horizontal plane with their centres coinciding with each other. Coil X has a current I flowing through it in the clockwise sense. What must be the current in coil Y to make the total magnetic field at the common centre of the two coils, zero? With the above currents flowing in the two coils, if the coil Y is now lifted vertically upwards through a distance R, what would be the net magnetic field at the centre of coil Y? OR Define current sensitivity and voltage sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer. Two moving coil meters, M1 and M2 have the following particulars: R1 = 10 Ω, N1 = 30, A1 = 3.6 × 10–3 m2, B1 = 0.25 T R2 = 14 Ω, N2 = 42, A2 = 1.8 × 10–3 m2, B2 = 0.50 T (The spring constants are identical for the two meters). Determine the ratio of (a) current sensitivity and (b) voltage sensitivity of M2 and M1. How can a galvanometer be converted into (i) an ammeter and (ii) a voltmeter of required range? *******************************************






![NAME: Quiz #5: Phys142 1. [4pts] Find the resulting current through](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006404813_1-90fcf53f79a7b619eafe061618bfacc1-150x150.png)